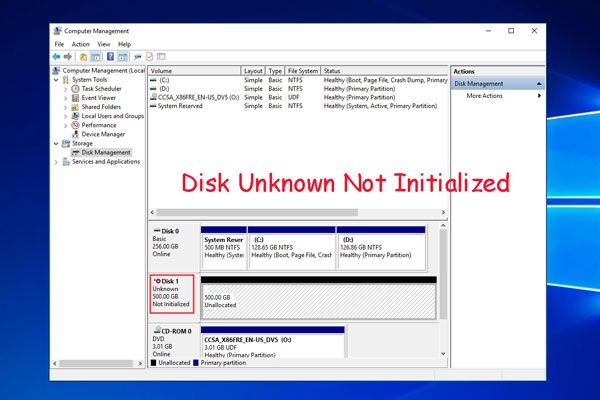
Disk unknown not initialised is an error message that may appear when your computer cannot recognise a storage device connected to it. This usually indicates that the disk has not been properly prepared for use and needs to be initialised before it can be accessed.
Some key questions about disk unknown not initialised include:
- What causes the disk unknown not initialised error?
- How can I fix a disk that is not initialised?
- What does initialising a disk do?
- Can I recover data from an uninitialised disk?
What Causes the Disk Unknown Not Initialised Error?
There are a few potential causes of the disk unknown not initialised error:
- Connecting a new hard drive that has never been formatted or partitioned before
- Corruption of the master boot record (MBR) or partition table
- Using a disk from another operating system like Linux or Mac OS on a Windows PC
- Removing a secondary internal hard drive and reconnecting it
- Hardware failure or damage to the disk
Essentially, this error occurs when the operating system cannot find a valid master boot record or partition table on the disk, which contains key data about the disk’s layout and file system. Without this data, the OS does not know how to access the disk or what to do with it.
Master Boot Record
The master boot record (MBR) is a small boot sector located on the first sector of a hard disk that contains information about the disk’s partitions. It includes the partition table detailing the start and end points of each partition and their sizes.
The MBR allows the computer to navigate the disk and locate the boot loader files on the active primary partition. If the MBR is corrupted or damaged, the computer cannot start up from the hard disk.
Partition Table
The partition table is part of the master boot record that defines the partitions on the storage device. It contains entries specifying the size, location, type and other details about each partition on the disk.
If this table is corrupted or lost, the operating system cannot identify the individual partitions and will see the disk as having an unknown structure or as being uninitialized.
How to Fix an Uninitialized Disk
If you encounter the disk unknown not initialised error, there are a few steps you can take to try and fix it:
- Try a different SATA port or USB port – In case of a loose connection.
- Update disk driver – An outdated disk driver can prevent recognition.
- Initialize the disk in Disk Management.
- Use diskpart to clean and recreate the MBR.
- Format the disk to create a new partition table.
- Use data recovery software to rescue files and then reformat.
Initialize Disk in Disk Management
The easiest solution is often to simply initialize the disk in Windows Disk Management:
- Go to Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Computer Management > Disk Management.
- Find the unknown disk and right click it.
- Select “Initialize Disk” and agree to the warning.
- Choose MBR or GPT and click OK.
- The disk should now show up as “Unallocated”.
- Right click it and create a new partition.
- Format the partition to finalise it.
This will rebuild the partition table and make the disk accessible again. However, initializing will erase existing data on the disk.
Use Diskpart to Clean and Recreate MBR
Diskpart is a command line disk partitioning tool in Windows. You can use it to wipe and recreate the MBR from scratch:
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator.
- Type “diskpart” and press Enter.
- Type “list disk” to identify the target disk number.
- Select it by typing “select disk X” (replace X with the disk number).
- Type “clean” to erase the existing MBR and partitions.
- Type “create partition primary” to recreate the MBR.
- Type “format quick fs=ntfs” to create a new blank NTFS partition.
- Type “assign” to make the partition active.
- Type “exit” to finish.
This should make the disk recognizable again but will also delete existing data.
What Initializing a Disk Does
Initializing a disk essentially erases any existing partition table and master boot record data on the drive and creates a new blank MBR and partition table.
Specifically, what initializing a disk does is:
- Erases the existing master boot record (MBR).
- Erases the existing partition table.
- Overwrites the first sector with a new blank MBR.
- Creates a fresh blank partition table.
- Marks the disk as unallocated space without partitions.
- Allows new partitions to be created on the blank disk.
This gives the operating system a clean slate to work with in terms of allocating partitions and formatting the disk. However, it also means that any existing partitions and data on the drive will be erased in the process.
MBR vs GPT Initialization
There are two types of initialization – Master Boot Record (MBR) and GUID Partition Table (GPT):
- MBR – Traditional BIOS partitioning scheme limited to 4 primary partitions. Used on Windows and Linux PCs.
- GPT – Newer UEFI partitioning scheme supporting unlimited partitions. Used on newer Windows and Mac computers.
Most consumerWindows PCs still use MBR initialization. GPT offers more flexibility for managing complex storage configurations.
Recovering Data from Uninitialized Disk
As initializing a disk erases all existing partitions and data, you may want to try and recover data first if the disk contains important files.
Data recovery options include:
- Using data recovery software to scan disk sectors for recoverable file fragments.
- Attaching the disk as a secondary drive on another computer to access contents.
- Using a Linux Live CD to mount the disk read-only and copy data.
- Sending to a professional data recovery service to repair and recover data.
If the disk has failed completely these options may not work. But if the issue is just an unclear partition table, data should still be present on a physical level and recoverable.
Be very careful not to write anything new to the disk before data recovery, as this could overwrite your files permanently.
When to Initialize a Disk
There are a few situations where you may need to initialize a disk:
- New hard drive – Brand new internal or external hard drives need to be initialized before partitioning and formatting.
- Disk errors – Initializing can fix errors like device not recognized or disk not initialized and recreate the MBR.
- Changing partition style – If converting a disk from MBR to GPT or vice versa, it needs to be reinitialized.
- OS migration – Moving a disk from a Linux/Mac system to Windows may require initializing to recreate the MBR.
- Disk corruption – Severe virus infection, power loss during writes, or physical damage may require reinitializing.
In general, initializing should only be done on new disks or as a last resort when other repair methods have failed. Trying recovery software or repairs first is advisable if the disk contains important data.
When Not to Initialize a Disk
You should avoid initializing a disk in these situations:
- The disk contains important data that has not been backed up.
- You have not exhausted other repair options like Update Driver, CHKDSK, or SFC.
- The issue can be fixed by a simple format vs full initialization.
- The disk uses a partition style your OS does not support.
- The disk has bad sectors indicating hardware failure.
Initializing should not be your first troubleshooting step when dealing with disk errors, as it will completely erase data. Be cautious and explore other options before proceeding.
Conclusion
Disk unknown not initialised errors occur when the master boot record or partition table on a drive becomes damaged or corrupted. Initializing writes a new blank MBR and partition structure to make the disk usable again.
However, this erases all existing data. So recovering data first should be attempted if possible. Initialization is best reserved for new disks or those already backed up.
With the right precautions, initializing a problematic disk can bring it back to a functional state. But it is a serious data-destructive operation that merits caution and care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes of the disk unknown not initialised error?
Common causes include connecting a new unformatted disk, a corrupted master boot record, damaged partition table, hardware issues, removing and reattaching a drive, or moving a disk between operating systems.
Can I access data on an unknown uninitialized disk?
No, you cannot directly access data on an uninitialized disk. But data recovery software or services may be able to recover data before initializing erases everything.
Is it safe to initialize a disk in Disk Management?
Initializing a disk in Disk Management is safe but will permanently erase all data on the disk. So backup any important data first.
How long does it take to initialize a hard drive?
It typically takes less than a minute to initialize a hard drive, regardless of its capacity. The process simply writes a new MBR and partition table.
Can I convert a disk from GPT to MBR without losing data?
No, converting between GPT and MBR styles requires reinitializing the disk which will erase all data. Backup first and then reinitialize.
| Error Message | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Disk Unknown Not Initialized | Damaged partition table | Initialize disk in Disk Management |
| You must initialize a disk before Logical Disk Manager can access it | Disk contains unrecognized partitions | Delete partitions and recreate in Disk Management |
| The device is not ready | Loose disk connection | Reseat SATA or USB cable |
| Incorrect Function | Corrupted system files | Run SFC and DISM scans |
| Disk not initialized and no valid partition table | Damaged master boot record | Use Diskpart to clean and recreate MBR |