Yes, it is possible to configure RAID 5 in Windows. RAID 5 combines disk striping with parity for fault tolerance, providing a balance of performance and reliability. While RAID 5 was traditionally done via hardware RAID controllers, modern versions of Windows include built-in software RAID capabilities that allow configuring RAID 5.
What is RAID 5?
RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks. It is a method of combining multiple disk drives into a logical unit. RAID 5 is a specific RAID level that stripes data across three or more disks, while also generating parity information that gets written across the disk array.
The parity allows the array to recover data if one of the disks fails. For example, in a 3-disk RAID 5 array, Disks 1 and 2 contain striped user data, while Disk 3 contains parity information calculated from Disks 1 and 2. If Disk 2 fails, the RAID software can use Disks 1 and 3 to reconstruct the data that was on Disk 2.
This provides fault tolerance and protection against a single disk failure. Meanwhile, RAID 5 still provides increased performance compared to a single disk because data is distributed across multiple disks that can operate in parallel.
Advantages of RAID 5
Some key advantages of RAID 5 include:
- Fault tolerance – RAID 5 can survive a single disk failure without data loss.
- Good performance – Data is striped, allowing parallel access across multiple disks for better speed.
- Efficiency – RAID 5 requires less disk overhead compared to RAID 1 mirroring.
- Capacity – RAID 5 makes use of most of the available disk space for user data.
Disadvantages of RAID 5
Some potential disadvantages include:
- Slower writes – Writes are slower due to parity calculation.
- Not suited for large drives – Rebuilding large failed drives takes a long time, increasing risk.
- Read performance impact – Reading data requires computing parity info.
- No fault tolerance during rebuild – If another disk fails during rebuild, data is lost.
RAID 5 Hardware and Software Implementations
RAID 5 can be implemented via dedicated hardware RAID controllers. These are cards installed in the computer that handle the RAID calculations and abstraction. However, RAID 5 can also be implemented in software.
Software RAID does the RAID calculation on the main system CPU and memory. This avoids the cost of a RAID card. Software RAID 5 became more common as modern processors and RAM capacities increased over the years.
How to Configure RAID 5 in Windows
All modern Windows versions, including consumer versions like Windows 10 and 11, can support software RAID 5 configurations. Here is an overview of how to configure RAID 5 in Windows:
- Ensure compatible disks – Use new blank disks. May require converting disks to dynamic disks.
- Open Disk Management – Search for “Create and format hard disk partitions” and open.
- Create new spanned volume – Right click and select to combine available disks.
- Convert to RAID-5 volume – Right click the spanned volume and select “Convert to RAID-5.”
- Configure RAID-5 properties – Select desired stripe size and check “Enable disk striping.”
- Initialize and format RAID-5 volume – Right click and initialize, then format the volume.
The RAID-5 volume can then be accessed like any other disk volume in Windows for data storage and retrieval. The RAID protection is handled automatically in the background.
Advantages of Software RAID 5 in Windows
The advantages of using Windows built-in software RAID 5 include:
- No added cost – Uses existing hardware, avoiding cost of a RAID card.
- Easy to configure – Can be set up through the Windows interface without advanced technical skills.
- Portability – The RAID volume can be moved to another Windows system without controller dependency.
- Scalability – Additional disks can be added easily to grow the array.
Disadvantages of Software RAID 5 in Windows
Some potential downsides to consider:
- No battery-backed cache – Risk of data in cache being lost on power failure.
- No onboard monitoring – Harder to monitor disk health without a hardware controller.
- Requires resources – Software RAID consumes extra CPU and memory resources.
- No dedicated processing – RAID tasks share resources with the operating system and other programs.
Performance Considerations
The performance of software RAID 5 in Windows depends on several factors:
- Disk speed – Faster spindle or SSD disks provide better throughput.
- Available CPU power – Software RAID taxes the CPU, so a multi-core processor helps.
- Available memory – Parity calculations are performed in memory before writing.
- Stripe size – Match stripe size to typical I/O request size for optimal performance.
In general, a modern PC with a quad core CPU, 8GB of RAM, and SSD disks should provide decent RAID 5 performance for everyday applications and moderate workloads. For busy production servers or large databases, hardware RAID 5 may still be preferable.
Reliability Considerations
The reliability of a software RAID 5 implementation in Windows depends on several aspects:
- Quality of disks – Consumer-grade disks are more prone to failure versus enterprise models.
- Number of disks – More disks means more chances for failure. Recommend limiting to 6 disks.
- Monitoring – Lack of controller logs makes preventative monitoring difficult.
- Backups – No redundant power or cache, so backups are critical.
While Windows software RAID 5 can work well for home or small office use, critical business data may warrant additional redundancy via backups or a dedicated hardware RAID controller.
Alternatives to Software RAID 5 in Windows
Some alternatives to consider beyond Windows software RAID 5 include:
- Hardware RAID – Provides dedicated disk controllers for higher performance and reliability.
- Third-party software RAID – Options like ZFS or MDADM for more advanced management.
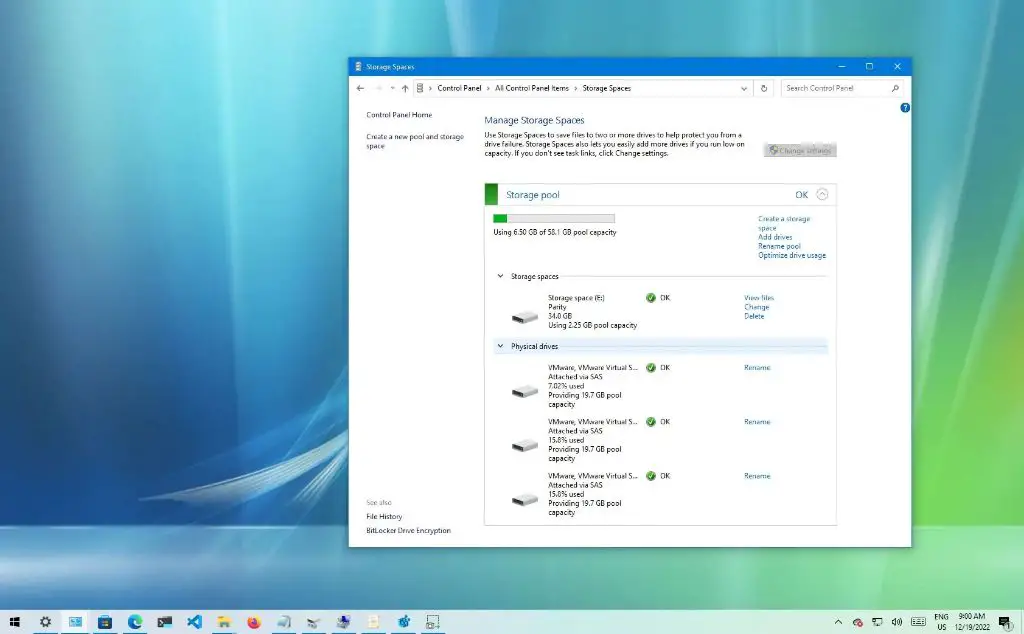
- Storage Spaces – Microsoft’s alternative to software RAID integrated into Windows.
- Cloud storage – Provides redundancy without local RAID configuration.
Conclusion
Configuring RAID 5 in Windows is possible using built-in software RAID capabilities. This allows creating a fault tolerant volume without additional hardware. Software RAID 5 can provide good performance and data protection for home or small business users.
However, those with demanding workloads or critical data should weigh the advantages of hardware RAID controllers versus software RAID. Broad deployment in large enterprises is still better suited to dedicated RAID cards. But for small-scale use cases, Windows software RAID 5 provides a capable data storage solution.