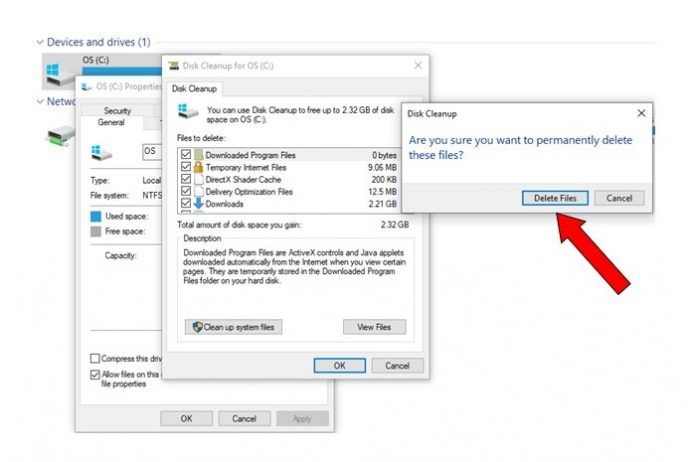
Disk Cleanup is a built-in tool in Windows that helps free up storage space on your hard drive by removing unnecessary and temporary files. By deleting these files, Disk Cleanup aims to speed up your computer and improve performance by giving your computer more available hard drive space.
Over time, temporary internet files, downloads, recycle bin files, and other data can accumulate and take up significant storage space. Disk Cleanup targets these files that are safe to remove and often not needed anymore. By removing gigabytes of these unneeded files, the goal is to have more free space available and prevent low disk space issues.
What is Disk Cleanup?
Disk Cleanup is a utility included in Windows that allows users to clean up unnecessary files on their computer to free up disk space (https://businesscomputertechnicians.com/disk-cleanup/). It scans the hard drive looking for files that are no longer needed or useful such as temporary files, downloads, items in the Recycle Bin, and various system files and caches. Disk Cleanup analyzes these files and allows users to securely delete them to recover storage space (https://www.compuhoy.com/how-does-disk-cleanup-work-in-windows-10/).
Specifically, Disk Cleanup looks for several categories of files such as:
- Temporary internet files stored by browsers
- Temporary system files created during installations and updates
- Recycle Bin contents
- System error logs and reports
- Outdated ActiveX controls and .NET Framework assemblies
By removing these unnecessary files, Disk Cleanup aims to regain hard drive space and improve computer performance by clearing out data clutter (https://www.bollyinside.com/what-is/wiki/disk-cleanup).
Temp Files
Temporary files, also called temp files, are files that are created and stored on a computer’s hard drive by programs and applications. They can contain data, parts of programs, or other information that is needed temporarily. Some common examples of temporary files include:
Internet cache files – Stores copies of web pages, images and other web content locally so pages load faster on future visits. The cache builds up over time and can take up significant disk space.1
Installation files – Downloaded installation files for programs and software are usually saved as temporary files until the installation process is complete.
Error logs – Programs and applications create log files to record errors, crashes and other diagnostic information. These logs can rapidly accumulate.
Temporary application files – Programs often create temp files to store data while in use, but forget to delete them afterwards.
The main reason temporary files build up is because most applications don’t self-manage and automatically delete their own temp files. Over time, gigs of temp files can accumulate and take up considerable drive space. Running Disk Cleanup scans the drive and safely deletes these unnecessary temporary files, freeing up storage capacity.
Downloads
Over time, your Downloads folder can accumulate many files that take up storage space on your hard drive. According to an Apple Support thread, deleting items from your Downloads folder can make your system run faster if your hard drive is close to being full (source). Old and unused downloads are often safe to delete, as pointed out in Lifewire’s guide (source). Not all downloads are needed indefinitely – sometimes they are only temporary installers or documents that have been moved elsewhere after use.
To clear out your Downloads folder, first check which files are still useful or needed for reference. For the rest, you can select and delete them. On Windows 10 and 11, you can also clear your entire download history from Settings > System > Storage > Temporary files (source). Removing old and unnecessary downloads helps free up drive space and reduces clutter.
Recycle Bin
The Recycle Bin is a holding place on your computer for files that have been deleted. When you delete a file, it is not immediately removed from your hard drive. Instead, it goes to the Recycle Bin where it can easily be recovered if needed. Files remain in the Recycle Bin until the bin is emptied. Once the Recycle Bin is emptied, the files are permanently deleted from the hard drive.
Full Recycle Bins do not inherently slow down your computer. As noted in this Quora discussion, the Recycle Bin is just storing file references rather than the actual files themselves. However, a full Recycle Bin can reduce the amount of available disk space on your computer. Less free space can potentially lead to slower performance over time as your operating system has less room to manage normal functions.
It’s generally recommended to periodically empty your Recycle Bin when it contains unneeded files. This frees up valuable disk space. According to this Techwalla article, emptying the Recycle Bin itself does not directly speed up your computer. The increased free space may lead to minor performance improvements, but other factors like CPU speed play a larger role.
System Files
Windows stores various system files that it uses to run the operating system and installed programs. Over time, these cached system files can build up and take up hard drive space. Some of the main types of system files that accumulate include:
Windows Update Files – These are installer files downloaded when Windows Update is run to install updates. The installation files are kept in the C:\Windows\SoftwareDistribution folder. These can build up over time as more updates are installed (Microsoft).
Temporary Files – Programs create temp files as they run for caching data. These temp folders can build up over time. The main temp folders are C:\Windows\Temp and C:\Users\[User]\AppData\Local\Temp (WinAero).
System Cache and Logs – Windows stores system cache and log files that can accumulate. These help Windows run but can be cleared out periodically.
Driver Installers – When new drivers are installed, the installer files get stored in C:\Windows\DriverCache. Over time this folder can grow large.
Clearing out these unnecessary system files can help free up drive space and potentially improve performance by reducing disk usage.
Browser Data
Browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Edge, and Safari store temporary internet files, cookies, and cached information from websites you visit to load pages faster on future visits. Over time, this browser data can build up and take up space on your hard drive. Clearing your browser’s cache and cookies can free up storage space and speed up page loading.
Disk Cleanup specifically targets the temporary internet files, stored cookies, history, and other data cached by Internet Explorer and Microsoft Edge. Deleting this browser data can potentially help page load performance, especially if your browser’s cache has become bloated over time.
According to Maximize Your Browser Speed: A Guide to Clearing Your Cache, clearing your browser’s cache forces the browser to download fresh copies of website files, images, and other resources instead of relying on locally stored versions. This ensures you have the most recent website content instead of outdated cached copies.
However, the impact on actual page load speeds may be minimal in many cases. As noted by How to Clear your Browsers Cache and Cookies, web browsers are optimized to manage the cache size on their own. You may only see a performance difference if the browser cache has become extremely large over time.
Does It Help Performance?
There is evidence that Disk Cleanup can provide moderate improvements to system performance by freeing up disk space. According to an article on The Training Lady, running Disk Cleanup can “improve the performance of your PC” by removing unnecessary files https://www.thetraininglady.com/windows-disk-cleanup/. Specifically, Disk Cleanup targets temporary files, downloads, the recycle bin, browser data, and other system files that may build up over time and take up storage space. By deleting these files, Disk Cleanup can free up disk space and resources for active processes and applications.
However, an article on Minitool explains that while Disk Cleanup can temporarily free up space, the performance boost is limited if old files continue accumulating or new programs and files keep getting added https://www.minitool.com/partition-disk/disk-cleanup-wont-open.html. So running Disk Cleanup periodically can provide a “quick fix” but does not completely optimize or speed up a computer in the long run. Metrics like boot time, program launch speed, and general system responsiveness may improve temporarily after cleanup. But as storage space gets used up again, performance can slow down once more.
Overall, Disk Cleanup can provide a modest, short-term improvement to performance by removing unnecessary disk space usage. But it is not a complete solution for maximizing speed and requires periodically running cleanup to maintain any benefits.
Limitations
While Disk Cleanup can help free up space by deleting unnecessary files, its impact on system performance is often minimal. There are several scenarios where running Disk Cleanup provides little benefit:
Disk almost full – If your disk is nearly full, deleting a few gigabytes of files may not free up enough space for Windows to operate efficiently. Performance tends to degrade rapidly as disk usage approaches maximum capacity.
Hardware bottleneck – Disk Cleanup only affects disk usage, not CPU, RAM, or other hardware. If your performance issues stem from an older CPU, insufficient memory, or other components, cleaning up the disk will provide minimal improvements.
In general, Disk Cleanup is most effective when disk space is moderately low and hardware is modern. On a newer PC with plenty of disk space, running Disk Cleanup periodically may have negligible impact on system performance.
Conclusion
In summary, Disk Cleanup can help free up disk space by removing temporary files, downloads, Recycle Bin contents, and unused system files. Removing these unneeded files can potentially improve computer performance slightly by eliminating clutter and freeing up space. However, the performance boost is typically minimal, and Disk Cleanup has some limitations in what it can delete.
The main files Disk Cleanup targets are temporary internet files, logs, temporary program files, Recycle Bin contents, and other data that applications and Windows aren’t currently using. By removing a few gigabytes of these files, Disk Cleanup might provide a small speed increase.
However, Disk Cleanup only scratches the surface of removing unnecessary files, and it cannot delete redundant program files, caches, and other deeply embedded clutter on the disk. The performance gains from Disk Cleanup will likely be subtle on modern computers with plenty of storage space available.
In summary, Disk Cleanup can provide a minor improvement in disk space and performance by removing some unneeded files. But it is not a substitute for a full disk optimization software suite and other system maintenance tasks. The speed boost will generally be modest at best after running Disk Cleanup.