Macs can read both NTFS and FAT32 formatted drives, but by default, Macs are only able to write to FAT32 drives. NTFS is Microsoft’s proprietary file system format, while FAT32 is an open standard that is compatible across platforms. So for external drives that need to be used between Windows and Mac, FAT32 is generally the preferred format.
Quick Answers
Here are quick answers to common questions about Mac’s ability to read NTFS and FAT32:
- Can Mac read NTFS drives? Yes, Mac can read NTFS drives but cannot write to them by default.
- Can Mac read FAT32 drives? Yes, Mac can both read and write to FAT32 drives.
- Does Mac support NTFS? Mac supports reading NTFS drives but not writing to them natively. You need third-party software to enable Mac to write to NTFS.
- What format do I need for external hard drive for Mac and PC? FAT32 is the best cross-platform external hard drive format to use between Mac and Windows PCs.
NTFS vs FAT32
NTFS and FAT32 are the two main file system formats used for hard drives and external storage devices. NTFS is newer and has more features, but FAT32 is more universally compatible across operating systems.
NTFS stands for New Technology File System. It was introduced by Microsoft in the 1990s as an upgrade over the older FAT32 file system. NTFS has many improvements over FAT32:
- Supports larger partition sizes – up to 256 TB.
- Better security with file/folder encryption and permissions.
- Faster performance for high volume storage.
- Compression to optimize hard drive space.
However, NTFS is proprietary to Microsoft and not as widely supported on other platforms. By default, Mac operating systems can only read NTFS drives and do not have native write support.
In contrast, FAT32 (File Allocation Table 32) is an open standard file system supported by all major operating systems including Windows, macOS, Linux, etc. However, it lacks some of the advanced features of NTFS:
- Max volume size only 32 GB (but can format larger drives with sectors).
- No built-in encryption or compression.
- Lower performance compared to NTFS.
The advantage FAT32 has over NTFS is its universal compatibility with Mac, Windows and other OS. That makes it ideal for external portable drives that are shared between different computers.
Mac Read NTFS Drives
By default, Mac operating systems like macOS Catalina and Big Sur include built-in support for reading NTFS drives. So if you connect an NTFS formatted external hard drive, USB flash drive or SSD drive, you will be able to access the files and folders on the drive and copy data from the drive to your Mac computer.
However, the default Mac NTFS driver is read-only. That means by default Mac cannot write or make any changes to the NTFS drive. You will get an error that the disk is read-only if trying to copy files from the Mac to an NTFS drive or edit anything on the drive.
Why Can’t Mac Write to NTFS?
Apple intentionally did not enable NTFS write abilities for MacOS because NTFS is a proprietary file system owned by Microsoft. Without permission and the documentation of the file system’s specifications, Apple cannot legally implement full read/write support due to copyright issues.
Microsoft developed NTFS solely for Windows NT systems in the 1990s. That is why Windows fully supports read/write on NTFS while Apple is limited to read-only on Mac machines. Microsoft has not made NTFS an open standard that can be universally implemented by other platforms.
Enable NTFS Write on Mac
To enable full read/write access on NTFS drives from your Mac, you need to use a third-party driver or NTFS app. These add-on tools provide NTFS write support by reverse engineering how the file system works.
Here are some options to enable NTFS write support on Mac:
- Paragon NTFS for Mac – Paid driver with 10 day free trial. Simple install and setup.
- Mounty for NTFS – Free and open source NTFS driver. Lightweight app.
- Tuxera NTFS for Mac – Paid NTFS driver with 14 day free trial.
- Microsoft NTFS for Mac by Paragon Software – Official Microsoft licensed driver. 14 day free trial.
These solutions work by modifying the native NTFS driver in MacOS to add write capabilities. Some solutions like Paragon also offer additional benefits like faster performance, automatic mounting, etc.
Mac Read/Write FAT32 Drives
In contrast to NTFS, Apple provides full native support for reading and writing to FAT32 drives on Mac computers. No additional software is needed.
When you connect an external drive or flash drive formatted as FAT32, MacOS will automatically read and write files just like a native Mac volume. You can freely:
- Copy files to and from the FAT32 drive
- Edit documents stored on the FAT32 drive
- Write new files and folders to the drive from Finder
- Delete or move files on the FAT32 drive
- Format the drive to FAT32 from Disk Utility
This seamless read/write ability makes FAT32 the ideal file system to use for external drives that are shared between Windows and Mac computers.
Limits of FAT32 on Mac
While Mac fully supports FAT32 read/write, there are some limitations with the FAT32 file system:
- Individual file size limit of 4GB
- Total volume size limit of 32GB (can be larger but not bootable)
- No built-in encryption
- Lower performance compared to NTFS on Windows
For larger external hard drives that don’t need cross-platform use, it is better to format in a native file system for higher performance. Mac drives are best formatted with either APFS or HFS+.
External Drive File System Recommendations
Here are recommendations for which file system to use when formatting external drives for use with Mac and Windows PCs:
| Drive Use Case | Recommended File System |
|---|---|
| External drive just for Mac | APFS or HFS+ |
| External drive just for Windows | NTFS |
| External drive for both Mac and Windows | FAT32 |
| Large external drive for backup or media | exFAT |
For external portable hard drives or flash drives that need to transfer files between Mac and Windows, FAT32 is the tried and true compatible file system to use.
HFS+ used to be common for drives shared between Mac and Windows but is legacy. FAT32 has wider compatibility. exFAT overcomes FAT32 limits but may not work on old OS versions.
Tips for FAT32 External Drives on Mac
Here are some tips for using an external FAT32 drive with your Mac:
- Use Disk Utility to easily format any drive as FAT32.
- FAT32 limits file sizes to 4GB so split larger files before copying.
- For media like movies, format larger drives as exFAT instead.
- Always eject the FAT32 drive safely before unplugging.
- Defragment the drive occasionally for better performance.
- Consider NTFS if the drive will mainly connect to Windows PCs.
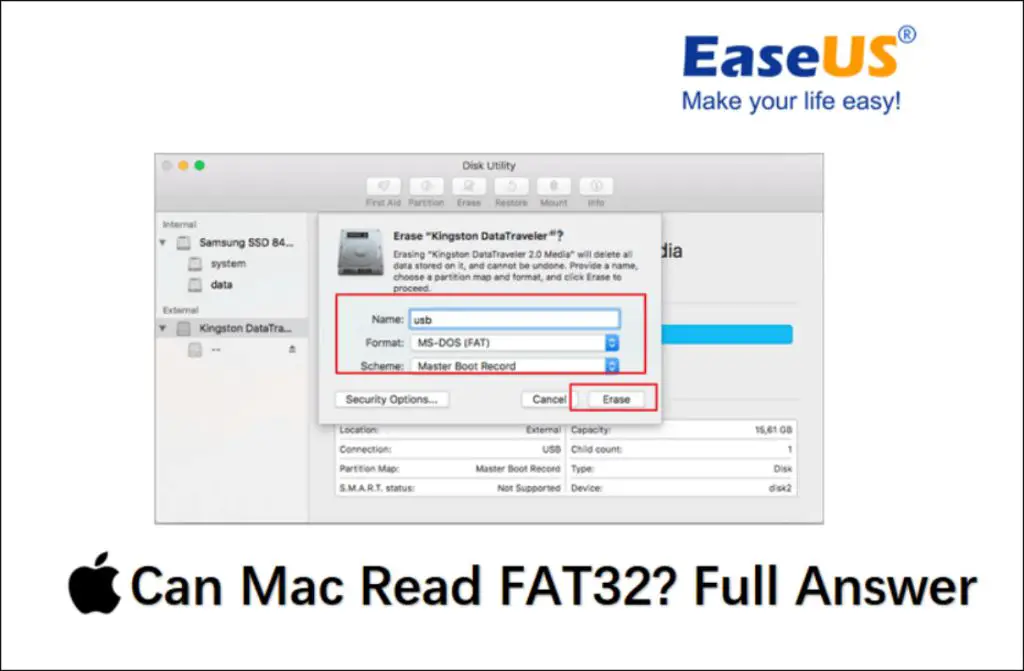
Format Drive to FAT32 on Mac
Formatting an external drive to FAT32 on a Mac is simple using the built-in Disk Utility application. Here is how to format to FAT32 on Mac:
- Connect the external drive to the Mac.
- Launch Disk Utility (in Applications > Utilities folder)
- Select the drive in the sidebar.
- Click Erase at the top.
- Choose “MS-DOS (FAT)” as format.
- Give the drive a name and click Erase.
The drive will quickly format to a compatible FAT32 file system. Then you can use it with both Mac and Windows PCs.
Other Ways to Format FAT32 on Mac
Besides Disk Utility, you can also use the command line or other tools to format as FAT32 on Mac:
- Command line – Use the
diskutilcommand. - Terminal – The
newfs_msdoscommand formats FAT32. - SuperDuper – The popular drive cloning app has formatting options.
- Drive utilities – Apps like DriveDx have FAT32 formatting tools.
But Disk Utility will be the easiest way for most users to quickly format an external drive with FAT32 on Mac.
Format NTFS Drives on Mac
You may want to format an external drive with NTFS if the drive will primarily connect to Windows PCs. Here are your options for formatting NTFS on Mac:
- Let Windows format the drive when you first connect.
- Use Disk Utility “Erase” and choose “Windows NT File System” (NTFS).
- Use third-party NTFS apps that provide format tools.
- Connect to a Windows PC and format the drive from Windows.
The easiest way is to simply connect the new external drive to a Windows PC first. Windows will automatically prompt to format unrecognized new drives, allowing you to select NTFS as the file system.
Format NTFS from Mac Terminal
You can format an NTFS drive from the command line using Terminal on your Mac. Here are the steps:
- Connect the external drive to format.
- Launch Terminal (in /Applications/Utilities).
- Type
diskutil listto get disk identifiers. - Use
diskutil eraseDisk NTFS "NAME" DISK_ID(replace NAME and ID). - The drive will format to NTFS.
Make sure to replace “NAME” with what you want to label the drive and “DISK_ID” with the full identifier like disk2s1 from the diskutil list output.
ExFAT as Cross-Platform Format
While FAT32 is the tried and true cross-platform file system, exFAT is a newer format that avoids FAT32’s limits while maintaining compatibility on modern OS versions.
exFAT advantages:
- No file size or partition size limits.
- Faster than FAT32 for large volumes.
- Supported by macOS and Windows (not Linux).
The advantages make exFAT worth considering for external drives, especially larger ones used for backups, media libraries, etc. Just check if the drive uses older OS versions that may not support exFAT.
To format exFAT in Mac Disk Utility, choose “exFAT” in the “Erase” format dropdown. You can also format exFAT from Windows Disk Management.
Tips for Using NTFS on Mac
Here are some useful tips for using NTFS drives on your Mac:
- Install NTFS apps like Paragon NTFS for full read/write access.
- Connect NTFS drives to Windows PCs for best performance.
- Eject NTFS drives properly before disconnecting from Mac.
- Limit disk access to read-only if using without NTFS software.
- Can keep files up to 16 TB on a single NTFS drive.
- Always backup important data on the NTFS drive.
While Mac can read NTFS drives, some apps may have compatibility issues. So NTFS will work best when the drive is accessed mainly from Windows PCs.
Troubleshooting NTFS Drives on Mac
Here are some troubleshooting tips if you have issues using NTFS drives on your Mac:
- Mounting issues – Try disconnecting and reconnecting the drive.
- Read-only disk – Make sure you have write permissions enabled with third-party NTFS apps.
- Corrupted files – Run chkdsk in Windows to check for file system errors.
- Slow performance – Defragment the NTFS drive on a Windows PC.
- Unmounting issues – Use the
diskutil unmountcommand in Terminal. - Missing files – Use data recovery software to restore deleted files.
For persistent mounting issues, reformatting the NTFS drive may be required. Backup your files first before reformatting.
Conclusion
In summary, Mac can read both NTFS and FAT32 drives but needs third-party software to write to NTFS. FAT32 provides universal compatibility for Mac and PC but has limits like 4GB file sizes. For external drives, use FAT32 if sharing between Mac and Windows. NTFS is best for drives used mainly with Windows. And consider exFAT for large cross-platform drives.