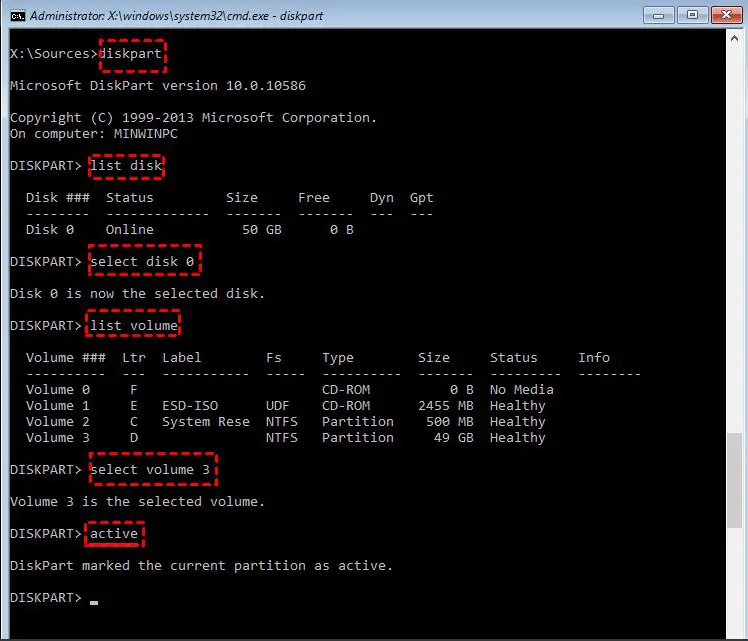
Making a partition bootable allows your computer to load an operating system from that partition. This can be useful for installing a new operating system, running multiple operating systems on one computer, or recovering your current operating system if something goes wrong. Here are some quick answers to common questions about making partitions bootable:
What is a partition?
A partition is a section of your computer’s hard drive that acts as if it were a physically separate hard drive. Partitions allow you to divide your hard drive into segments that can serve different purposes. For example, you may have one partition for your operating system and applications, and another partition just for data storage.
What does it mean to make a partition bootable?
Making a partition bootable means configuring that partition so that your computer knows it can load an operating system from there. When you turn on your computer, it looks for a bootable partition to start up the operating system. So setting a partition as bootable allows that partition to be used for booting.
Why would I want to make a partition bootable?
Here are some common reasons you may want to make a partition bootable:
- To install a new operating system – When installing a new OS, you need to make the target partition bootable so your computer can start up the new OS.
- To boot into multiple operating systems – Having multiple bootable partitions allows you to dual boot different OSes on one computer.
- To repair your current OS – Making a partition with a recovery image bootable can help you reboot into the recovery OS and troubleshoot issues.
How do I make a partition bootable?
The steps to make a partition bootable depend on a few factors, like what operating system you want to install and what boot mode (BIOS or UEFI) your computer uses. But the general process looks like this:
- Create a bootable installer drive – This is typically a USB drive or DVD you can boot from to begin the OS installation.
- Open your computer’s firmware settings – Access the BIOS or UEFI settings menu on startup.
- Change the boot order – Set your installer drive as the first boot option so your computer tries booting from it first.
- Use the installer to format the target partition – When going through the OS installation, format the partition you want to make bootable.
- Install boot files like a bootloader – Your OS installer will add the files needed to make the partition bootable.
The specifics can vary, so refer to your operating system’s installation guide. But those are the essential steps that allow your firmware to recognize the partition as a bootable drive.
How do I create a bootable installer drive?
Creating a bootable installer drive is the first step in making your partition bootable for a new OS. Here’s how to make one:
On Windows:
- Use the Media Creation Tool – This utility from Microsoft lets you make a bootable Windows install USB drive.
- Try Rufus – Rufus is a free third-party tool for making bootable USB drives for various ISO files.
- Burn a DVD – You can burn the ISO file to a blank DVD to make it bootable if your computer supports booting from DVD.
On Mac:
- Use Disk Utility – Disk Utility has an option to restore an ISO image to a USB drive to make it bootable.
- Try a third-party tool – Apps like UNetbootin or BalenaEtcher can create bootable drive from ISOs on Mac.
- Burn a DVD – Again, you can burn the ISO to a blank DVD if your Mac supports booting from DVD.
On Linux:
- Use dd – The dd command can directly copy an ISO to a drive to make it bootable.
- Try UNetbootin – UNetbootin is also available on Linux for easy USB drive creation.
- Use Disk Utility – GUI disk utility tools included in many Linux distros also have bootable USB creation options.
Refer to your installer ISO instructions for the officially recommend method. But these are some easy ways to create bootable media on each operating system.
How do I change the boot order in my firmware?
To boot from your new installation drive, you need to change the boot order in your firmware settings so the USB or DVD boots first:
For BIOS systems:
- Access your BIOS settings – Typically by pressing F2, F10 or Delete during startup.
- Go to the Boot or Boot Order section – The navigation varies between manufacturers.
- Move your desired boot drive up – Use the arrow keys and confirm buttons to reorder devices.
- Save changes and exit BIOS.
For UEFI systems:
- Access your UEFI settings – Typically by pressing F2, F10 or Delete during startup.
- Go to the Boot Order or Boot Configuration section.
- Drag your desired boot drive up the list – Mouse and touchscreen navigation is usually supported.
- Save changes and exit UEFI.
Refer to your computer or motherboard manual for the exact keys and steps. But changing the boot order ensures your system tries the installation drive first before booting from your regular hard drive.
How do I format the target partition?
When going through the operating system installer, you’ll reach a disk partitioning stage. Here you need to select the target partition you want to make bootable and choose to format it. Formatting erases the partition and prepares it for the new OS.
If the partition is already formatted correctly for your desired file system (like NTFS for Windows or ext4 for Linux), you may just need to delete all existing partitions and recreate them. Follow your installer’s formatting instructions closely.
What boot files need to be installed?
For the partition to be bootable, your operating system files need certain boot components installed to that partition. This usually happens automatically during OS installation.
Key files needed to make a partition bootable include:
- Bootloader – Software like GRUB that boots up the operating system kernel.
- Kernel – The core operating system files.
- Device drivers – Software to run hardware like storage controllers and network adapters.
As long as you follow the OS installation steps normally, it will handle installing these boot components to the partition you selected. Some installers offer advanced options to customize where boot files are written if desired.
How can I troubleshoot boot issues?
If you have problems getting your computer to boot from the new partition, here are some troubleshooting tips:
- Try rebooting again – Sometimes boot order changes don’t get applied until you restart.
- Check boot order again – Confirm the installer drive is first in your firmware boot order menu.
- Try a different port/drive – If using a USB drive, change ports and check the drive on another computer if possible.
- Recreate installer drive – Reformatting the drive and writing the installer ISO again may help.
- Disable fast boot – Fast boot features in Windows 8 and 10 may interfere with bootable drives.
- Update firmware – A firmware update from your manufacturer could improve boot compatibility.
If you still can’t get the selected partition to boot, there may be a deeper issue. You may need to seek help from the operating system or hardware manufacturer.
Conclusion
Making a partition bootable involves a few key steps:
- Creating an installer drive you can boot from
- Changing your boot order to the installer drive
- Formatting the target partition
- Installing boot files like a bootloader to the partition
Following your operating system’s installation guide closely will walk you through making the partition bootable. If you run into issues getting the computer to boot, changing boot order, recreating installer media and updating firmware are some troubleshooting steps to try.
Setting a partition as bootable opens up many possibilities like dual booting multiple operating systems, repairing your current OS, or replacing your existing OS with a new one. Just be sure to back up any important data first! With the right preparation, you can get your partition bootable for whatever bootable purpose you need.