Quick Summary
If you have accidentally replaced or deleted a file on your Mac and don’t have Time Machine backups, there are still some options for trying to recover the lost file:
- Use data recovery software like Disk Drill to scan your drive and recover deleted files
- Check your Trash and recently deleted folders for the original file
- Use your Mac’s Versions feature to restore a previous version of the file
- Recover the file from a backup like iCloud Drive, Dropbox, or another cloud storage service
- Try using terminal commands like ‘ls -lT’ to find deleted files still on your drive
- Take your Mac to a data recovery specialist for professional file recovery
While the original overwritten file may be unrecoverable, one of these options may help you restore a recently deleted version or recover the file from another location.
What Happens When You Replace or Overwrite a File on Mac
When you overwrite an existing file on your Mac by replacing it with a new file of the same name, the original contents of the file are lost as the new data overwrites the sectors on your drive previously occupied by the original file.
Unlike when you move a file to the Trash, no copy is made to a temporary ‘recoverable’ location. The original data is simply overwritten by the new data, making it essentially unrecoverable once replaced.
This makes accidentally replacing files a difficult data loss scenario. However simply deleting a file will send it to the Trash, keeping the original intact and giving you a better chance of recovery.
Why Replaced Files Are Hard to Recover
When a file is replaced, the original data gets overwritten at the physical level on the storage drive. The pointers to the original data’s location on the disk get updated to point to the new data. So the operating system no longer has a way to access the original data.
Even data recovery software is generally unable to bring back an overwritten file, as the original contents have been altered by the replace operation. This makes replacement far riskier than deletion when it comes to recoverability.
Mitigating Risks of Accidental File Replacement
Some measures you can take to avoid accidental file replacement include:
- Enable Time Machine backups on an external drive, allowing you to go back to a previous version if a file gets overwritten
- Use cloud syncing services like iCloud, Dropbox, or Google Drive to keep an online copy of files
- Use the Versions feature of Mac OS to save document history of changed files
- Exercise caution when reusing file names – add numbers, dates, or ‘version’ to file names to reduce risk
- Be extra careful when moving files between folders on your system to avoid overwriting
How to Recover an Overwritten File on Mac Without Time Machine
If you don’t have Time Machine backups or an off-site copy of the lost file, recovery becomes much trickier. But there are still some options you can try:
Data Recovery Software
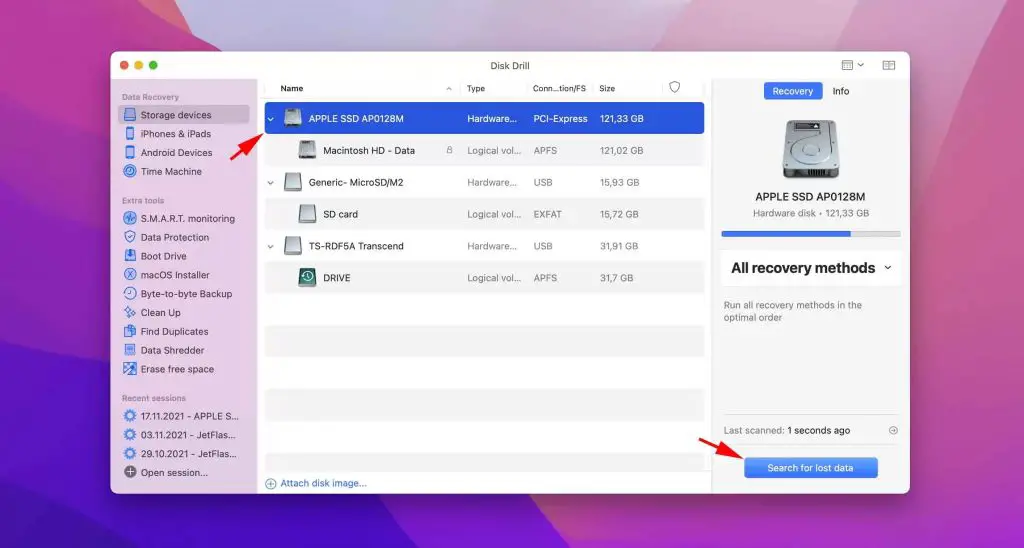
Data recovery programs like Disk Drill can help dig into your drive to find and restore recently deleted files. While overwritten data is difficult to recover, often remnants of old files remain that can be pieced together.
Disk Drill scans your entire drive and looks for files that have been marked by the operating system as deleted. Even if the original file has been partially overwritten, it may still be possible for the software to recover some or all of the data.
To use Disk Drill:
- Download and install Disk Drill from the developer’s website (https://www.cleverfiles.com)
- Launch Disk Drill and select your startup drive to scan
- Click “Recover” next to the name of the deleted file in the results list
- Preview the file and select a recovery destination
- Click the “Recover” button to restore the file
Disk Drill has both free and paid recovery tool options depending on your needs.
Check the Trash and Recently Deleted Folders
If you have emptied the Trash since deleting the original file, it likely won’t be here. But if the Trash hasn’t been emptied, look here for the originally deleted file before replacement.
On Mac OS, you can also find deleted files in the Recently Deleted folder for up to 30 days unless you override the saves:
- Go to the Finder menu > Go > Go to Folder
- Type in /.Trashes
- Open the ‘500’ folder and search for your deleted file
- Copy the file out of the Recently Deleted folder to recover it
Use Versions to Restore Previous File Version
The Versions feature of Mac OS saves snapshots of files whenever they are altered and closed. You can use this to restore previous versions of a file if you’ve overwritten it.
To restore a previous version:
- Find the overwritten file and right click it
- Click Browse All Versions
- Select the latest version before the file was overwritten
- Click Restore to copy this version back to its original location
This replaces the current file with the selected older version. Keep in mind Versions history is limited, so overwritten files may no longer have old snapshots available.
Recover from Cloud Storage or Backup
If you have cloud copies or backups of the overwritten file, restoring from one of these services can recover your lost data:
- iCloud Drive – Restore previous file versions from iCloud Drive backup
- Dropbox – Restore from 30 day file history or deleted files if still available
- Google Drive – Restore from Google Drive trash (if not emptied) or version history
- Other backup services – Retrieve the file from any other cloud backup service used
This option again relies on the file being retained in a cloud storage trash or history. But if available here, cloud recovery is often simple.
Terminal Commands to Try to Locate Deleted File
If you are comfortable with the command line, there are some terminal commands that may help surface deleted files still available on your drive:
- ls -lT – Lists files sorted by last modified date, so recently deleted may appear at end
- lsof | grep deleted – Finds open deleted files that may be recoverable
- Zap PRAM – Resets parameter RAM, which sometimes clears deleted file locks
Use these commands carefully, ideally on a disk copy rather than your primary drive, as they can alter system data if not used properly. But in some cases they may surface the original deleted file.
Take Your Mac to a Professional File Recovery Service
For the highest chance of recovering an overwritten file, even without Time Machine, your best option is to take your Mac to a professional data recovery shop. Services like DriveSavers use specialized tools to examine and restore data direct from the drive platters at a very low level.
These kinds of advanced data recovery operations are often expensive $500 or much more. But for critical files may be worthwhile if no other DIY options are successful.
Replacing Files to Avoid Losing Work Productivity
When you accidentally replace an important file, it can derail your workflow and cause frustration. But with redundant backups and recovery options, you can usually mitigate the damage and get back on track quickly.
Follow best practices like Time Machine and cloud syncing to minimize risk. But also know recovery tools are available for when mistakes do happen.
With preparation and care, an accidental overwrite doesn’t have to lead to losing vital data and productivity.
Conclusion
Recovering overwritten files on Mac without Time Machine or other backups is a challenge. But recovery software, previous versions, cloud copies, terminal commands, and professional help provide options for getting back lost data.
Be vigilant to avoid file replacement accidents. But know that recovery solutions can often salvage your work, even in a worst case overwrite scenario.