Having a file on your desktop that refuses to be deleted can be incredibly frustrating. No matter how many times you try to send it to the Recycle Bin, the pesky file remains firmly in place. Fortunately, there are several troubleshooting steps you can take to forcibly remove a stubborn desktop file.
Quick Fixes to Try First
Before you pull out the big guns, there are a few quick and easy things you can attempt to delete the problematic file:
- Restart your computer – This resets everything and cleans out any glitches that could be preventing the file deletion.
- Use Shift + Delete – This keyboard shortcut bypasses the Recycle Bin so the file can’t linger.
- Delete via command prompt – Using the “del” command in the command prompt gives you more power over file deletion.
- Update your antivirus – An outdated antivirus can sometimes block deletions needed to maintain system security.
- Check the file permissions – Make sure you have full ownership permissions for the file and desktop folder.
If the file still remains after trying these basic fixes, it’s time to dig a little deeper into troubleshooting your uncooperative desktop file.
Investigate File Properties for Clues
Looking at the file’s properties sheet can sometimes reveal what’s blocking the deletion. Here are some important things to examine:
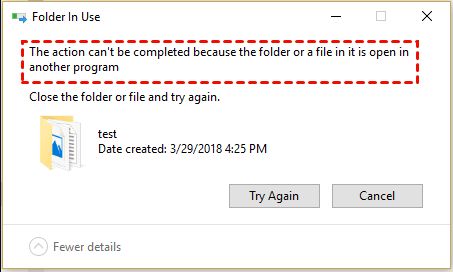
- File in Use – A file may not delete if it is currently open in another program. Be sure to fully close the file before attempting to delete it.
- Read-only Attribute – Check the properties box for the read-only attribute. Uncheck it if enabled.
- Location – Pay attention to the file location listed. An incorrect or unset location can prevent deletion.
- Parent Folder Permissions – The permissions on the parent folder override file-level permissions. Make sure you have full access to the desktop folder.
Taking note of any oddities in the file properties can help you identify what might be blocking removal and determine how to enable deletion.
Try Deleting in Safe Mode
Booting your computer into Safe Mode loads a minimal version of Windows with only essential drivers and services active. This strips away potential interferences that could block a file deletion.
To access Safe Mode on Windows 10:
- Open the Start menu and click the Power button > Hold Shift and click Restart.
- On the Choose an option screen, select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart.
- After your PC restarts, you’ll see a list of startup settings. Press 5 or F5 to boot into Safe Mode.
Once in Safe Mode, try deleting the stubborn file again. If it’s successful here, something loading at regular startup was likely blocking the file removal.
Unhide Hidden Files
Another aspect to check – is the file actually hidden? A hidden file won’t display in File Explorer, even though it still takes up space and remains on your desktop.
To view all hidden desktop files in Windows 10:
- Open File Explorer and navigate to the View tab.
- Check the Hidden items box.
- Your desktop will refresh to display all hidden files and folders.
If you find the bothersome file here, you can delete it normally now that it’s unhidden.
Revoke File Permissions
Refusing to be deleted may indicate the file has overly permissive access controls. Try resetting its permissions before attempting removal again.
To revoke all permissions on a file in Windows:
- Right-click the file and select Properties.
- Go to the Security tab and click Advanced.
- Click Disable inheritance > Convert inherited permissions.
- Remove all listed permissions so nothing has access to the file.
Once all permissions are revoked, apply your own user account full control to regain access. Test if the file now deletes successfully.
Delete via Command Prompt
Using the Command Prompt gives you advanced control over file deletion that can help remove a particularly stubborn desktop file.
To delete a file via Command Prompt:
- Open the Start menu and search for “cmd” to open the command prompt.
- Type cd Desktop and press Enter to navigate to your desktop folder.
- Type del filename and press Enter, replacing filename with your file.
- Type dir to confirm the file no longer appears on your desktop.
The Command Prompt approach forces deletion even if the file is in use or lacks appropriate permissions. You may need to run the Command Prompt as Administrator to gain full access.
How File Deletions Work in Windows
To better troubleshoot stubborn files, it helps to understand what happens behind the scenes when you delete a file in Windows.
When you delete a file, Windows doesn’t immediately remove it from your hard drive. Instead, it does two things:
- Removes the file directory entry – This cuts off system access to the file.
- Marks the disk space as free – The space used by the file is now considered available for new data.
The actual file contents remain on the disk until overwritten by something else. This allows you to recover deleted files easily with tools like Recuva.
Problems can occur if the file directory entry remains but the space is marked free. The file seems to stick around and resist deletion.
Using the Command Prompt or Safe Mode boot forces a rewrite of the file table. The read-only attribute, permissions, and other issues are overridden so the file can be deleted fully.
Reset the Desktop Icon Cache
If you believe the desktop file icon itself is corrupt, resetting the icon cache may help remove it.
To reset the desktop icon cache in Windows 10:
- Press Windows + R to open the Run box.
- Type control folders and click OK.
- Double-click the Desktop folder.
- Select the View tab and click Reset Icon Cache.
This will rebuild the cache and apply your desktop icon layout again. A corrupt icon should disappear after resetting the cache.
How to Delete Files That Keep Reappearing
In some cases, a file may reappear on your desktop after being deleted repeatedly. This is typically caused by one of two things:
- Backup software – Some backup tools will re-sync deleted files from the cloud storage. Disable syncing to prevent restores.
- Malware infection – Malware may continuously generate the file. Run security scans to detect and remove any infection.
For reappearing files, focus on finding and stopping the source that keeps restoring the file rather than trying to delete it again and again.
When to Use Third-Party File Deletion Tools
If the above troubleshooting still doesn’t remove the pesky desktop file, turning to a third-party file deletion tool may help:
- Unlocker – Unlocks files so they can be deleted even if locked by Windows.
- Remo File Eraser – Wipes out hard-to-delete files while bypassing Recycle Bin.
- Eraser – Completely scrubs target files from your system and prevents recovery.
Advanced file deletion utilities can delete protected system files and bypass locks that prevent standard deletion. This gives you the forceful removal power needed for the most stubborn desktop files.
Recover Deleted Files if Needed
During all this file deletion troubleshooting, don’t forget about file recovery options in case you delete something important accidentally:
- Windows Backup History – Recover previous file versions from backup.
- Recycle Bin – Stores copies of recently deleted files.
- Cloud storage – If synced to cloud, restore the file from there.
- Data recovery software – Scan and recover deleted files from disk.
So don’t worry about testing different deletion methods – you can retrieve any unintended file deletions if needed.
When to Do a Clean Windows Install
As a last resort, doing a completely clean install of Windows may be required to fully remove a file that persists through all other deletion attempts. Reinstalling Windows resets all user data, accounts, registries, and programs.
Before reinstalling Windows:
- Back up any data and files you want to keep.
- Have your Windows license key ready to activate.
- Download the latest Windows ISO file and create bootable install media.
After conducting a fresh Windows installation, you can restore your files selectively – leaving behind any problematic ones.
Conclusion
Desktop files that refuse deletion can certainly be frustrating. Fortunately, Windows provides a few different approaches you can attempt to force file removal.
A few key tips include:
- Check the file properties for clues.
- Try Safe Mode to eliminate interferences.
- Unhide hidden files.
- Use Command Prompt for advanced deletion.
- Reset icon cache if needed.
For the most stubborn files, third-party deletion tools and completely reformatting the drive may be necessary. With the right troubleshooting steps, you can conquer unwanted desktop files!