SD cards, also known as secure digital cards, are a common type of removable flash memory card used in many electronic devices such as digital cameras, smartphones, tablets, and more. But with different sizes, speeds, and specifications, it can sometimes be tricky to identify exactly what kind of SD card you have. This article will provide a guide on how to identify the key details of an SD card.
What is an SD Card?
An SD card, short for Secure Digital card, is a small flash memory card designed to provide storage for digital devices. SD cards are commonly used in many consumer electronic devices such as digital cameras, camcorders, smartphones, tablets, media players, video game consoles, GPS units, drones, and more. Here are some key things to know about SD cards:
- Non-volatile memory – SD cards use flash memory chips to store data. The data is retained even when power is turned off.
- Removable – SD cards are designed to be removed and transferred between compatible devices.
- Small and lightweight – SD cards are compact in size, roughly the size of a postage stamp.
- Durable – SD cards have no moving parts and are shockproof, dustproof, waterproof, and X-ray proof.
- Compatible – SD cards use a universal compatibility standard that allows them to work across many different devices.
Overall, the main purpose of an SD card is to provide reliable, removable data storage that can easily be transferred between devices. The portability and universal compatibility of SD cards have made them a widely popular storage solution.
SD Card Sizes
SD cards come in a variety of storage capacities. The original SD card design started at 32MB, but over the years capacities have grown enormously. Here are some of the common SD card sizes available today:
- SD – Original SD card with capacities up to 2GB.
- SDHC – SD High Capacity cards with capacities ranging from 4GB to 32GB.
- SDXC – SD eXtended Capacity cards with capacities from 64GB to 2TB.
- SDIO – SD Input/Output cards that combine storage with input/output functions.
- microSD – Miniaturized version of SD cards often used in smartphones. Have the same sizes and speeds as regular SD cards.
The SDHC, SDXC, and SDIO specifications outline technical features that allow for higher capacities and faster speeds. But in general, the larger the gigabyte (GB) number, the more data the SD card can store.
SD Card Speeds
In addition to varying in storage size, SD cards also differ in their data transfer speeds. Faster cards allow you to transfer data like photos, videos, music, and other files more quickly. SD card speed is measured in megabits per second (Mbps). There are several speed classes:
- Class 2 – Minimum write speed of 2 Mbps
- Class 4 – Minimum write speed of 4 Mbps
- Class 6 – Minimum write speed of 6 Mbps
- Class 10 – Minimum write speed of 10 Mbps
- UHS Speed Class 1 – Minimum write speed of 10 Mbps
- UHS Speed Class 3 – Minimum write speed of 30 Mbps
The speed class is typically marked by a number inside a C with a circle around it (e.g. Class 10). UHS (Ultra High Speed) cards are optimized for high-definition video recording and fast action photography. The higher the speed class number, the faster the card can write data.
Identifying Key Details on an SD Card
Now that you know the basics of SD card sizes and speeds, here are some key things to look for when trying to identify the details of an SD card:
1. Check the Size Marking
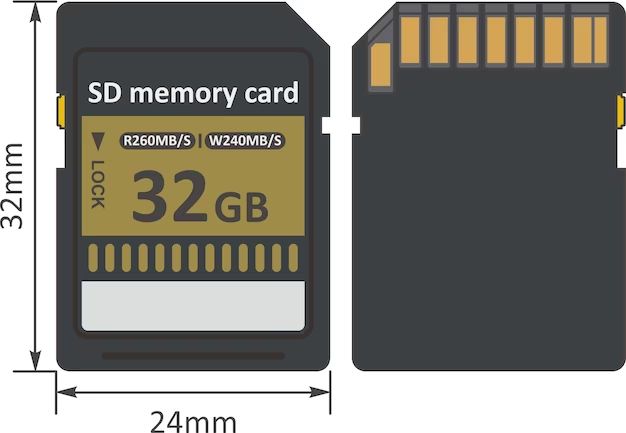
Look at the front or back of the SD card for a size marking, such as “32GB” or “16GB.” This indicates the total data storage capacity of the card. Higher numbers mean more gigabytes (GB) of storage space.
2. Look for Speed Class Markings
Find a speed class symbol, such as “C10” or “U3,” on the front or back. This gives you the minimum write speed that the card supports. Higher numbers mean faster transfer speeds.
3. Note Physical Size
Measure the physical dimensions of the card. Full-size SD cards are 32 x 24 x 2.1 mm while microSD cards are much smaller at 15 x 11 x 1 mm.
4. Check Format Type
See if “SDHC” or “SDXC” is written on the front or back. SDHC cards range from 4GB to 32GB while SDXC holds from 64GB up to 2TB.
5. Look for Brand and Model
The brand name and model number are typically printed on the front. This can provide more specific details about that SD card version.
6. Insert into Device
Put the SD card into a compatible device like a computer, camera, or tablet. Details like capacity and speed class may show up when the card is recognized.
7. Use a Card Reader
A dedicated SD card reader can be a useful tool for getting more information on an SD card. Once inserted, details on size, format, and speed will be displayed.
SD Standards and Versions
In addition to size and speed, SD cards can be identified by understanding the different SD standards and versions. Some key standards include:
- SDHC – Introduced capacities from 4GB up to 32GB. Uses FAT32 file system.
- SDXC – Allows capacities from 64GB to 2TB. Uses exFAT file system.
- UHS-I – Interface for 104 Mbps bus speed. Includes UHS speed classes.
- UHS-II – Faster 312 Mbps bus speed for advanced applications.
- UHS-III – Upcoming ultra-fast standard with 624 Mbps bus speed.
Identifying which standards an SD card is compatible with can provide more information on expected performance and compatibility with devices.
Common SD Card Versions
| SD Card Version | Details |
|---|---|
| SD | Original version up to 2GB capacity. |
| SDHC | High capacity from 4GB to 32GB. |
| SDXC | Extended capacity from 64GB up to 2TB. |
| microSD | Miniaturized version of SD card. |
| miniSD | Predecessor to microSD, now obsolete. |
Identifying Counterfeit vs Genuine SD Cards
With SD cards becoming more affordable, counterfeit and fake SD cards have also become more commonplace. Some signs that an SD card may be counterfeit include:
- Too low price compared to legit cards with same specs
- Generic or no brand name
- Poor print quality on markings
- Does not match advertised capacity
- SD adapter doesn’t fit properly
- Slow performance that does not match speed class
Reputable and well-known brands like SanDisk, Samsung, Sony, Kingston and others are less likely to manufacture counterfeit cards. Checking user reviews can also help determine if a card is genuine. While fake cards may look identical to the real thing, their poor reliability can lead to data errors, corruption, and loss.
SD Card Terminology
There are some common terms used when describing SD cards that are helpful to know when identifying key details:
- RW – Rewritable, can be erased and reused multiple times
- ROM – Read-only memory, pre-written and not erasable
- SDA – SD adapter or converter between miniSD, microSD, and full-size SD
- Lock – Locks card as read-only to prevent accidentally deleting or overwriting data
- HC – High capacity, 4GB to 32GB capacity range
- XC – eXtended capacity, 64GB and larger capacities
Conclusion
Identifying and understanding the key specifications of an SD card enables you to select the right card for your device and intended use case. The main factors to look for are the storage capacity, speed class rating, physical size, and SD standards compatibility. Checking the brand, markings, packaging, and reading reviews can verify if a card is genuine. With counterfeit cards being common, it pays to buy from reputable sources and understand exactly what kind of SD card you are purchasing.