RAID 0 is a type of hard drive array that uses striping to split data evenly across two or more drives. This allows for faster read and write speeds since the workload is distributed across multiple drives. M.2 SSDs are a type of solid state drive that utilize the PCIe bus, allowing for very fast data transfer speeds. By combining these two technologies, it is possible to achieve blazing fast read and write speeds.
However, while RAID 0 M.2 SSDs offer performance benefits, the array lacks redundancy. If one drive fails, all data will be lost. Additionally, the performance gains depend on the workload and may be minimal for many real-world use cases. This article will benchmark RAID 0 performance on M.2 SSDs and analyze whether RAID 0 is worth it for most M.2 SSD uses.
What is RAID 0?
RAID 0, also known as disk striping, is a storage technology that combines multiple disk drives into one logical unit. Data is split and distributed evenly across two or more drives simultaneously. This allows for faster read and write speeds compared to a single drive, since the workload is spread across multiple disks.
With RAID 0, data is broken down into blocks called stripes that get written across the member disks one by one in turn. For example, stripe 1 gets written to disk 1, stripe 2 gets written to disk 2, stripe 3 to disk 3 and so on. This allows each drive to read and write data independently and in parallel, increasing overall performance.
The main benefit of RAID 0 is increased input/output operations per second (IOPS) and bandwidth. By spreading data across multiple disks, the workload is shared between drives. More drives means more performance capability.
Benefits of RAID 0
RAID 0 offers two main benefits compared to a single drive configuration: increased speed and combined capacity.1
By striping data across multiple drives, RAID 0 allows for parallel read and write operations. This means multiple drives can be accessed simultaneously, greatly improving overall performance compared to a single drive. Many benchmarks have shown RAID 0 can double or even triple the read/write speeds of a single SSD.2
RAID 0 also combines the capacities of multiple drives into one large volume. For example, two 500 GB SSDs in RAID 0 would create a single 1 TB volume. This provides more storage capacity than a single drive could offer.
For these reasons, RAID 0 is a popular choice for applications where performance and capacity are more important than fault tolerance and redundancy. Common RAID 0 use cases include gaming PCs, video editing workstations, and small business file servers where backups are routinely performed.
What are M.2 SSDs?
M.2 SSDs are a form factor of solid state drives that utilize the M.2 connector standard. This allows M.2 SSDs to be very compact in size while still providing fast performance. The key aspects of M.2 SSDs are:
Form Factor – M.2 SSDs come in a thin, rectangular card shape, resembling a stick of RAM. They are designed to fit into the M.2 slot on a motherboard. M.2 sizes are designated by width and length, such as 22x80mm or 22x42mm. This compact shape allows easy integration into small devices.[https://www.exabytes.sg/blog/nvme-vs-m-2-vs-sata-ssd/]
Interface – M.2 SSDs can utilize different interface protocols, the main ones being SATA, PCIe NVMe, and AHCI NVMe. SATA M.2 drives provide similar performance to 2.5″ SATA SSDs. NVMe M.2 drives deliver much faster speeds through PCIe lanes, making them ideal for performance PCs.
M.2 SSD Performance
M.2 SSDs offer incredibly fast performance compared to traditional SATA SSDs. This is thanks to the PCIe interface which allows for much higher bandwidth than SATA. There are several key performance metrics to look at for M.2 SSDs:
- Sequential Read Speed – This measures how fast large files can be read sequentially. Top performing PCIe 4.0 M.2 SSDs today can reach read speeds over 7,000 MB/s.
- Sequential Write Speed – Similar to reads but measures sequential write performance. The fastest M.2 SSDs can hit write speeds around 5,000-7,000 MB/s.
- Random Read/Write Speeds – Measures IOPS (inputs/outputs per second) for random 4K reads/writes. Top M.2 SSDs can exceed 800K IOPS for random reads and 700K IOPS for writes.
- Latency – How fast the SSD can respond to read/write requests. The best NVMe M.2 drives have extremely low latency in the range of 10-20 microseconds.
In general, higher end PCIe 4.0 M.2 SSDs significantly outperform SATA and even PCIe 3.0 M.2 drives. For example, the Samsung 980 Pro PCIe 4.0 SSD has been benchmarked at over 6,900 MB/s seq. read, 5,000 MB/s seq. write speeds, and well over 800K IOPS for random reads/writes. This level of performance is 3-4x higher than SATA SSDs.
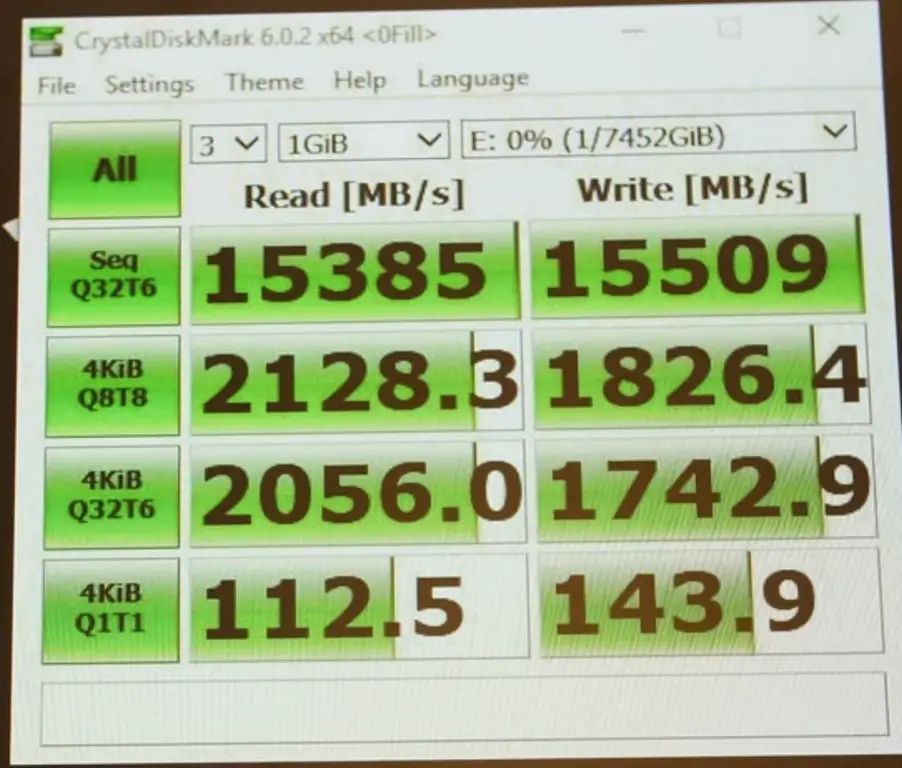
RAID 0 M.2 SSD Benchmark Results
Benchmarks reveal significant performance gains from configuring M.2 SSDs in RAID 0. According to tests by Alienware owners, two 2TB M.2 NVMe SSDs in RAID 0 achieved sequential read speeds over 6,000 MB/s and writes near 5,000 MB/s [1]. This is nearly double the sequential speeds of a single high-end NVMe drive.
Tom’s Hardware community tests also confirm RAID 0 performance benefits for M.2 SSDs. In their benchmarks, two 512GB M.2 NVMe SSDs in RAID 0 scored 7,000 MB/s sequential reads and 6,100 MB/s writes [2], handily beating even the fastest individual M.2 drives. Real-world usage reflected these synthetic benchmark gains, with dramatically faster game and application load times.
However, some experts argue the performance gains are not worth the increased failure risk and cost [2]. For consumer usage, a single high-end NVMe SSD may provide good enough performance for most needs.
Real-World Performance Gains
In real-world usage, RAID 0 with M.2 SSDs can provide noticeable performance improvements for certain workloads that benefit from increased read/write speeds. However, the gains are often dependent on the specific workload.
For gaming, loading times can be significantly reduced with RAID 0 M.2 SSDs. According to tests by Eteknix, game load times were 20-50% faster compared to a single M.2 SSD. This allows games to load their huge worlds faster so you can start playing quicker.
File transfers like moving large videos or project files also see a boost. In benchmarks, RAID 0 reaches over 6GB/s sequential read/write versus 3GB/s on a single SSD. This effectively doubles the transfer speed, cutting file transfer times in half.
Overall, RAID 0 M.2 SSDs provide a tangible real-world benefit for large file transfers and applications that need fast access to data like games. For general tasks like booting Windows or launching applications, the gains will be less noticeable versus a single fast SSD.
Is RAID 0 Worth it for M.2 SSDs?
When considering whether RAID 0 is worth it for M.2 SSDs, there are a few factors to weigh:
Cost – Setting up RAID 0 with two M.2 SSDs essentially doubles the cost versus buying just one SSD. M.2 SSDs are already more expensive than standard SATA SSDs. Going RAID 0 adds a significant expense.
Performance Gains – While synthetic benchmarks will show huge throughput gains with RAID 0, real-world usage may not benefit as much. M.2 SSDs are already extremely fast compared to hard drives. The performance boost may not be noticeable for many consumer workloads [1].
Failure Risk – With RAID 0 there is no redundancy. If one drive fails, all data across both drives is lost. The chance of failure doubles with two drives versus one. Regular backups are essential to mitigate this risk.
Use Cases – For tasks like video editing, 3D modeling, scientific computing where large files are continuously read/written, RAID 0 can provide more impactful gains. For general consumers the benefits are less substantial.
Overall, RAID 0 M.2 SSDs can make sense for niche professional use cases, but for most consumers the added cost and failure risk outweigh the minor performance improvements in daily use. Carefully consider whether the speed boost is truly worth it.
Alternatives to M.2 SSD RAID 0
While RAID 0 can provide a performance boost for M.2 SSDs, there are some alternatives that can deliver fast speeds without the risks of RAID 0:
PCIe 4.0 M.2 SSDs – The latest generation of PCIe 4.0 M.2 drives like the Samsung 980 Pro offer blazing fast sequential read/write speeds up to 7,000/5,000 MB/s. For many users, a single high-end PCIe 4.0 drive can provide exceptional performance without RAID.
Larger capacity M.2 SSD – Rather than combining two 1TB SSDs in RAID 0, a single 2TB M.2 SSD like the Sabrent Rocket Q provides great performance with lower overhead and risk. The extra capacity also reduces the need to manage multiple drives.
The bottom line is that modern PCIe 4.0 M.2 SSDs and larger capacity drives can in many cases deliver great performance on their own, reducing the need for the complexity and risks of RAID 0 striping.
Conclusion
In summary, combining multiple M.2 SSDs in RAID 0 can provide significant performance improvements over a single SSD. Benchmarks show RAID 0 M.2 arrays can achieve incredible sequential read/write speeds beyond 3,000 MB/s along with substantially faster 4K random reads and writes.
The real-world benefits will depend on your actual workload. For tasks like video editing, 3D modeling, data analytics, and other bandwidth-intensive operations, RAID 0 M.2 delivers much faster load times and workflow speeds. The potential downsides are increased risk of failure and higher costs.
For most regular desktop users and gamers, a single fast PCIe 3.0 or PCIe 4.0 M.2 SSD will be sufficient. But power users working with large files can benefit greatly from the performance of RAID 0 M.2 configurations.
Just be sure to backup critical data, as RAID 0 provides no redundancy. And carefully weigh the costs against alternatives like a single higher capacity premium M.2 drive.