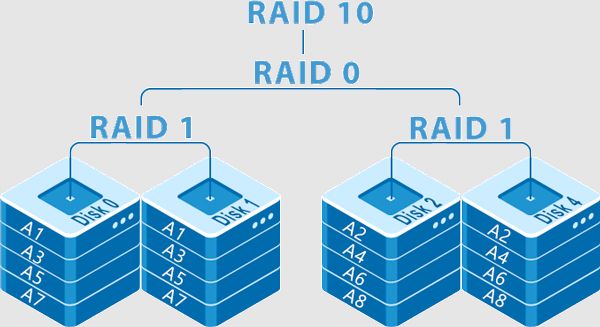
RAID 10, also known as RAID 1+0, is a RAID configuration that combines disk mirroring and disk striping to protect data. RAID 10 provides high performance and fault tolerance but reduces the total capacity of the array by half. While RAID 10 is a robust RAID level, it is still susceptible to failures and errors that can lead to data loss or an inaccessible array.
What causes a RAID 10 failure?
There are several potential causes of a RAID 10 failure:
- Disk failure – If one of the drives in the mirrored set fails, the RAID controller will switch to the other disk in the mirror. But if a second drive fails before the first failed drive is replaced, data loss will occur.
- Controller failure – The RAID controller coordinates the array and if it fails, the disks will become inaccessible.
- Accidental deletion – Accidentally deleting or overwriting RAID configurations can destroy the array.
- Software issues – Bugs, viruses, or failures during firmware updates can corrupt the array.
- Overheating – Excessive drive heat can lead to failures.
- Power surges – Electrical spikes can damage RAID components.
- Physical damage – Impacts, drops, fire or water damage to the server can destroy the drives.
Steps to recover a degraded or failed RAID 10 array
If your RAID 10 array fails or becomes degraded, follow these general steps for recovery:
- Stop all I/O to the array – As soon as you notice the array is degraded or inaccessible, stop all read/write operations to prevent further data loss.
- Identify and troubleshoot the failure – Check event logs for alerts about the faulty component. Run the RAID software management tool to identify the role of the failed disk.
- Replace failed drives – Replace any faulty drives with new drives of the same model and capacity. The RAID controller will automatically rebuild the drive’s data from the mirror.
- Repair accidental deletion – If the array was accidentally deleted, attempt to rebuild it in the RAID management software.
- Fix controller issues – If the controller failed, you may need to replace it with an identical model. Examine logs for firmware or hardware failures.
- Restore from backup – If drives cannot be rebuilt, restore data from a separate backup source to fully recover the array.
Detailed steps to recover RAID 10
Here are the detailed steps to take when recovering both fully failed and degraded RAID 10 arrays:
Recovering Degraded RAID 10
If a single disk fails in the RAID 10 array, it can be rebuilt using the following process:
- Stop all read/write operations to the array.
- Replace the failed hard drive with a new, identical drive.
- Open the RAID management software and locate the degraded array.
- Initiate a rebuild process for the new drive. The data will be mirrored from the surviving partner drive.
- The management software will indicate when the rebuild is complete and the array is restored to normal redundancy.
- Resume operations to the array once rebuilding completes without errors.
Recovering Fully Failed RAID 10
If the RAID 10 array suffers multiple drive failures or a catastrophic event, a full recovery process is required:
- Stop all I/O to the array and power down the RAID controller/server if possible.
- Replace any physically damaged drives or RAID components like batteries or controllers.
- Reseat drives and cables to ensure proper connections.
- Power on the server and RAID controller and allow it to detect the array.
- If the array is not automatically detected, open the RAID software and try to manually rescan or rebuild the array.
- If rebuilding fails, the array configuration data may be corrupted or lost. Attempt to manually recreate the array.
- With the array rebuilt, any previous data will still be missing. Restore data from a backup.
- Repair or update any RAID controller firmware or drivers if needed.
- Monitor the rebuilt array for errors before resuming full operations.
Tips for recovering RAID 10
Follow these best practices when attempting to recover a RAID 10 array:
- Always back up critical data outside the array to simplify recovery.
- Use RAID controller and drive models that support advanced recovery features.
- Note the original RAID parameters like stripe size and use the same settings when rebuilding.
- Keep spare drives ready to quickly replace failed drives.
- Monitor the array health using management software logs and alerts.
- Ensure proper cooling, voltages, and UPS protection to avoid environmental damage.
- Consider a standby RAID controller that can take over if the main controller fails.
RAID 10 data recovery scenarios
Here are some examples of recoveries for common RAID 10 failure scenarios:
Scenario 1 – Rebuild after single drive failure
1. RAID 10 array with 8 total disks experiences right side drive failure on disk 4.
2. Administrator pulls failed disk 4 and replaces with new drive.
3. RAID controller detects failed drive and begins rebuilding disk 4’s data from mirrored data on disk 3.
4. After rebuilding completes, the RAID 10 array is restored to full redundancy.
Scenario 2 – Restore after accidental RAID delete
1. Administrator accidentally deletes existing 8 disk RAID 10 array while modifying server settings.
2. The RAID controller still detects the drives but no longer sees RAID array.
3. Administrator recreates the RAID 10 array in the management software using the same configuration.
4. The data from the previous array now needs to be restored from backup to complete recovery.
Scenario 3 – Full recovery after controller failure
1. Power surge damages the RAID controller module, making the RAID 10 array inaccessible.
2. Administrator replaces the RAID controller with an identical model.
3. The new controller does not detect the existing array.
4. Administrator manually rebuilds the array in the controller software based on the original RAID parameters.
5. Critical business data then restored from tape backup.
Choosing a data recovery service
For recovery situations beyond the administrator’s technical abilities, a RAID data recovery service may be required. Look for a service with:
- Experience recovering complex RAID configurations like RAID 10.
- Class 100 clean room facilities to safely repair drives.
- Access to manufacturer-level disk repair tools and platforms.
- Strong technical expertise recovering data from failed RAID firmware or controllers.
- A proven track record recovering data for clients.
- Upfront pricing with no hidden fees or obligations.
A data recovery specialist can often salvage data even from RAID arrays that appear completely failed or inaccessible. But the process is time-sensitive, so contact a recovery service as soon as possible after a failure.
Preventing RAID 10 failures
Taking preventative measures can help avoid many RAID 10 failures:
- Use enterprise-class RAID controllers and drives designed for 24/7 operation.
- Monitor drive and array health using tools like SMART and logging.
- Keep firmware, drivers, and management software updated.
- Ensure proper ventilation and cooling for drives.
- Use UPS and power conditioning equipment.
- Install drives properly to avoid vibration and overheating.
- Perform regular integrity checks on the array.
- Scrub drives periodically to fix bad sectors.
For the best fault tolerance:
- Use at least 8-12 drives in the array to withstand multiple drive failures.
- Select drives with technologies like TLER to prevent drive dropouts during rebuilds.
- Enable notifications for array events to quickly detect problems.
- Have hot spare drives ready to immediately begin rebuilds.
Conclusion
Recovering a failed or degraded RAID 10 array requires carefully following the rebuild process outlined in the RAID management software. Preventing disasters in the first place through monitoring and maintenance is even more critical. If problems occur beyond the administrator’s ability, timely engagement of a professional data recovery service can often salvage data from even severely corrupted RAID 10 arrays.