Files can be deleted from your computer’s hard drive in many ways, either intentionally or by accident. When a file is deleted, the space it previously occupied becomes available to be overwritten with new data. The original file itself is still technically present on the drive until that space is reused, but it is no longer accessible through normal means.
The goal of recovering deleted files is to rescue these inaccessible files before they get permanently overwritten. There are various methods that can potentially restore deleted files, ranging from using the Recycle Bin, to system restore points, to third party data recovery software. This guide will focus on free methods to undelete files without relying on paid software.
How File Deletion Works
When you delete a file on your computer, the data is not immediately erased from the hard drive. Instead, the operating system removes the file’s entry from the file table and marks the sectors containing the file’s data as free space available for future write operations (Source 1). The file contents remain on the drive until they are overwritten by new data.
This is because the file system uses file pointers to keep track of where data is stored on the drive. When a file is saved, the file system allocates a section of the hard drive to store the data and updates the file table with the pointer location. Deleting a file removes the pointer, but does not touch the underlying data. The original data remains intact in that location until the sectors are reused by new files.
Therefore, deleted files can often be recovered by restoring the original file pointers or scanning the drive for familiar data patterns associated with specific file types. As long as the original data remains accessible and has not been overwritten, there is a good chance of recovering deleted files.
When Can Deleted Files Be Recovered?
When a file is deleted, the operating system simply marks the space that file occupied as available for overwrite. The actual contents of the file remain on the disk until that space is needed for new data. According to osgamers.com, “You are not sure when a deleted file can be overwritten. So, there is no fixed answer to how long is too long for successful recovery” https://osgamers.com/faq/how-to-recover-deleted-files. Once a file has been overwritten with new data, it is impossible to recover.
For the best chances of recovering deleted files, it is crucial to act quickly before the operating system allocates that disk space to new files. The longer you wait, the greater the risk that portions of the deleted files will become permanently unrecoverable.
Recovering from Recycle Bin
When files are deleted on a Windows computer, they are sent to the Recycle Bin by default. The Recycle Bin acts as a temporary holding place for deleted files, allowing you to restore them if deleted accidentally. Therefore, the first step when trying to recover deleted files is always to check the Recycle Bin.
To restore files from the Recycle Bin in Windows 10 or 11, open the Recycle Bin icon on your desktop or go to Start > Recycle Bin. Locate the file(s) or folder(s) you want to restore, right-click on them, and select “Restore”. The items will be returned to their original location.
However, if the Recycle Bin has been emptied, the files are permanently deleted. In this case, you will need to use data recovery software to attempt to recover them. Programs like EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard scan your drives to find and restore deleted files, even if the Recycle Bin has been emptied. Just avoid continuing to save new data to the drive you want to recover files from.
So checking the Recycle Bin for your deleted files should always be step one. But if you find the bin emptied, recovery software provides the best chance for getting those files back.
Using System Restore
One method to recover deleted files without software is to use System Restore. System Restore is a built-in Windows utility that automatically creates restore points – snapshots of the system state including files, folders, and registry settings. System Restore enables reverting your system to a previous restore point to undo changes made to files or programs.
To recover deleted files using System Restore:
- Open the Start menu and search for “System Restore”. Select “Create a restore point” or “Restore system files and settings”.
- In the System Restore wizard, choose “Restore my computer to an earlier time” and click Next.
- On the next screen, select the most relevant restore point when the deleted files still existed. Look at the date and time of each restore point.
- Confirm your restore point and click Next. Allow time for the restoration process.
- Once complete, your files and system settings are restored to the selected time. Check if the deleted files now exist again.
System Restore rolls back system changes while preserving personal files, making it useful for recovering accidentally deleted data. However, System Restore removes restore points during the process, so it may not recover files deleted long ago. Also, System Restore does not work if System Protection is disabled.
Restore Previous Versions
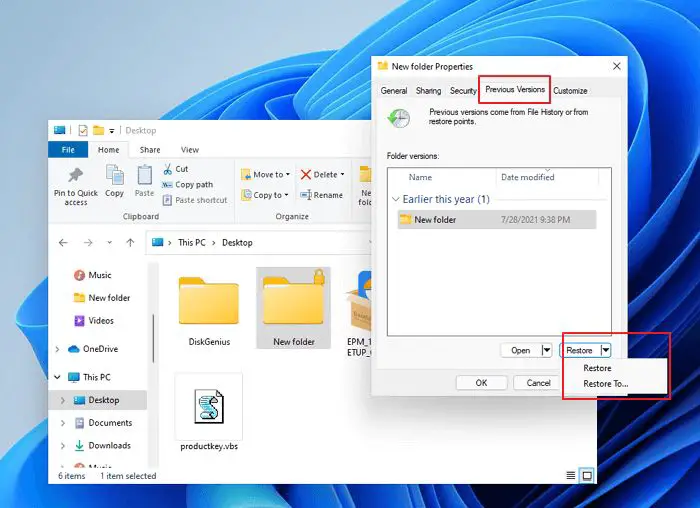
Windows includes a feature called Previous Versions that can help recover deleted files and folders. This feature takes snapshots of your system at certain points and saves them as restore points. You can access these previous versions to restore deleted files and folders.
Here are the steps to restore deleted files using Previous Versions in Windows:
- Navigate to the location where the file or folder was deleted.
- Right-click in the empty space and select “Restore previous versions” from the menu.
- The Previous Versions window will open. Select the most recent snapshot or restore point taken before the file was deleted.
- A folder hierarchy will appear showing the files and folders as they existed at the time of the snapshot. Navigate to the deleted file or folder and select “Restore” to recover it.
- Choose a new location to save the restored file or folder.
This allows you to rollback selected files and folders to a previous state as a way to recover content that has been lost or deleted. Keep in mind that previous versions are only available if System Restore has been enabled on your Windows installation.
For more details, see this guide: How to Recover Deleted Files Using Previous versions in Windows
Undelete from Command Prompt
The Windows Command Prompt provides access to several useful system commands, including the “undelete” command. This can help recover deleted files under the right circumstances. Here’s how it works:
First, open the Command Prompt as an administrator. Go to Start, search for “cmd”, right-click on the result, and choose Run as administrator.
At the prompt, type “undelete” followed by the location of the deleted files. For example:
undelete c:\users\yourname\documents\*.*
This will attempt to recover all deleted files from the Documents folder for the user “yourname”.
You can also specify a path, filename, or wildcard to target specific deleted files. For instance:
undelete c:\users\yourname\documents\report.docx
However, you need to know the original path and filename of the deleted file for this method.
The undelete command uses data in the Master File Table to restore deleted files that have not yet been overwritten. However, it can only recover files deleted recently, as the MFT data is eventually reused by the system. Undelete also cannot recover files from a reformatted or corrupted drive [1].
While the undelete command has limitations, it provides a quick way to attempt recovering recently deleted files without third-party software. Just be sure to run it soon after any accidental deletions.
Recover with Data Recovery Software
One of the best options for recovering deleted files for free is to use a quality data recovery tool like Recuva or TestDisk. These are free data recovery programs that allow you to thoroughly scan your hard drive and external devices to find traces of deleted files and restore them.
With Recuva, you simply download and install the software, select the drive you want to scan, choose the file types you’re looking for, and start the scan. Recuva will dig deep to find any recoverable files and present them in an easy to browse window. You can then select which files you want to restore and save them to another location.
TestDisk operates in a similar way, scanning drives for recoverable data. It has the ability to rebuild corrupted partition tables and recover lost partitions as well. For deleted files, you select a disk to scan, choose a partition to analyze, select the types of files to recover, and start the search. Recovered files can then be saved to an external device or location of your choice.
As long as the deleted files haven’t been overwritten by new data, these recovery tools stand an excellent chance of restoring them through deep scanning. Just be sure to save the recovered files to a different drive than the one you’re scanning to avoid overwriting them again.
Use a Live CD
One way to recover deleted files on a Windows computer without installing any software is to use a Linux live CD. A live CD allows you to boot into a Linux operating system from a CD/DVD or USB drive without installing anything on the hard drive. Many Linux distributions come as live CDs, such as Ubuntu, Knoppix, and Debian.
To use a live CD for recovering deleted files on Windows:
- Download the ISO image for the Linux distribution and create a bootable CD/DVD or USB drive.
- Boot the computer from the live CD/USB instead of the hard drive.
- Once booted into the Linux system, the internal hard drives will be mounted and accessible through the graphical file manager.
- Navigate to the drive and directory where the deleted files originally existed.
- The graphical interface allows browsing deleted files as if they still exist and copying them to an external drive or the live system.
The advantage of using a Linux live CD is it provides a simple graphical way to access the Windows drive and recover files without installing anything. The live system is read-only and will not modify the drive. Some distributions like Parted Magic include data recovery tools as well.
Conclusion
There are a few different methods you can try to recover deleted files for free without any software. The most important thing is to act quickly after accidentally deleting files, before they get overwritten by new data on your hard drive. Trying to restore files from the Recycle Bin or using System Restore are good first steps. You may also be able to restore previous versions of files if you had System Protection enabled. Using the command prompt to undelete files can work if you know the right commands. As a last resort, you can use a Live CD or bootable USB to try to recover deleted files from the hard drive. Just remember that the sooner you try to restore deleted files, the better your chances of getting them back. Don’t install any new programs or save new files until you’ve exhausted your options for free recovery.