exFAT and NTFS are two common file systems used for external drives on both Windows and Mac computers. exFAT, which stands for Extended File Allocation Table, is optimized for flash drives and SD cards while NTFS, which stands for New Technology File System, was designed for internal drives on Windows PCs. Both offer advantages and disadvantages when it comes to compatibility, performance, reliability, file size limits, security, formatting options, ease of use, and the ability to repair drives.
This article provides an overview of exFAT and NTFS file systems, comparing the two formats to help you decide which is better for your storage needs when using a drive between Mac and Windows environments.
Compatibility
When it comes to compatibility across operating systems, exFAT has wider support than NTFS. exFAT is supported natively on Windows, macOS, and Linux. It is also supported on Android, though support was only added in Android 6.0 Marshmallow. On iOS, exFAT is supported on devices with 64-bit processors. In comparison, NTFS support on non-Windows devices is limited. While macOS includes read-only support for NTFS, write support requires third-party software. On Android, NTFS is only supported on some devices running Android 6.0 Marshmallow and higher. Linux also only has read-only support for NTFS without additional software.
Overall, exFAT has excellent cross-platform compatibility across Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS. NTFS compatibility is primarily limited to Windows, with limited read-only support on other platforms. For sharing external drives between Windows and macOS, exFAT is generally the better choice.
Sources:
[1] https://www.howtogeek.com/235596/whats-the-difference-between-fat32-exfat-and-ntfs/
[2] https://www.tutorialspoint.com/difference-between-fat32-exfat-and-ntfs-file-systems
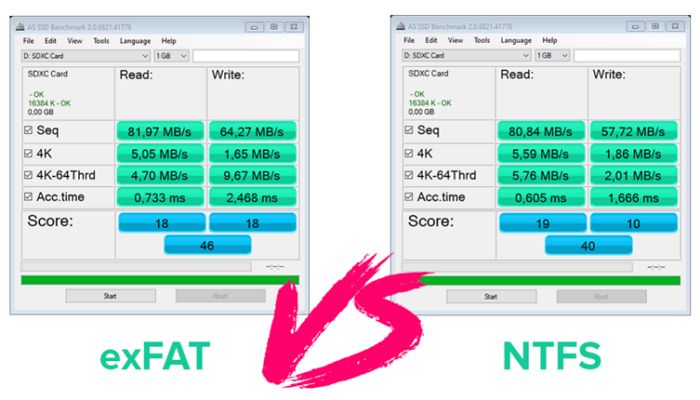
Performance
When considering read/write speeds, both exFAT and NTFS generally outperform FAT32. However, specific performance differences between exFAT and NTFS depend on factors like file size and storage medium.
For flash drives and SD cards, exFAT offers slightly faster read/write speeds compared to NTFS for smaller files. According to one test, exFAT delivered up to 9% faster performance than NTFS when reading medium-sized files from a USB 3.0 flash drive1. However, for larger files, NTFS pulled ahead.
On conventional hard drives, most tests show NTFS with a slight performance advantage over exFAT. But on SSDs, results are mixed. Some benchmarks give NTFS the edge for sequential reads/writes while others show exFAT edging out NTFS in random 4K performance.
Overall, both file systems offer reasonably fast performance. Unless you constantly transfer very large files, the differences are minor. For most everyday tasks, users are unlikely to notice a significant speed difference between exFAT and NTFS.
Reliability
When it comes to reliability and preventing corruption, NTFS is generally considered more robust than exFAT. NTFS utilizes journaling and other mechanisms to help recover from corruption events. As noted in this SuperUser Q&A, NTFS has journaling which can help the file system recover from corruption, whereas exFAT does not have journaling.
Some consider exFAT less reliable than even FAT32, since exFAT only uses 1 FAT compared to FAT32’s 2 FATs. However, as explained in this analysis on exFAT reliability, exFAT compensates for having 1 FAT via use of checksums. Overall, NTFS is still seen as more resilient and reliable.
According to this NTFS vs exFAT comparison, NTFS has been consistently proven more efficient at preventing and recovering from corruption issues, making it the more reliable choice.
File Size Limits
When it comes to maximum file size, exFAT and NTFS are very similar. Both file systems have theoretical limits of 16 exbibytes (about 16 billion terabytes) for maximum file size and 128 petabytes for maximum volume size, which are essentially unlimited for practical purposes (Source). However, NTFS does have some advantages when working with very large files over 4GB in size. The maximum file size for individual files on a FAT32 volume is 4GB, which can be limiting. NTFS is better optimized for performance with large files.
Security
When it comes to security features, NTFS is generally considered more secure than exFAT.
NTFS supports file encryption, permission controls, and auditing features that allow you to control access to files and folders. This makes it easier to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access.
In contrast, exFAT does not have any built-in encryption or permission features. Any file stored on an exFAT drive can be accessed by anyone with physical access to the drive.1
Additionally, NTFS utilizes journaling to improve recoverability in the event of corruption or crashes. exFAT does not have any journaling capabilities, which makes it more prone to data loss in the event of errors.2
In general, NTFS offers much more robust security protections. For drives used to store sensitive data, NTFS is likely the better choice.
Format Options
One key difference between exFAT and NTFS is flexibility in formatting drives. exFAT is compatible with more operating systems and devices than NTFS. For example, you can format external drives in exFAT to use between Windows PCs and Macs interchangeably. exFAT is also supported on some gaming consoles and other consumer devices that don’t support NTFS.
In contrast, NTFS is limited mostly to Windows PCs only. While read-only NTFS support can be enabled on Macs, full read-write compatibility requires special software. For flexible external storage to share across operating systems, exFAT offers wider native compatibility.
Ease of Use
Overall, exFAT is considered more user-friendly and easier to use than NTFS for most situations. One key reason is that exFAT is supported natively by both Windows and macOS without any additional software. NTFS, on the other hand, is proprietary to Windows and read-only by default on macOS. To get full read/write capabilities on a Mac, you would need to install third-party software like Paragon NTFS or Tuxera NTFS, adding an extra complication.
In terms of basic usability, exFAT is a lightweight file system without many complex features. It’s designed to be simple plug-and-play storage for transferring data between operating systems. NTFS has advanced features like file compression, encryption, permissions etc. For typical external storage uses, these extra features often go unused and only add complexity. The simplicity of exFAT makes it easier for an average user to manage.
When formatting external drives, Windows and MacOS can both create exFAT partitions easily using the native disk utility apps. Formatting to NTFS is only fully supported in Windows. Trying to create NTFS drives on Mac can be tricky without third-party tools. Overall, exFAT’s cross-platform accessibility and support makes it far simpler for an everyday user across Windows and Mac.
(Source: https://www.twit.community/t/ntfs-vs-exfat-which-format-to-choose-for-external-hard-drive/14340)
Repairing Drives
When it comes to the ability to repair corrupted drives, NTFS has some advantages over exFAT. NTFS employs journaling, which tracks file system changes and can assist in recovering corrupted drives. exFAT does not have any built-in journaling capabilities (Wondershare). If a drive formatted with exFAT becomes corrupted, third-party software tools may be required to attempt repairs. NTFS can leverage its journaling to self-heal and recover from some corruption issues. However, very severe corruption on NTFS volumes may still require manual repairs (SuperUser). Overall, NTFS’s journaling gives it an edge for built-in reparability over exFAT.
Conclusions
When choosing between exFAT and NTFS for a Mac, the best option is exFAT.
exFAT has much better compatibility with Macs compared to NTFS. While Macs can read NTFS drives, writing to them requires installing third-party software. exFAT works seamlessly for read and write on Macs without any additional software.
In terms of performance, exFAT and NTFS are fairly comparable. Neither has a clear speed advantage.
Reliability is a wash between exFAT and NTFS. Both are mature formats that are widely supported.
The main advantage of exFAT is the lack of extra steps needed to write to the drive from a Mac. While NTFS is fine for read-only use, the need to install additional software makes exFAT a better choice for full read/write usage across both Windows and Mac.
In conclusion, for an external drive that will be used with Macs, exFAT is the best option due to its seamless compatibility.