exFAT and NTFS are two common file systems used for external storage devices like USB flash drives and external hard drives. Both have advantages and disadvantages that make them better suited for certain use cases.
exFAT, which stands for Extended File Allocation Table, is optimized for flash memory like USB flash drives. It is the default file system for SDXC memory cards. exFAT allows for larger file sizes than the older FAT32 file system, supporting files larger than 4GB. It is lightweight and fast at formatting drives.
NTFS, which stands for New Technology File System, is the default file system for internal hard drives in Windows. It supports advanced features like file compression, encryption, permissions, and journaling. However, NTFS is slower at formatting drives and may be less compatible with other operating systems.
File Size Limits
exFAT does not impose any file size limits. According to ntfs.com, the maximum file size for exFAT is 16 exabytes (EB) 1. In comparison, NTFS has a maximum file size limit of 16 terabytes (TB) 2. FAT32 has a much lower file size limit of 4 gigabytes (GB) 2.
For most everyday uses, exFAT’s essentially unlimited file size makes it better than NTFS or FAT32. But for truly massive files beyond 16 TB, NTFS may still be required.
Partition Size Limits
The maximum partition size supported by NTFS is 256 TB according to this Reddit post. NTFS was designed by Microsoft to overcome the limitations of previous Windows file systems like FAT32.
In comparison, exFAT supports a maximum partition size of 128 PB (petabytes) based on information from ntfs.com. The exFAT file system was introduced in 2006 to bridge the gap between NTFS and FAT32 in terms of features and partition size limits.
So in summary, exFAT allows much larger maximum partition sizes compared to NTFS. This makes exFAT better suited for very large storage devices. But for most everyday thumb drives, the max partition size limits of either file system are likely sufficient.
Performance
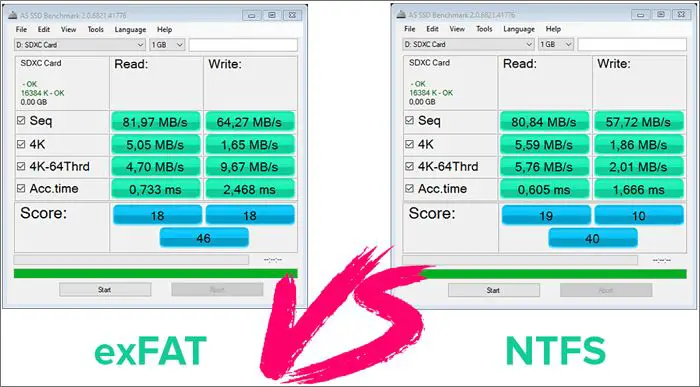
When it comes to read and write speeds, NTFS generally outperforms exFAT for internal drives. One test showed NTFS having 68% faster file deletion and 24% faster reads than exFAT on a USB 3.0 flash drive. This is likely because NTFS uses advanced features like file compression and disk caching that exFAT lacks.
However, for external drives, exFAT can sometimes be faster. This is because exFAT has lower overhead than NTFS since it doesn’t support as many complex features. The simpler design means exFAT doesn’t have to work as hard when reading and writing files. So for things like external hard drives that connect over USB, exFAT may have faster transfer speeds than NTFS in some cases.
Overall, for internal storage, NTFS is generally faster. But for external storage like USB flash drives, exFAT can potentially outperform NTFS in some situations.
Compatibility
When it comes to compatibility across operating systems and devices, NTFS, exFAT, and FAT32 each have their strengths and weaknesses.
NTFS is natively supported only by Windows. While macOS includes read-only support for NTFS, you need third party software to get full read/write access on Mac. NTFS has very limited compatibility with other devices like cameras, TVs, game consoles etc. So NTFS is best suited for storage that will be used primarily with Windows PCs.
exFAT has much broader compatibility than NTFS. It works across Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, game consoles, cameras etc. The main exceptions are older devices – for example, Xbox 360 doesn’t support exFAT. So exFAT is a good choice for external storage that will be used across different operating systems and devices.
FAT32 has the widest compatibility of the three file systems. It will work with all versions of Windows, Mac, Linux, game consoles, cameras and most other devices. However, it does have limitations like the 4GB individual file size limit. So FAT32 can be useful for smaller thumb drives that need universal compatibility.
In summary, if you need to share an external drive between Windows and Mac, exFAT is likely the best option. If you have older devices that need support, FAT32 may be required. And if you only use Windows, NTFS is fine.
Max File Name Length
The maximum supported file name length for the exFAT file system is 255 Unicode characters, according to the exFAT: File Name Directory Entry technical specifications page. For file names shorter than 16 characters, only one file name record is required. However, the entire file name is still represented by three 32-byte directory records, according to the Wikipedia article on exFAT. This allows for compatibility with FAT32 for shorter file names, while supporting much longer file names up to 255 characters.
In contrast, NTFS supports file names up to 255 characters as well, but stores them more efficiently in Unicode using a single file name record. So for very long file names, NTFS would have a small storage efficiency advantage over exFAT. However, both support the maximum 255 character Unicode file name length that most users would ever need.
Encryption
When it comes to native encryption capabilities, NTFS has a clear advantage over exFAT. NTFS supports built-in encryption through BitLocker on Windows and has some third party encryption tools available like VeraCrypt. ExFAT has no native encryption capabilities and would require third party tools.
Some users have reported success encrypting exFAT drives using VeraCrypt containers, but it requires creating the encrypted container file first rather than encrypting the full drive natively like you can with BitLocker and NTFS (source). This limits the flexibility and convenience of full drive encryption on exFAT.
In summary, NTFS’s native encryption through BitLocker gives it a significant advantage for encryption over exFAT on Windows devices.
Journaling
Journaling is a feature of some file systems that keeps track of changes before they are written to disk. This provides more protection against data corruption in case of sudden power loss or system crashes.
NTFS supports journaling, which means it logs all file system transactions before committing them to disk. This helps ensure file system integrity and prevents corruption 1.
On the other hand, exFAT does not have journaling capabilities. This makes it more prone to data corruption when unexpected shutdowns occur 2. The lack of journaling is a commonly cited downside of exFAT 3.
Stability
When it comes to stability and robustness against corruption, NTFS is generally considered more reliable than exFAT. NTFS uses journaling and other mechanisms to prevent and recover from corruption, whereas exFAT does not have any built-in data integrity features1. This means NTFS is less likely to become corrupted from sudden power loss or improper device removal.
exFAT only uses a single FAT table, compared to FAT32 which uses two FATs. Some view this as making exFAT potentially less robust against corruption2. However, Microsoft designed exFAT for flash media like SD cards and claims it has “keeps your data safe in case of unexpected power loss or ungraceful device removal”
Overall, NTFS offers stronger reliability mechanisms compared to exFAT. But for thumb drives and external storage that do not need the highest level of data integrity, exFAT can be an acceptable option while providing advantages like compatibility across devices.
Verdict
When choosing between exFAT and NTFS for a thumb drive, exFAT generally emerges as the recommended file system. Here’s a recap of the key pros and cons:
exFAT Pros:
- No realistic file size or partition size limits for thumb drives
- Faster at deleting and writing files compared to NTFS
- Wide compatibility with Windows, Mac, Linux, game consoles, cameras, etc.
exFAT Cons:
- Lacks journaling, so more prone to corruption from sudden removal or power loss
- Less robust permissions and encryption capabilities than NTFS
NTFS Pros:
- Journaling helps avoid corruption and data loss
- Advanced security features like permissions and encryption
NTFS Cons:
- Slower performance than exFAT for thumb drive uses
- Compatibility issues – doesn’t work on some devices
- Unnecessary features like journaling for thumb drive use
Overall, exFAT’s speed, compatibility, and lack of realistic limits make it the best choice for most users’ thumb drive needs today. While NTFS offers more security precautions, a thumb drive doesn’t require features like journaling or advanced permissions. Backing up your data routinely is a smarter precaution than relying on NTFS safeguards for your thumb drive files.