RAID 0 arrays offer great performance by striping data across multiple disks. However, this comes at the cost of fault tolerance – if any disk in the array fails, all data will be lost. So is it possible to recover a failed RAID 0 array?
What is RAID 0?
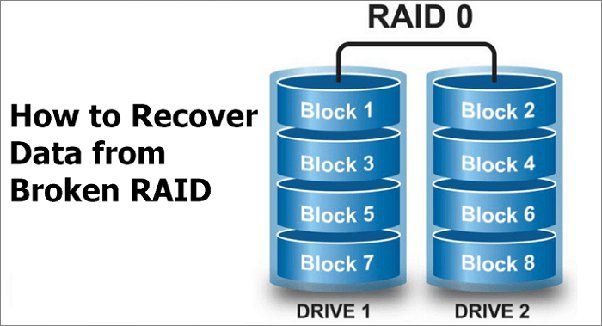
RAID 0 (also known as striping) splits data evenly across two or more disks. This allows for parallel I/O, improving performance. But RAID 0 provides no redundancy – if one disk fails, all data will be lost.
RAID 0 arrays stripe data across disks in blocks. If you have two disks, the first block of data is written to the first disk, the second block to the second disk, the third to the first disk again, and so on. This spreads data evenly across the disks.
Why recover RAID 0?
There are a few reasons you may want to attempt recovery of a failed RAID 0 array:
- To recover lost data and files that were not backed up elsewhere
- To avoid having to rebuild the array and restore from backups
- If part of the array is still intact, recovery may be partial or complete
- Data recovery services can be expensive – attempting self-recovery may save money
Being realistic about the chances of recovery is important. With RAID 0, the loss of a single disk means the entire array fails. But recovery may still be possible if only part of the array has actually failed.
Is complete RAID 0 recovery possible?
Complete recovery of a failed RAID 0 array is usually unlikely. Because data is striped across disks with no parity or duplication, the failure of any disk results in complete data loss across the array.
For complete recovery, every disk would need to remain intact. If any disk has failed or has errors, the stripped data on that disk is lost. And with no parity, that lost data cannot be recreated.
So unless all disks in the array are still fully readable, complete recovery of RAID 0 is not possible. The probability of full recovery decreases the more disks are in the array.
Partial RAID 0 recovery
While complete recovery may not be possible, partial RAID 0 recovery can be achieved if part of the array is still intact. For example:
- If one of two disks has failed, the data on the surviving disk can still be recovered.
- With a larger array, just one failed disk still allows recovery of data from the remaining disks.
- Even if multiple disks have errors, unaffected portions may be recoverable.
Software tools can help rebuild the array virtually using just the readable portions of the disks. This allows access to parts of the data, even if the full array cannot be restored.
Options for recovering RAID 0 data
If attempting DIY RAID 0 recovery, options include:
- Data recovery software – Specialized tools can reconstruct RAID arrays using readable disk data.
- Manual assembly – If disk order and block layout is known, files can be manually reconstructed.
- Disk imaging – Imaging disks before attempting recovery provides a backup if things go wrong.
But the best option is professional data recovery. Rebuilding RAID arrays is complex, and experts have specialized tools and clean room facilities when disk hardware repairs are required.
Factors affecting RAID 0 recoverability
Whether partial or complete RAID 0 recovery is possible depends on several key factors:
- Number of failed disks – More failed disks means less recoverable data.
- Extents of disk damage – If damage is minimal, more data may be recoverable.
- RAID stripe size – Smaller stripes mean less data loss per disk.
- Disk order and layout – Knowing the original configuration helps reconstruct the array.
With redundancy-free RAID 0 arrays, the name of the game is minimizing data loss. Even with partial disk failure, some data recovery is often possible.
RAID 0 recovery steps
Recovering a failed RAID 0 array involves several key steps:
- Stop using the array – Prevent further data writes to avoid overwriting data.
- Evaluate disk health – Check for electronic issues, head crashes, etc.
- Image disks – Safely image disks before attempting recovery.
- Rebuild virtual array – Use software to reconstruct the array virtually using readable disk data.
- Copy recovered data – Extract recovered files from the virtual array.
Following a process helps maximize recoverability. But the less damage to disks, the better the outcome will be.
RAID 0 recovery chances
The chances of recovering a RAID 0 array depend heavily on how many disks have failed:
| # Failed Disks | Recovery Chances |
| 0 | Excellent |
| 1 | Good to fair |
| 2 | Poor |
| 3+ | Very unlikely |
With a single disk failure, recovery is possible but decreases with each additional failed or corrupt drive. The probability drops rapidly as more disks fail.
Other factors affecting recovery chances
Beyond failed disks, other factors impacting RAID 0 recovery probability are:
- Extent of disk damage – Minor damage improves chances versus severe corruption.
- RAID stripe size – Smaller stripes mean less data loss per disk.
- Prompt power-down – Quickly powering off disks prevents further data loss.
- Professional vs. DIY recovery – Pros have better tools and skills.
Does RAID level matter?
RAID type has a major impact on recoverability. Compared to RAID 0 arrays, other RAID levels offer much better recovery chances thanks to parity and redundancy:
| RAID Type | Fault Tolerance | Recovery Chances |
| RAID 0 | None | Poor |
| RAID 1 | 1 disk fault tolerated | Excellent |
| RAID 5 | 1 disk fault tolerated | Good |
| RAID 6 | 2 disk faults tolerated | Excellent |
So using RAID 1, 5, 6, or 10 greatly improves your chances of recovery compared to RAID 0.
Can deleted RAID 0 data be recovered?
If a RAID 0 array fails, recovery depends on disk errors. But what if data is simply deleted accidentally?
Typically with deletion, data still remains on disk until overwritten by new content. So specialized undelete tools can recover deleted files on individual RAID 0 disks.
However, recovering the deleted file structure and filenames across the full array is much more difficult. The virtual reconstruction process is also needed to rebuild files scattered across multiple disks.
So undeletion from a RAID 0 array is possible, but remains challenging. Again, attempting recovery via a professional is recommended versus DIY options.
Preventing RAID 0 failure
While RAID 0 recovery is difficult, steps can be taken to help avoid array failures in the first place:
- Use enterprise-grade disks designed for RAID.
- Monitor disk health with SMART tools.
- Keep firmware, drivers, and RAID software updated.
- Avoid excessive load on array.
- Manage disk temperatures.
- Use an uninterrupted power supply.
- Back up critical data regularly.
Good preventative maintenance is crucial for RAID 0 arrays since the data loss impact of a failure is so high.
Should RAID 0 be avoided?
Due to the high risk, many experts recommend avoiding RAID 0 entirely for critical or highly valuable data. The performance gains come at the steep cost of complete vulnerability to disk failure.
Instead, RAID 10 provides the performance benefits of RAID 0 along with fault tolerance by mirroring. Or consider using a higher performing file system on top of individual disks.
Weigh the recovery risks carefully before choosing RAID 0 arrays for important data. And be sure to implement strong backups as well.
Conclusions
Recovering failed RAID 0 arrays is challenging but possible in certain situations. Complete recovery requires all disks intact. But even partial recovery can restore data if some disks survive.
RAID 0 recovery success depends heavily on:
- The number of failed disks.
- The extent of damage to disks.
- Prompt power-down after failure.
- Using professional recovery services.
While recovery is feasible, avoiding RAID 0 data loss in the first place is wise. Use redundancy for critical data. And make sure backups are in place in case disaster strikes.