The quick answer is that SD cards are a type of memory card, but not all memory cards are SD cards. SD cards are a specific format of removable flash memory card, while “memory card” is a more general term that encompasses various formats like SD, microSD, CompactFlash, and others.
What is an SD Card?
SD, which stands for Secure Digital, is a proprietary format of memory card developed in 1999 by Panasonic, SanDisk, and Toshiba. The SD design was based on the older MultiMediaCard (MMC) format, but included enhancements such as digital rights management and greater storage capacity. The most common uses for SD cards today are in digital cameras, camcorders, handheld computers, GPS devices, audio players, mobile phones, and gaming consoles.
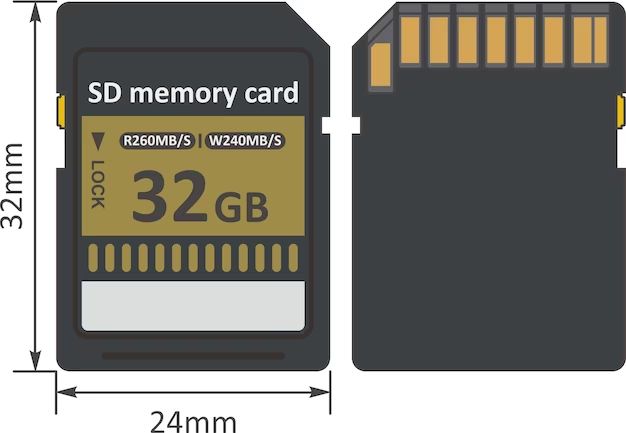
SD cards come in three form factors: standard-size, mini-size, and micro-size. The dimensions of a standard SD card are 32 mm × 24 mm × 2.1 mm. A miniSD card measures 21.5 mm × 20 mm × 1.4 mm, while microSD measures 15 mm × 11 mm × 1.0 mm. The different sizes allow SD cards to be used in devices with different space constraints.
SD card capacities range from 8 MB to 2 TB for standard size, with microSD cards currently reaching 1 TB. Speeds range from 2 MB/s for low-speed cards to 300 MB/s for the latest UHS-III cards. SD cards achieve these speeds using nonvolatile memory chips and controller processors that manage reading and writing data.
Types of SD Cards
There are several types and variations of SD cards:
- SDHC (Secure Digital High Capacity) – cards larger than 2 GB up to 32 GB
- SDXC (Secure Digital eXtended Capacity) – cards larger than 32 GB up to 2 TB
- SDIO (Secure Digital Input/Output) – cards that also allow device input/output functions
- miniSD – smaller version of the standard SD card
- microSD – smallest SD card for devices like phones and tablets
In addition, SD cards are assigned speed classes from 2 to 10, UHS-I and UHS-II to indicate their minimum sustained write speeds. Class 2 cards have the lowest speed of 2 MB/s, while UHS-III cards at Class 10 have the highest speeds up to 300 MB/s.
History of SD Cards
The SD card format evolved from earlier efforts in the 1990s to create a memory card standard. Below is a brief history:
- 1991 – Introduction of solid-state flash memory cards by SanDisk
- 1993 – SSDA alliance forms to create flash memory card standard
- 1995 – SSDA releases the MultiMediaCard (MMC) standard
- 1998 – Association of SD companies formed
- 1999 – SD format publicly announced
- 2000 – First SD cards introduced to consumers
- 2001 – miniSD format introduced
- 2003 – SDHC and SDXC announced for capacities over 2 GB
- 2005 – microSD format introduced
Since its inception, the SD format has gone through 9 major revisions to improve speed, capacity, and features. As of 2022, SD cards hold significant global market share as a consumer removable memory card format, competing mainly with CompactFlash.
Pros and Cons of SD Cards
Here are some key advantages and disadvantages of SD cards compared to other memory card formats:
Pros:
- Compact size – SD cards are very small, especially microSD
- High capacity – SDXC supports up to 2 TB currently
- Versatility – Used in many consumer devices; transferable
- Durability – Resilient to shock, vibration, water, magnets
- Speed – UHS-II and UHS-III support fast read/write speeds
- Security – Built-in DRM and write-protect features
- Convenience – Hot swappable in some devices
Cons:
- Proprietary – Unlike CompactFlash, SD is a proprietary format
- Vulnerable to file corruption – Power loss can cause data errors
- Not suited for high-end cameras – Lower speed compared to XQD or CFexpress
- Small size – Easier to misplace and damage
Common Uses of SD Cards
Due to their compact size and high capacity, SD cards have many diverse applications. Some of the most common uses are:
Digital cameras
One of the original and still primary uses of SD cards is as storage for digital cameras. The cards allow storing high-resolution image and video files.
Smartphones
MicroSD cards are commonly used in many Android phones and tablets to expand internal storage for apps, photos, videos, and other files.
Handheld consoles
Gaming devices like the Nintendo Switch utilize microSD cards so users can download more digital games.
Dashcams and security cameras
SD cards provide storage for extended capture of security footage. The cards can record continuously and be overwritten when full.
Drones
Many drones rely on SD cards to store photos and video footage captured during flight.
Music players
SD cards allow compact digital audio players to store significantly more songs than just built-in storage.
Buying and Using SD Cards
Capacity
When buying an SD card, the most important consideration is the capacity or amount of storage. Common sizes are 8GB, 16GB, 32GB, 64GB, 128GB, 256GB, 512GB, and 1TB. Choose a capacity suitable for your intended device and usage – more capacity allows storing more files.
Speed rating
Faster SD cards have higher speed class ratings from 2 to 10 or UHS designations. A higher speed rating allows capturing high-res photos/video more quickly. However, devices have speed limitations too – don’t overpay for an ultra-fast card your device can’t utilize fully.
Brand
Stick with major, reputable brands like SanDisk, Samsung, Sony, Kingston, and others. Avoid cheap, generic cards that may sacrifice performance and reliability.
Card reader
A memory card reader allows conveniently transferring files between your SD card and computer. USB card readers are inexpensive and handy accessories.
Formatting
Brand new SD cards may be formatted, but it’s good to reformat your card in the device you plan to use it in for best compatibility.
File management
Use your device’s interface or a file manager app to organize photos, videos, and other files on the SD card into folders so they don’t clutter up the root directory.
Ejecting
For safety, use your device’s eject feature before removing an SD card while the device is powered on. This avoids possible data corruption.
SD Card File Systems
SD cards can utilize different file systems depending on the formatting of the card:
FAT32
- Compatible with all OSes – Windows, Mac, Linux, mobile
- Max file size of 4GB, max capacity of 32GB
exFAT
- Compatible with newer OS versions – Windows, Mac, Linux, mobile
- Supports massive file sizes and capacities over 32GB
NTFS
- Standard Windows file system but read-only on Mac/Linux
- Max file size of 16TB
By default, SD cards come formatted with FAT32 for maximum device compatibility. But exFAT is generally recommended for cards over 32GB for greater support of large capacity, files, and 4K video.
SD vs. microSD
The microSD format is essentially a miniature version of the standard SD card. Here’s how the two compare:
| SD | microSD | |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensions | 32 x 24 x 2.1 mm | 15 x 11 x 1 mm |
| Weight | 2 grams | 0.25 grams |
| Capacity | Up to 2TB | Up to 1TB currently |
| Speed | UHS-I and UHS-II | UHS-I currently |
| Use cases | Cameras, consoles, audio | Phones, tablets, drones, action cams |
As the table illustrates, both formats share many similarities, but microSD is designed for smaller, portable devices where every bit of space counts. microSD cards come with SD adapters so they can be used in full-size SD card slots.
SD Card vs. Microchip
SD cards and microchips serve vastly different roles:
- SD cards are removable flash storage used for general file storage.
- Microchips are integrated circuits that perform computational tasks and run programs.
- SD cards simply store data written to them by a microchip.
- Microchips actively process data using billions of tiny transistors.
- SD cards are many times larger in physical size than microchips.
In summary, microchips empower the core functionality of devices while SD cards offer safe, expandable data storage and transfer.
SD Card vs. Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
SD cards and HDDs use different technologies for storing data:
| SD Card | Hard Disk Drive (HDD) | |
|---|---|---|
| Storage medium | NAND flash memory | Magnetic platters |
| Size | Very compact – 15 x 11 x 1 mm (microSD) | Larger – 2.5″ or 3.5″ drive enclosures |
| Capacity | Up to 2TB currently | Up to 10TB+ |
| Speed | Up to 300 MB/s (UHS-III) | Up to 210 MB/s (HDD) |
| Power usage | Low – consumes less energy | Higher power draw |
| Durability | Withstands shock, vibration, magnets, temperature better | More fragile with moving parts |
| Price (per GB) | More expensive | Cheaper per GB |
In summary, HDDs offer more raw storage capacity for less money, while SD cards are extremely compact but more costly per GB. SD cards withstand harsh conditions better and draw less power. Both serve important data storage roles depending on the application and form factor needs.
SD Card vs. SSD
Below is a comparison between SD cards and solid state drives (SSDs):
- SD cards are removable flash cards that top out around 2TB capacity currently.
- SSDs refers to solid state storage drives that can be installed in PCs, servers, etc. with capacities up to around 100TB.
- The underlying NAND flash memory technology is similar between both.
- SD cards are designed for portable use cases like cameras, while SSDs are designed for storage scalability.
- SSDs achieve much faster speeds using more advanced parallelism and interfaces like SATA/PCIe.
- SD cards are limited by their small physical size – they cannot dissipate heat as well as SSDs.
- SD cards excel at small, removable storage but SSDs are vastly faster and can store much more data.
In essence, SD cards and SSDs both utilize flash storage but with vastly different use cases – SD cards for light portable duty and SSDs for heavy desktop/server workloads.
Are All Memory Cards Considered SD Cards?
No, SD cards are just one specific type of memory card. There are numerous memory card formats, which include but are not limited to:
- SD card (Secure Digital)
- microSD card
- CompactFlash (CF)
- Memory Stick
- MultiMediaCard (MMC)
- SmartMedia
- xD-Picture Card
- PC Card (PCMCIA)
- MiniCard
Each memory card format uses different underlying technologies, connectors, sizes, and protocols. SD cards are the most ubiquitous memory card format today but are certainly not the only kind. “Memory card” is an umbrella term for removable data storage cards in general.
Conclusion
In summary:
- SD cards are a specific proprietary memory card format developed in 1999, now widely used in consumer tech devices.
- “Memory card” is a broad term for any removable data storage card.
- SD cards are one of several memory card types along with CompactFlash, SmartMedia, etc.
- SD utilizes flash memory and comes in standard, mini, and micro sizes.
- Key uses include digital cameras, phones, handheld consoles, drones, and other portable devices.
- SD cards excel in versatility, compact size, speed, durability, and capacity over 1TB.
So in conclusion, all SD cards are memory cards due to their removable flash storage capability. But not all memory cards are SD cards, since memory card refers to any removable storage card of various formats and technologies beyond just SD.