When configuring a computer, one of the most important decisions is whether to use a traditional hard disk drive (HDD) or solid state drive (SSD) for the boot drive. The boot drive contains the operating system and critical software, so its performance has a major impact on the overall speed and responsiveness of a system. This article examines the key factors to consider when choosing between an HDD and SSD boot drive.
What is the difference between an HDD and SSD?
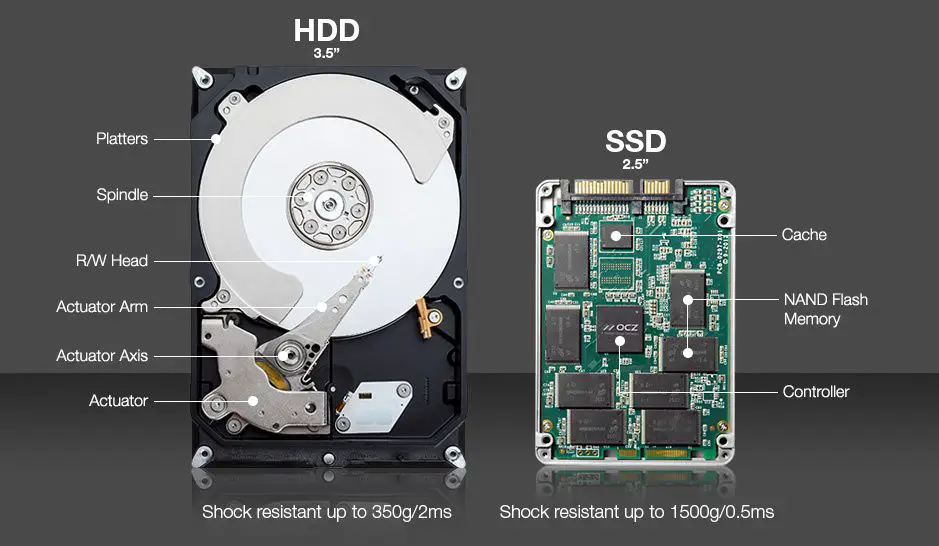
A hard disk drive (HDD) uses magnetic storage to store and retrieve data. It has moving mechanical parts including platters and a read/write head. In contrast, a solid state drive (SSD) uses flash memory chips to store data electronically. SSDs have no moving parts, making them more resistant to physical damage.
Some key differences between HDDs and SSDs that impact performance:
- SSDs have much faster access times and data transfer speeds compared to HDDs.
- HDDs are good for storing large amounts of data long-term, while SSDs are faster for active use and booting.
- SSDs use less power, generate less heat, and produce no noise compared to HDDs.
- HDDs are less expensive per gigabyte than SSDs.
Boot Drive Performance Factors
When choosing a boot drive, some key factors that impact performance include:
Drive Interface
The interface between the drive and computer impacts transfer speeds. Common options for both HDDs and SSDs include:
- SATA – Up to 6Gbps transfer speed
- PCIe/NVMe – Up to 5,000Mbps+ transfer speed
NVMe SSDs with a PCIe interface offer the fastest speeds and lowest latency.
Drive Capacity
Larger capacity drives typically have faster sequential read/write performance. For an HDD boot drive, choose at least 500GB capacity. For SSDs, 250GB or larger is recommended.
Drive Cache
The cache buffers data for faster access. Larger caches improve performance. For HDDs, 64MB cache is good. For SSDs, look for drives with DRAM cache.
Internal Data Transfer Speed
This measures how fast data can be accessed from the drive’s flash chips or platters. Look at metrics like sequential read/write speeds and random access speeds. SSDs are much faster than HDDs internally.
Benefits of an SSD Boot Drive
Using an SSD as the primary boot drive offers several benefits:
Faster Boot and App Load Times
SSDs can boot in under 10 seconds, while HDD boot times are typically 30-40 seconds or more. App launch times are also faster with SSDs.
Faster File Transfers and Saves
The higher data transfer speeds of SSDs allow files like documents, photos, videos to open and save much quicker.
Improved Overall System Responsiveness
With an SSD, simple tasks like opening files, switching apps, and browsing files feel snappier and more responsive due to the near instantaneous data access.
More Reliable and Durable
SSDs have no moving parts, making them less prone to failure due to physical shock. They are better suited to mobile use.
Cooler and Quieter
SSDs run silent without any noise from spinning platters or moving heads. They also consume less power and run cooler.
Benefits of an HDD Boot Drive
HDDs do offer some benefits as the primary boot drive:
Lower Cost Per Gigabyte
HDDs are significantly cheaper than SSDs for the same capacity. A 1TB HDD is around 3-4x less expensive than a 1TB SSD.
Good Sequential Speeds
While HDDs are slower at random access, sequential data transfer speeds can reach over 150MB/s on high performance HDDs, which is sufficient for some tasks.
High Capacities Available
HDDs are available at very high capacities up to 10TB+ for less money. This can provide ample storage for large files.
Maturity of Technology
HDDs have decades of development. The technology is well proven and understood. There is less risk of issues like limited write endurance cycles on earlier SSDs.
Performance Comparison
Here is a performance comparison between a high end HDD and SDD:
| Spec | Seagate Barracuda HDD | Samsung Evo SSD |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | SATA 6Gb/s | PCIe NVMe |
| Sequential Read Speed | 210 MB/s | 3,500 MB/s |
| Sequential Write Speed | 210 MB/s | 3,300 MB/s |
| Random Read Speed | 0.9 ms | 0.15 ms |
| Random Write Speed | 2.0 ms | 0.15 ms |
As you can see, the SSD provides significantly faster sequential transfer speeds, while absolutely blowing away the HDD on random access speeds due to the instant lookups of flash memory.
OS and Software Considerations
The operating system and software used also impact bott drive performance.
Operating System
Windows 10 and 11 are optimized to take advantage of SSD capabilities like TRIM and NVMe drivers. Using an SSD provides the biggest speed boost on modern Windows versions.
Software and Applications
Applications like games and video editing tools will benefit the most from SSD faster speeds. Productivity apps and web browsing don’t rely as much on drive performance.
Upgrade Considerations
Clean vs Clone
When upgrading to an SSD boot drive, you can either do a clean OS install which requires reinstalling apps, or clone the HDD over to the SSD. Cloning is faster and easier but can carry over HDD issues.
Replacing HDD with SSD
You may want to keep the HDD for additional storage and replace it in the computer with the SSD for booting. Or you can use an external HDD enclosure to supplement the smaller SSD.
Dual Drive Configurations
It’s also possible to run both an SSD and HDD, installing apps and OS to the SSD for speed while storing data on the HDD. Some computers support multiple drive bays, or you can add an SSD in an M.2 slot.
Ideal Uses for HDD vs SSD Boot Drives
Some ideal uses for each drive type:
HDD Boot Drives
- Basic home and office PCs for basic tasks
- File and media storage servers
- CCTV and surveillance DVR systems
SSD Boot Drives
- Gaming PCs and workstations
- Audio and video editing rigs
- High performance laptops
- Mission critical business systems
Conclusion
For most general purpose and high performance PCs, an SSD is strongly recommended as the boot drive for the faster boot times, application launch speeds, and overall system responsiveness it provides. HDDs are slower but cheaper, so work well for basic home PCs or when large storage capacity is needed. Dual drive setups with an SSD boot drive and HDD data drive offer a balance of speed and storage capacity.