VHD (Virtual Hard Disk) and VHDX are disk image file formats used in virtualization environments like Microsoft Hyper-V. VHD was introduced in Windows Server 2008, while VHDX was introduced later in Windows Server 2012 as an enhanced replacement for VHD.
VHD uses the older .vhd file extension, while VHDX uses the newer .vhdx extension. When creating new virtual machines, VHDX is generally recommended over VHD for its improved features.
However, many existing virtual machines still use the older VHD format. This raises the question of whether it is worthwhile to convert existing VHD virtual disks to the newer VHDX format to take advantage of its benefits. This article will examine the pros and cons of converting from VHD to VHDX to help determine if it is the right choice.
Background on VHD
The VHD (Virtual Hard Disk) file format was introduced by Connectix in 1995 as part of their Virtual PC virtualization software. It allows for the creation of virtual hard disk files that can be mounted by virtual machines as if they were physical disk drives (Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/VHD_(file_format)).
Some key features of the VHD format include:
- Ability to represent both fixed and dynamically expanding virtual disks
- Support for virtual disks up to 2040 GB in size
- Built-in checksum features for data integrity
- Compatibility across major virtualization platforms like Virtual PC, Virtual Server, Hyper-V, and VMware
The VHD format became popular in data centers and enterprise environments because it provided a standardized way to encapsulate virtual hard disks for use in different virtualization solutions. It enabled greater flexibility and portability for virtual machines.
Background on VHDX
The VHDX disk image format was introduced by Microsoft in Windows Server 2012 and Windows 8. It was designed to replace and improve upon the older VHD format. Some key features of the VHDX format include:
Larger disk size capacity – VHDX supports virtual disks up to 64 TB, compared to 2 TB for VHD. This allows for much larger workloads and applications.1
Data integrity and resiliency – VHDX utilizes a checksum method to better detect and prevent data corruption. It also has in-built mechanisms for fixing errors.2
Performance optimizations – VHDX provides better performance for newer hardware platforms by utilizing larger block sizes and asynchronous I/O operations.
In summary, VHDX was designed to be an improved and more modern virtual disk format to meet the demands of enterprise workloads and large scale virtualization deployments.
Benefits of Converting to VHDX
There are several key benefits to converting from the older VHD format to the newer VHDX format:
Improved capacity – VHDX supports virtual hard disk sizes up to 64 TB, compared to VHD’s limit of 2 TB. This allows for much larger virtual machines and workloads. https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/windows/it-pro/windows-server-2012-r2-and-2012/hh831446(v=ws.11)
Protection against corruption – VHDX utilizes checksums to prevent and detect data corruption. This improves resiliency and uptime. https://www.techtarget.com/searchstorage/tip/Microsoft-VHDX-format-Understanding-benefits-conversion-process
Performance optimizations – VHDX introduces larger block sizes and optimizations such as TRIM support for improved performance. https://www.nakivo.com/blog/work-hyper-v-vhd-vhdx-files-essential-basics/
Downsides of Converting to VHDX
While VHDX offers some benefits over VHD, there are also some downsides to consider before converting:
Incompatibility with older operating systems – One of the main downsides of VHDX is that it is not compatible with older Windows OS versions prior to Windows Server 2012 and Windows 8. So if you need to use the virtual disk image on a legacy OS, VHDX will not work. VHD has much wider OS support.
Increased file size – Due to the addition of integrity streams and larger block sizes, VHDX files are typically 10-15% larger than equivalent VHD files. This increased storage requirement may not be ideal in all use cases 1.
Cannot be used for boot images – VHDX cannot be used as bootable operating system images like VHD can. So VHDX cannot be used for solutions like boot-from-VHD.
Overall, the main downsides are incompatibility with older Windows versions, larger storage footprint, and lack of boot support. So these limitations need to be considered before converting VHD to VHDX.
When to Convert VHD to VHDX
There are a few key situations when it makes sense to convert your VHD files to the newer VHDX format:
For new VM deployments – If you are deploying new virtual machines, it is recommended to use VHDX instead of VHD. The VHDX format comes with a range of enhancements and is generally considered the standard for new VMs.
If you need a larger virtual disk size – One of the advantages of VHDX is that it supports virtual hard disk sizes up to 64 TB, compared to VHD which maxes out at 2 TB. If you need a disk larger than 2 TB, you will need to use the VHDX format.
If you are experiencing corruption issues – The VHDX format provides greater resilience to corruption. If you are having frequent corruption problems with VHD files, converting to VHDX may help avoid this.
Overall, if you are deploying new VMs, need a larger disk size, or are seeing corruption issues, converting your VHD files to VHDX is recommended.
When Not to Convert VHD to VHDX
There are some cases where you may not want to convert your VHD files to VHDX format:
Compatibility Requirements with Older Operating Systems
VHDX format is not supported by operating systems older than Windows Server 2012 and Windows 8 (1). If you need to use the virtual hard drive with an older OS like Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2, you should keep it in VHD format. Converting to VHDX would make the virtual disk unbootable and unusable on those legacy systems.
Limited Storage Space
VHDX files require more storage space than VHDs. The footer in VHDX is 8MB versus 1MB in VHD, so converting can increase storage needs (2). If you have limited storage capacity, sticking with VHD may be preferable to save space. However, the benefits of VHDX may outweigh this drawback in many cases.
In summary, compatibility requirements with older operating systems that don’t support VHDX and limited storage capacity are two scenarios where you may want to avoid converting VHD to VHDX format.
(1) https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/troubleshoot/system-center/vmm/convert-between-vhd-vhdx-formats
(2) https://www.nucleustechnologies.com/blog/how-to-convert-vhd-to-vhdx-file/
How to Convert VHD to VHDX
There are a few different tools that can be used to convert a VHD file to VHDX format. The easiest method is to use the Hyper-V Manager in Windows. Hyper-V includes built-in functionality to convert virtual hard disks between VHD and VHDX formats.
To convert a VHD to VHDX using Hyper-V Manager:
- Open Hyper-V Manager and locate the VHD file you want to convert.
- Right-click on the VHD file and select “Edit Disk.”
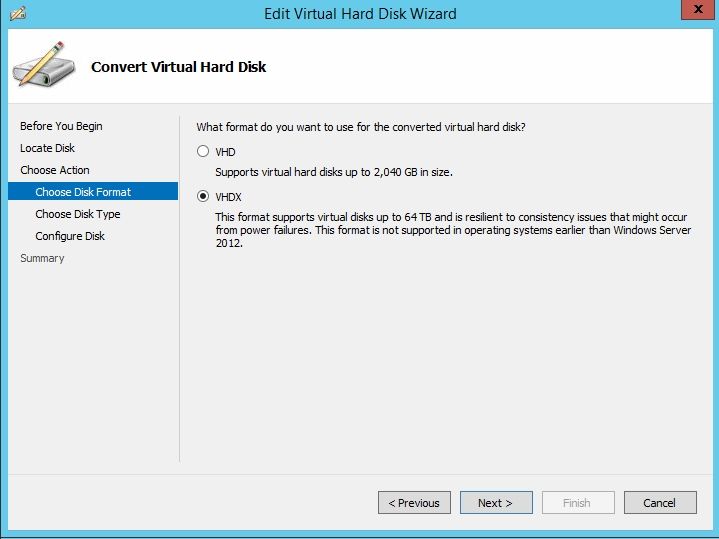
- In the Edit Virtual Hard Disk Wizard, select “Convert” on the first page.
- On the next page, select VHDX as the disk format to convert to.
- Complete the wizard to finish the conversion process.
The conversion process can also be automated with PowerShell commands. Microsoft provides sample PowerShell scripts for converting VHD to VHDX (https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/troubleshoot/system-center/vmm/convert-between-vhd-vhdx-formats).
There are also third-party tools like StarWind V2V Converter that can perform VHD to VHDX conversion. Overall, Hyper-V Manager provides the simplest method for most use cases.
Testing and Validation
After converting a VHD to VHDX, it is crucial to thoroughly test and validate the new VHDX file before putting it into production. There are several best practices to follow:
First, verify that the VHDX can be mounted and attached to a virtual machine. Boot the VM and validate that the operating system loads correctly without any errors or crashes. Check that applications function as expected.
Next, validate disk performance by running benchmarking tools on the VHDX and comparing results to the original VHD. Look for any degradation in read/write speeds.
Also test out backup and restore procedures on the new VHDX file. Confirm backups complete successfully and restores work properly.
Check management and monitoring tools to ensure the VHDX is being detected accurately. Validate any alerting and reporting features.
Run an anti-virus scanner, chkdsk, and sfc /scannow on the VHDX to verify integrity of the file system. Make sure no corruption occurred during conversion.
Finally, test failover capabilities by simulating different failure scenarios like network outages or host crashes. Verify redundancy and failover works correctly.
Taking the time to thoroughly validate and test a converted VHDX will help catch any issues before the disk goes into a production environment. Test all use cases to confirm seamless compatibility and performance.
Conclusion
In summary, converting from VHD to VHDX offers several benefits including larger storage capacity, better performance, and new features like 4K sector alignment. However, there are also downsides to consider such as compatibility issues with older operating systems and the fact that conversion is a one-way process. Overall, converting to VHDX makes the most sense when you need those expanded capabilities and are not limited by OS compatibility restraints. If none of the VHDX benefits are required, it may be best to simply stay with the VHD format.
The key considerations are weighing your need for features like larger size, better performance, and 4K alignment vs. compatibility with older operating systems that do not support VHDX. Evaluate your specific use case and environment. If you decide moving to VHDX is advantageous, be sure to have ample storage space and thoroughly test converted VHDX files before deploying into production.
In conclusion, VHD to VHDX conversion brings tradeoffs. Carefully evaluate your needs and environment to determine if transitioning to the newer format is the right choice for your virtual hard disks.