FAT32 and exFAT are variations of the File Allocation Table (FAT) file system originally developed for MS-DOS. The FAT file system was introduced in 1977 and became the standard file system for consumer devices.
FAT32 was introduced in 1996 as an update to the original FAT16 file system. It increased the maximum file size to 4GB and maximum partition size to 2TB. FAT32 was the standard file system for Windows 98 and ME.
exFAT was introduced by Microsoft in 2006 as an update to FAT32. It supports larger file sizes up to 16EB and larger partition sizes up to 1ZB. exFAT aimed to bridge the gap between FAT32 and NTFS for flash memory devices like SD cards and USB drives.
FAT32 Overview
The File Allocation Table 32 (FAT32) file system was introduced in 1996 by Microsoft with the release of Windows 95 OSR2. It was developed as an upgrade to the older FAT file system to support larger disk sizes (Wikipedia). FAT32 improves upon FAT by increasing the maximum number of clusters from 65,536 to 232 or 4,294,967,296 clusters. This significantly expands the maximum volume size to 8TB from the previous limit of 4GB in FAT16. The maximum file size limit also increased from 4GB to 4TB with FAT32. Additionally, FAT32 reduces disk fragmentation and improves support for smaller clusters, allowing more efficient use of disk space.
exFAT Overview
exFAT was released by Microsoft in 2006 for use in embedded devices running Windows CE like digital cameras and media players. According to the Microsoft documentation on the exFAT file system specification, it was designed for use on flash drives and SD cards where FAT32 is not ideal. exFAT enables support for larger files over 4GB and larger partitions over 32GB while still maintaining compatibility with older systems.
Some key characteristics of exFAT as noted in the Wikipedia overview on exFAT include:
- Supports individual files larger than 4GB
- File size limit of 16EiB (Exbibyte)
- Partition size limit of 128 PiB (pebibyte)
- Uses less overhead than NTFS
- Built on the older FAT file system, making it compatible with older devices
Overall, exFAT was created by Microsoft as an optimized file system for flash media and maintains compatibility with older systems, unlike NTFS. It broke the 4GB file size barrier while enabling larger partition sizes than FAT32.
File Size Limits
One of the main differences between FAT32 and exFAT is the maximum file size they support. FAT32 has a limit of 4GB per file (Source). This means any file larger than 4GB cannot be stored on a FAT32 formatted drive or SD card.
In contrast, exFAT supports enormous maximum file sizes up to 16 exabytes (EB), which is approximately 16 billion GB (Source). For reference, 1 EB is over 1 million terabytes. This essentially removes any file size limitation, allowing you to store files of any size.
The much higher maximum file size limit is one of exFAT’s major advantages over FAT32. For the Nintendo Switch, this means you can store very large games without worrying about hitting a 4GB cap. ExFAT is better suited for large game file storage.
Partition Size Limits
One of the main differences between FAT32 and exFAT is the maximum partition size each file system supports. FAT32 has a limit of 32GB for any single partition, which can be restrictive for larger external hard drives and SSDs. On the other hand, exFAT supports a massive maximum partition size of 128 petabytes (PB).
According to exFAT vs. FAT32 Comparison, FAT32 caps out at 8TB for the total drive size, while exFAT goes up to 128PB. So if you want to use a single partition on a large capacity drive over 32GB, exFAT is required.
The much higher possible partition size makes exFAT better suited for external storage with very large capacity. However, FAT32 may still be preferable for smaller flash drives or SD cards under 32GB.
Compatibility
FAT32 has much wider device compatibility compared to exFAT. According to the How-To Geek article “FAT32 vs. exFAT vs. NTFS: What’s the Difference?”, FAT32 is compatible with more devices than exFAT and NTFS file systems (https://www.howtogeek.com/235596/whats-the-difference-between-fat32-exfat-and-ntfs/). Although exFAT was designed as a replacement for FAT32, many older devices still only support FAT32 and are not compatible with exFAT. For maximum compatibility across different devices, especially older ones, FAT32 is the preferred file system.
Performance
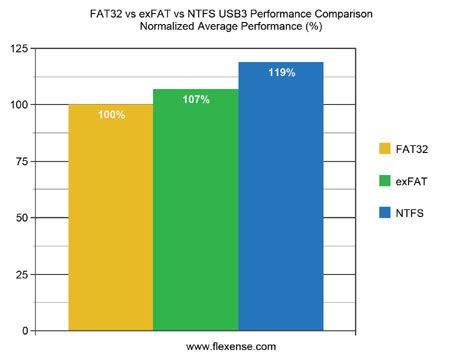
When it comes to performance, exFAT has some advantages over FAT32, especially when handling larger files. According to Flexense, exFAT delivers up to 9% better performance than FAT32 when reading medium to large sized files from a USB flash drive. This is because exFAT uses larger cluster sizes, which allows it to read bigger files more efficiently compared to FAT32.
FAT32, which uses smaller cluster sizes, is fine for smaller files. But for larger files, the numerous small clusters FAT32 requires to store the data can hurt performance. exFAT’s larger cluster sizes allow it to handle large files more efficiently with less lookup tables needed. So if you are working with files over 4GB in size, exFAT will provide faster read/write speeds compared to FAT32.
Reliability
When it comes to reliability, FAT32 is generally considered more reliable and less prone to corruption compared to exFAT. This is because FAT32 uses mirrored file allocation tables, while exFAT only uses one (except for TexFAT on Windows CE) [1]. The mirrored FATs provide redundancy that can help recover from corruption.
In general, exFAT is more prone to corruption, especially if not properly ejected or if power is lost during writes [2]. This is because exFAT does not keep redundant copies of the file allocation table. FAT32 is considered more robust in this regard.
For applications demanding high reliability like external hard drives, FAT32’s added redundancy makes it a better choice over exFAT in many cases.
Nintendo Switch Use Cases
The Nintendo Switch has a few key use cases that impact the storage needs for the console. These primarily relate to game cartridge sizes and the need for external storage.
The Nintendo Switch uses proprietary game cards for its physical games. These game cards can range in size from 1GB for simpler indie games to 32GB for larger AAA games. Some of the largest Switch games like NBA 2K18 and LA Noire require a 32GB game card due to their size (Source: https://www.nintendo.com/us/switch/tech-specs/).
For digital games purchased from the Nintendo eShop, the storage requirements can be much higher. Major titles like The Legend of Zelda: Breath of the Wild require 13.4GB of storage. The 32GB of onboard storage on the base Switch model fills up quickly, requiring most users to utilize external storage via microSD cards.
In order to have a reasonable number of digital games installed and ready to play, most recommendations suggest at least a 64GB microSD card. 128GB and 256GB cards are also popular for users who plan to build a large digital library of games (Source: https://www.imore.com/which-size-microsd-card-best-nintendo-switch).
Recommendation
In most cases, FAT32 is the recommended file system to use for your Nintendo Switch SD card. FAT32 has the widest compatibility with the Switch and other devices, and is less prone to corruption than exFAT. The main downside of FAT32 is the 4GB per file size limit, but this is generally not an issue unless you need to store very large individual files on your Switch.
exFAT can also be used if you need to store files larger than 4GB, as it supports file sizes up to 16EB. However, exFAT is more prone to corruption and has less universal compatibility than FAT32. Some older Switch models may also not recognize exFAT cards properly.
In summary:
- Use FAT32 if you don’t have any files larger than 4GB.
- Use exFAT only if you need to store individual files over 4GB in size.
- Format to FAT32 unless you have a specific need for exFAT.
Formatting to FAT32 will provide the most reliable and compatible experience for most Switch users. Only use exFAT if you absolutely need support for larger file sizes.