A hybrid drive is a storage device that combines a traditional hard disk drive (HDD) with a solid-state drive (SSD) (1). The goal is to provide the large storage capacity of an HDD along with some of the speed benefits of an SSD.
Hybrid drives first started appearing in 2007 when companies like Samsung and Seagate introduced early prototypes (2). The goal was to address growing demands for faster storage devices as file sizes increased and more data needed to be accessed quickly.
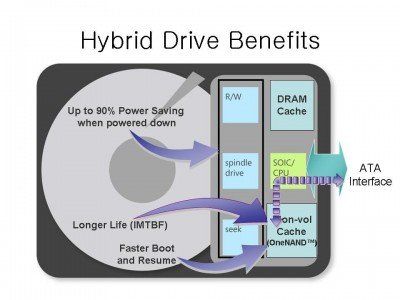
Hybrid drives work by using a small SSD cache (usually 8-32GB) along with a traditional HDD. Frequently accessed data like the operating system and applications are stored on the faster SSD portion, while less accessed data like documents and media files reside on the HDD. The drive will learn over time which files are accessed most and cache those on the SSD for faster access.
How Hybrid Drives Work
Hybrid drives contain both a traditional hard disk drive (HDD) and a smaller solid state drive (SSD). The HDD provides large storage capacity at a lower cost per gigabyte, while the SSD provides faster performance for improved speed (HP).
The SSD is used as a cache to store frequently accessed data, taking advantage of the fast read/write speeds of flash memory. The HDD stores the bulk of the data. Manufacturers use proprietary caching algorithms to determine which data gets stored on the faster SSD portion (TechTarget).
Two common caching approaches used in hybrid drives are adaptive memory technology and automated tiered storage. Adaptive memory identifies frequently used files and copies them to the SSD to speed up access. Automated tiered storage monitors data access patterns over time and optimizes data placement between the HDD and SSD (TechTarget).
By combining an HDD and SSD together with advanced caching algorithms, hybrid drives aim to balance storage capacity, performance, and cost-effectiveness.
Benefits of Hybrid Drives
Hybrid drives provide a number of benefits compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid state drives (SSDs). One of the biggest advantages of hybrid drives is that they are faster than HDDs, but cheaper than SSDs (Drivesaversdatarecovery.com, 2021). The SSD cache built into hybrid drives improves performance dramatically compared to a standard HDD. This is because frequently accessed data can be stored on the faster SSD portion of the drive, resulting in quicker boot times and faster application launches (Platinumdatarecovery.com, 2023).
Additionally, hybrid drives offer a easy upgrade path for those currently using HDDs in their computers. Since hybrid drives use the same SATA interface and form factors as HDDs, they can be swapped in as a direct replacement. This allows users to gain improved speed without having to migrate data or reformat their existing hard drive (TechTarget, n.d.). Overall, hybrid drives strike a balance between affordability, capacity, and performance that make them appealing compared to HDDs and SSDs for many consumer use cases.
Use Cases
Hybrid drives are commonly used in desktop computers, laptops, and game consoles where a balance of storage capacity and speed is needed.
For desktop computers, hybrid drives provide more storage than solid state drives (SSDs) at a lower cost, while still improving boot times and load times for frequently accessed files compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs). The large capacity makes them suitable for storing photos, videos, games, and media files. TechTarget notes hybrid drives are a popular upgrade choice for desktop PC users looking for better performance without sacrificing storage space.
Laptops benefit from hybrid drives in a similar way. The limited space in laptops means large capacity SSDs are not an option for most users. Hybrid drives allow for faster boot times and resume from sleep compared to HDDs, while providing much more storage than small SSDs. Their balance of speed and capacity make them a good choice for laptops used for gaming, media editing, and other storage-intensive tasks. Lenovo states hybrid drives are standard in many of their laptop product lines.
For game consoles, the large capacity hybrid drives offer is ideal for storing the many gigabytes games now require. The improved speed compared to HDDs provides faster load times and smoother gameplay. Major console makers like Sony and Microsoft offer hybrid drives as storage options for their consoles to satisfy gamers’ need for both capacity and performance.
Hybrid Drive Performance
Hybrid drives aim to combine the performance of SSDs with the storage capacity of HDDs. Various benchmarks have been run to compare hybrid drive performance to HDDs and SSDs for common computing tasks.
According to testing by Seagate using the PCMark Vantage benchmark, their hybrid drives showed significant performance improvements over traditional hard drives for applications like starting up Windows, loading games, booting games levels, and other common tasks that involve reading data from storage. In many tests, the hybrid drive was able to match the performance of a dedicated SSD while providing more total capacity at a lower cost per gigabyte.
UL’s new PCMark 10 Storage Benchmarks also provide a way to compare overall storage performance. Their testing showed hybrid drives scoring 2-3x higher than traditional HDDs, although still lagging behind dedicated SATA and NVMe SSDs. The hybrid drive SSD cache helps accelerate many daily tasks, though very intensive storage access still favors pure SSD storage.
In summary, benchmarks demonstrate hybrid drives can provide a nice performance boost over HDDs for many common workloads like booting, game loading, and general application usage. Their strengths lie in their balance of affordability, capacity, and improved responsiveness compared to traditional hard drives.
Major Hybrid Drive Manufacturers
Some of the major manufacturers of hybrid drives include:
Seagate – Seagate is one of the largest manufacturers of hybrid drives. Some of Seagate’s popular hybrid drive models include the Seagate Laptop SSHD, Seagate Desktop SSHD, and Seagate FireCuda. Seagate combines flash memory with traditional hard disk drives to deliver improved performance over traditional HDDs.
Toshiba – Toshiba offers a line of hybrid drives under its MQ series. These combine 8GB of NAND flash memory with up to 1TB of HDD capacity. Models include the MQ01ABD050H, MQ01ABD075H, and MQ01ABD100H. Toshiba MQ series hybrid drives deliver excellent performance for desktops, all-in-one PCs, and other devices.
Western Digital – Western Digital sells hybrid drives under its WD Black brand, targeted at gamers, high-performance PCs, and workstations. Some models include the WD Black2 Dual Drive and the WD Black SSHD. These hybrid drives offer flash memory to accelerate frequently accessed data and programs.
Purchasing Considerations
When considering a hybrid drive purchase, there are several key factors to weigh:
Capacity needs – Assess how much storage capacity you require. Hybrid drives offer capacities from 500GB to 2TB typically. Determine if a hybrid drive offers enough space for your needs or if a higher capacity traditional HDD or SSD is required.
Form factors – Hybrid drives come in standard internal drive form factors like 2.5″ and 3.5″ for desktops/laptops and M.2 for ultrabooks. Ensure the form factor fits your system.
Budget – Hybrid drives are more affordable than pure SSDs but costlier than HDDs. A 500GB hybrid may cost around $50-70 while a 500GB SSD is around $60-100. Determine your budget trade-off between capacity, speed, and cost.
Performance needs – Hybrid drives don’t match SSD speeds but offer a performance boost over HDDs. If peak speeds are critical, go full SSD. For a balance of speed and capacity on a budget, hybrid drives are a good compromise.
Consider factors like usage – boot drive vs. data storage, time-sensitive applications, multitasking needs – and choose the storage type that best aligns with your priorities.
Hybrid Drive Reliability
Hybrid drives tend to have good reliability compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs), but may not match the exceptional lifespan of solid state drives (SSDs). According to a study by AnandTech, the average annual failure rate for HDDs is around 4%, while hybrid drives see a lower 2.8% annual failure rate. SSDs have the lowest failure rates, averaging only 1.4% annually.
In terms of lifespan, HDDs tend to last around 3-5 years on average before failure. Hybrid drives can extend that lifespan slightly thanks to the SSD caching, with most drives lasting 5-7 years. SSDs have a much longer 10+ year expected lifespan under normal use.
Manufacturers typically provide 3-5 year warranties on hybrid drives and HDDs, while SSD warranties range from 5-10 years. So while hybrid drives offer a nice middle-ground for reliability, SSDs are still the most durable long-term storage option before needing replacement.
Future Outlook
The future of hybrid drives looks uncertain as their popularity and production are expected to decline in the coming years.
Hybrid drives face stiff competition from solid state drives (SSDs), which are faster, more reliable, and increasingly affordable [1]. As SSD prices continue to drop, fewer consumers are likely to choose hybrid drives.
Major hard drive manufacturers are scaling back production of hybrid drives. For example, Seagate discontinued their Laptop SSHD line in 2016 [2]. While some companies like Toshiba still offer hybrid drives, they make up a small percentage of overall storage shipments.
However, some experts predict hybrid drive technology will continue evolving. Advancements in flash memory and caching algorithms could potentially boost hybrid drive performance. Automakers are also researching ways to improve hybrid powertrains for better fuel efficiency and driving range [3]. But it remains to be seen if these innovations will be enough to secure hybrid drives a place in the storage markets of the future.
Conclusion
Hybrid drives offer an excellent compromise between the affordability of standard hard disk drives and the performance boost from solid state drives. By combining a small amount of fast SSD storage with a larger capacity HDD, hybrid drives can deliver better speeds for frequently accessed files and programs while still providing substantial storage space at a lower price point.
For the average consumer looking to give their computer a performance upgrade without breaking the bank, hybrid drives are a smart middle ground option. The speed gains may not be as dramatic as transitioning fully to an SSD, but hybrid drives come at a fraction of the price. This makes them a great choice for system builders or anyone looking to extend the life of an aging computer.
As SSD prices continue to drop over time, hybrid drives may become less necessary. But for now, they occupy an important space in the storage market, blending the best attributes of HDDs and SSDs into a single practical storage solution.