Adobe Photoshop is the dominant photo editing and graphics software on the market. According to Statista, Photoshop has a market share of 37% in the graphic design software market as of 2023, with over 15 million active monthly users.
Photoshop is commonly used by photographers, graphic designers, web designers, and creative professionals for image editing, compositing, and digital art. It offers features for photo retouching, color correction, collage creation, digital painting, and more. Photoshop is part of Adobe’s Creative Cloud, giving users access to cloud storage, Adobe fonts, and integration with other Creative Cloud apps.
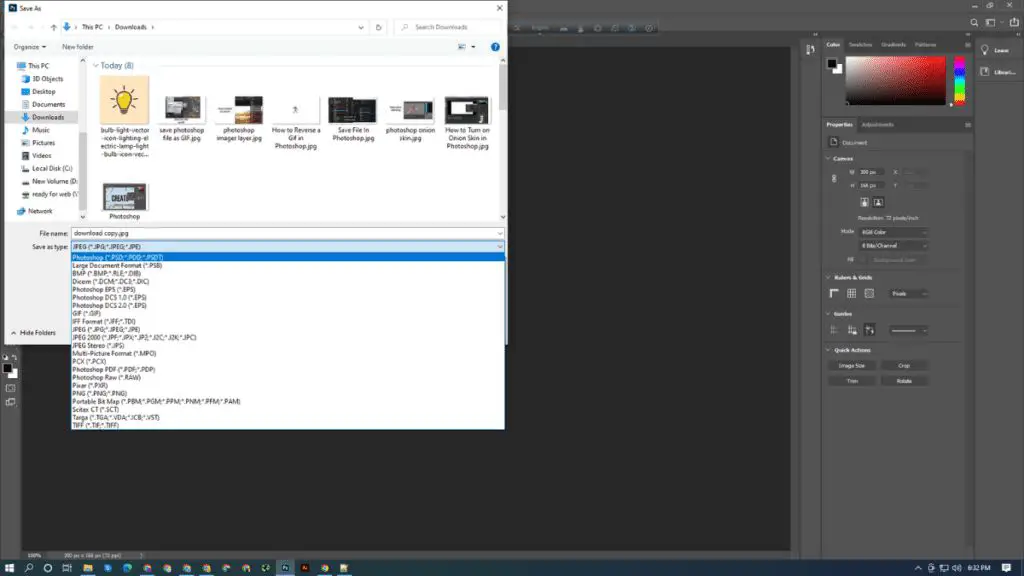
With its wide range of capabilities, Photoshop works with many different file formats. The native PSD format offers the most editing flexibility and retains all Photoshop data. But Photoshop can also open and save files in common image formats like JPEG, GIF, PNG, and TIFF for sharing and publishing.
Native Photoshop Format (PSD)
PSD is the default file format used by Adobe Photoshop. It stands for “Photoshop Document” and uses the .psd file extension. PSD files support all features available in Photoshop like layers, masks, transparency, text, and effects [1]. This makes PSD the best format for saving Photoshop projects that need to be edited further.
The downside is that PSD files tend to have large file sizes compared to other formats like JPG or PNG. This is because PSD stores all editing information instead of compressing or flattening image data. The layers, effects, and other extra information make the file size much larger. PSD files take up storage space but allow non-destructive editing. This trade-off makes PSD ideal for working on images within Photoshop that require future editing.
TIFF
TIFF, or Tagged Image File Format, is one of the highest quality image formats supported natively by Photoshop (helpx.adobe.com). It is a lossless format, meaning no image quality is lost during compression. TIFFs retain all of the original image data, resulting in large file sizes compared to lossy formats like JPEG.
Some key benefits of using TIFF in Photoshop include:
– Supports layers and transparency – TIFFs can preserve all the layers and transparency information from a Photoshop document. This makes TIFF a good choice if you need to send a file to someone else for additional editing.
– Lossless compression – As mentioned above, TIFF uses lossless compression so you don’t lose image quality when saving.
– Wide compatibility – TIFF is supported across Mac, Windows, and Linux operating systems and can be opened by virtually any image editing or desktop publishing application.
– Print quality – TIFF provides excellent print quality since there is no loss of detail or colors during compression. Photographers often use TIFF when printing their work.
The main downside to TIFF is the large file size, which takes up storage space and can be slower to transfer online. But for print or archiving high resolution images, TIFF remains a top choice supported natively in Photoshop.
JPEG
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) is a commonly used lossy compression format for images. As a lossy format, JPEG compresses images by selectively discarding data, which can result in some loss of quality. However, this also allows JPEG files to have much smaller file sizes compared to uncompressed formats like TIFF (Source).
The advantage of smaller files sizes makes JPEG a popular choice for storing or sharing photographs and digital artwork online. The compression can be adjusted to optimize for quality or smaller file size depending on the intended use. However, JPEG does not support transparency and is therefore not the best choice for images with transparent areas (Source).
GIF
GIF stands for Graphics Interchange Format. GIF is a bitmap image format that supports up to 8 bits per pixel, allowing a single image to reference a palette of up to 256 distinct colors. GIFs also support animation, allowing a separate palette of up to 256 colors for each frame.
One of the key features of the GIF format is its ability to store multiple images within a single file, which can be displayed sequentially to create simple animated images. GIFs can loop infinitely or play through once. GIF animation supports transparency via a transparent color index, allowing portions of each frame to render as transparent.
However, there is a 500 frame limit when exporting GIF animations in Photoshop (Source). Furthermore, the 256 color limit often requires dithering or loss of color depth for photographs and complex images, making GIF less suitable for static images.
PNG
PNG (Portable Network Graphics) is another popular image format option in Photoshop. PNG uses lossless compression, meaning no image quality is lost during compression. This makes it a good choice for images with flat colors or simple gradients where quality is paramount.
One of the key benefits of PNG is its support for transparency. PNGs can contain transparent pixels, making them perfect for images with irregular shapes or transparency that need to be preserved. PNG is often a better alternative to GIF for images with transparency.
PNG also offers better color support than GIF, with the ability to store 24-bit color compared to GIF’s 8-bit palette. This makes PNG a more versatile format with superior color representation. Overall, PNG strikes a great balance between small file size, image quality, and web compatibility.
PDF (Portable Document Format) is a commonly used file format for saving Photoshop documents. Some key advantages of the PDF format include:
PDF is a vector-based format, which means it preserves image quality if you need to scale or zoom the artwork. The format supports both raster and vector data.
Text remains editable and selectable in PDF files. You can open a Photoshop PDF document in various programs and still be able to edit or copy text.
PDFs have wide device support and can be viewed on desktops, mobile devices, tablets, and more. The format works consistently across platforms.
Overall, Photoshop’s PDF support makes it easy to share artwork with others while retaining image quality, text editability, and multi-platform compatibility.
Source: https://helpx.adobe.com/photoshop/using/saving-pdf-files.html
BMP
BMP stands for bitmap image file. It is an uncompressed raster graphics format that is native to the Microsoft Windows operating system. BMP images contain raw, uncompressed raster data with no compression at all [1]. This makes BMP files well-suited for storing high-quality digital photographic images, but they come with large file sizes compared to compressed formats like JPG.
Since BMP files contain uncompressed bitmap data, they are ideal for storing and displaying digital images without any loss of quality. However, the tradeoff is that these files can be very large, using a lot of disk space. BMP images can store up to 16 million distinct colors, making them useful for handling photos and digital artwork where high color depths are required [2].
Overall, the BMP format is best suited for storing high-resolution digital images where file size is not a concern. It maintains maximum image quality but lacks the smaller file sizes of compressed formats. BMP remains widely supported across Windows applications and is a key raster graphics format on the Windows platform.
PSB
PSB stands for Adobe Photoshop Big or Photoshop Large Document. It is an extension of the PSD format that was introduced in Photoshop CS. PSB allows for much larger file sizes than the standard PSD format.
According to Adobe, the PSB format supports documents up to 300,000 pixels in any dimension as compared to PSD which caps out at 30,000 pixels. This allows PSB files to be substantially larger with some at over 4GB in size. The PSB format retains all the same features as PSD such as layers, effects, and transparency.1
PSB is designed for extremely large and complex files where the image dimensions exceed the PSD limit. Photographers working with high resolution images or graphic designers assembling artwork with many layers may require the PSB format. It maintains full compatibility will all Photoshop features and plugins.
Conclusion
Photoshop offers a variety of file formats to save your work, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The most commonly used formats include:
- PSD – Photoshop’s native format that preserves all editing capabilities.
- TIFF – A lossless format good for printing.
- JPEG – A lossy format good for photos at smaller file sizes.
- GIF – A lossless format best for images with few colors.
- PNG – A lossless, compressed format good for web images.
When choosing a format, consider how you intend to use the image. PSD is best for further editing, while JPEG is suitable for web photos and PNG works well for web graphics. TIFF and PNG are lossless formats ideal for printing. Evaluate your priorities for image quality, file size, and editing capabilities to select the best format for your needs.