As our devices become more integrated into our daily lives, protecting them from malware is more important than ever. Malware, short for “malicious software”, refers to programs and files that are designed to damage or do other unwanted actions on a device. With the right precautions, you can help keep your device malware-free.
Quick Answers
The three main methods for protecting devices from malware are:
- Using antivirus/anti-malware software
- Practicing safe browsing habits
- Keeping devices and software up-to-date
What is Malware?
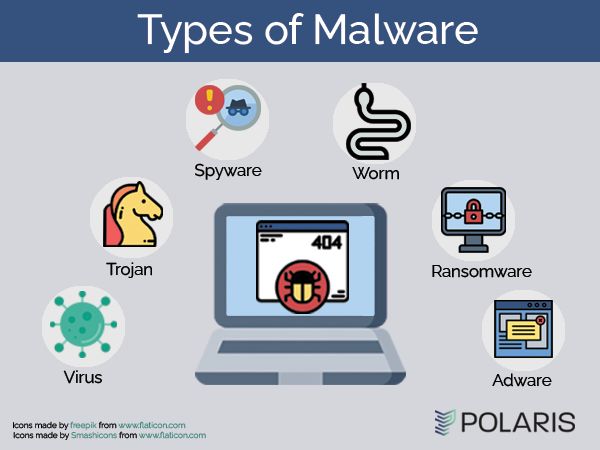
Malware is an umbrella term for various types of harmful software that cybercriminals use to compromise devices and systems. Some of the most common types of malware include:
- Viruses – Malicious programs that replicate by infecting other files or programs.
- Worms – Malware that spreads by exploiting vulnerabilities in operating systems.
- Trojan horses – Malicious programs that masquerade as legitimate software.
- Spyware – Software that gathers data about a user’s device or activity without consent.
- Adware – Software that displays unwanted advertisements.
- Ransomware – Malware that encrypts files and demands payment for decryption.
Malware can infect various types of devices, including computers, mobile devices, and even IoT devices. Its impacts can range from annoying pop-ups and slowed performance to full system lockouts and data theft. That’s why taking steps to prevent malware is critical for any internet-connected device.
Method 1: Use Antivirus/Anti-Malware Software
One of the most important defenses against malware is to use antivirus or anti-malware software. This type of program is designed to detect, block, and remove malware from devices.
Antivirus software works by scanning files, programs, and system areas for any code identified as malware. It does this by comparing them against huge databases of known malware signatures. Any matches trigger the antivirus to quarantine or delete the threats. Anti-malware tools also use advanced heuristics to identify malware by behavior, in case it’s not yet in malware databases.
Some key benefits of antivirus/anti-malware tools include:
- Real-time scanning during file downloads, website visits, app use, etc.
- Scheduled system scans to proactively detect dormant threats
- Quarantining infected files before they cause harm
- Automatically removing identified malware
- Blocking malicious website connections
- Protecting against ransomware encryption attempts
Leading antivirus and internet security suite providers include Norton, McAfee, AVG, Avast, Bitdefender, Kaspersky, and more. Many provide basic real-time malware protection for free, then offer advanced tools and features in paid versions. These can add firewalls, online backup, identity protection, parental controls, and performance optimization.
For the best protection, antivirus software should be installed and running with real-time scanning enabled on all of your internet-connected devices. Be sure to keep the software updated as well, as malware signatures are added to its database daily.
Key Antivirus Software Features
- Real-time scanning
- Scheduled system scans
- Malware signature database
- Quarantine of threats
- Automated removal
- Firewall
- Web blocking
- Ransomware protection
Method 2: Practice Safe Browsing Habits
Your online habits can greatly impact your malware risk. Carelessly downloading files and visiting questionable sites are easy ways to get infected. Here are some key safe browsing practices to reduce your malware exposure:
Only Download from Trusted Sources
One of the top malware infection methods is downloading infected files from untrusted sources. This includes:
- Peer-to-peer sharing sites
- Illegal file download sites
- Unknown app stores or repositories
- Clicking links in spam emails
Stick to downloading software, apps, files, and media from known, reputable sources like official vendor sites and app stores. This drastically cuts your malware risk.
Watch Out for Suspicious Links
Clicking an infected link can instantly load malware onto your device. Be wary of:
- Links in unsolicited emails
- Sketchy pop-up or banner ads
- URL shortener links
- Misspelled or odd looking domains
Hover over any link to preview its actual destination before clicking. If in doubt, avoid clicking altogether. Stick to sites you know and trust.
Don’t Open Email Attachments Recklessly
Email attachments are used to spread various malware types like viruses and trojans. Be cautious before opening any attachment from an unknown or unverified sender. Check for warning signs:
- Generic greetings like “Hello” or “Hi there”
- Suspicious domain names in the sender’s email address
- Typos and grammatical errors
- Unexpected attachments from known contacts
When in doubt, confirm with the sender before opening to verify legitimacy.
Browse Securely
General secure browsing measures will further protect you from malware threats:
- Only login to sites using HTTPS connections
- Don’t stay logged into accounts on public devices
- Clear cookies, cache, and browsing history regularly
- Use anonymous private browsing modes
- Don’t auto-save passwords in browsers
Practicing safe habits like these when web browsing or opening emails can significantly reduce your malware risk from infected sites, links, and attachments.
Method 3: Keep Devices and Software Up-to-Date
Allowing your devices and software to become outdated makes you an easy malware target. Cybercriminals actively scan for systems with security holes to exploit. Staying updated with the latest patches and versions keeps you much safer. This applies to:
Device Operating Systems
Always install available operating system and firmware updates on your devices promptly. These often contain vital security fixes:
- Windows updates
- macOS updates
- Linux distribution updates
- Android and iOS updates
- Router firmware updates
- Smart device firmware updates
Set devices to automatically install updates when possible for convenience.
Software Applications
Application vulnerabilities get exploited frequently as well. Patch promptly by:
- Updating to the latest versions of applications
- Installing patches for programs like Adobe Flash or Reader
- Using auto-updating apps like web browsers whenever possible
Monitor software vendors’ update releases and news for knowledge of any major exploits or bugs.
Security Software
As mentioned earlier, it’s critical to keep antivirus software updated with the latest malware signatures. Also ensure any firewalls, VPNs, password managers, and other security tools stay updated.
Other Tips for Preventing Malware
Some other best practices that help guard against malware include:
- Enable firewalls on devices to monitor network traffic.
- Install ad blockers in web browsers to avoid malware-laden ads.
- Avoid using administrator accounts for everyday tasks on computers.
- Connect devices through a virtual private network (VPN) when on public Wi-Fi.
- Turn off wireless connections like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth when not in use.
- Regularly back up important data in case of malware encrypting files.
- Close browser windows when done using the internet.
- Disable macros in applications like Microsoft Office to block exploits.
- Carefully review app permissions before installing on mobile devices.
What To Do If You Get Malware
Even with great precautions, malware sometimes finds its way onto devices. If you suspect a malware infection:
- Run a full system scan using updated antivirus software.
- Isolate the infected device from other local devices and networks immediately.
- Change passwords for any accounts logged into on the infected device.
- Back up data and prepare for a system restore or reset if needed.
- Notify contacts if emails were sent from an infected device.
- Watch for signs of identity theft or further infection.
Catching and terminating malware quickly can greatly limit any harm done. In severe cases, though, the only fix may be fully wiping the infected device and reinstalling the operating system.
Conclusion
Malware represents a constant threat to our personal and professional devices. But following security best practices of real-time scanning, safe browsing, prompt updating, and more can provide excellent protection. Block malware at the door with robust antivirus software. Be cautious when downloading files and clicking links. Keep all your software patched and upgraded. And ensure you have backups ready to recover from any infection.
Vigilance and proactive security habits will harden your devices as difficult targets. Keep your guard up with consistent precautions and you can avoid becoming just another victim of destructive malware.