Code 43 is an error message that you may see when trying to use a USB device on your Windows PC. It indicates that Windows has failed to recognize the USB device and therefore cannot load the appropriate driver software for it. This prevents the device from functioning properly when connected to the computer via USB.
There are a few potential causes for a code 43 error with a USB device. The most common reasons include:
- Faulty or incompatible hardware drivers
- Corrupt registry entries
- Insufficient USB power/current
- Damaged USB ports
- Malfunctioning USB device
In many cases, code 43 issues can be resolved by updating drivers, tweaking registry settings, adjusting USB selective suspend settings, or using a different USB port on your computer. However, if the USB device itself is malfunctioning, it may need to be replaced.
What Does the Code 43 Error Mean Specifically?
The code 43 error message is quite generic and doesn’t provide much detail on what exactly is wrong with the USB device. Specifically, it means that Windows has failed to load the device driver software that allows it to recognize and communicate with the connected USB hardware.
Code 43 errors originate from the Windows plug-and-play manager. Plug-and-play is the process that allows Windows to automatically recognize and configure devices when they are connected. Part of this process involves loading the appropriate drivers.
If the drivers fail to load properly, Windows has no way to identify or interact with the USB device, despite it being physically connected. The generic code 43 message is its way of signaling that device driver loading has failed.
The technical terminology for this type of error is an IRP_MJ_CREATE error. IRP stands for I/O Request Packet, which is how devices communicate with the operating system. MJ_CREATE refers to the process of loading the device driver software. So in essence, Windows is reporting that IRP_MJ_CREATE has failed for the USB device, resulting in code 43.
What Are the Common Causes of a Code 43 Error?
There are several potential reasons why Windows might fail to load the appropriate drivers and produce the code 43 message for a USB device:
Outdated, Missing or Faulty Device Drivers
One of the most common culprits is device drivers that are outdated, corrupted, or simply incompatible with the hardware. Windows relies on device drivers to provide the necessary code to interface with USB peripherals. If the drivers are outdated or corrupted, they may fail to properly initialize the hardware. Missing device drivers will also result in a failure to load.
Corrupt Registry Settings
The Windows registry contains important configuration settings and mappings that associate a particular device with the proper drivers. If these registry entries get corrupted or modified incorrectly, it can prevent device drivers from loading during plug-and-play.
Insufficient USB Power Delivery
Some USB devices have higher power requirements, especially those with motors or actuators. If your USB ports cannot deliver enough power to the device, it may fail to initialize and load its drivers correctly. This is a common issue with external hard drives connected to underpowered USB hubs.
Damaged or Unreliable USB Ports
Problems with the physical USB ports on your computer could also produce code 43 errors. This includes USB ports that are damaged, excessively worn out, or simply unreliable at consistently delivering adequate power and data transfer. Defective hardware manifests in unexpected errors like code 43.
Malfunctioning USB Device Hardware
Lastly, if there are no issues with drivers, power delivery, or USB ports, the code 43 error may imply a hardware defect or malfunction in the USB device itself. If the device is damaged or defective, it may fail to respond properly during the driver loading process.
How to Fix Code 43 Errors for USB Devices
If you encounter a code 43 error with your USB device, there are a number of troubleshooting steps you can take to try and resolve it:
Update or Reinstall Device Drivers
As the issue often relates to device drivers, the first step is to make sure you have the latest version installed. Outdated drivers are a leading cause of code 43 errors. For generic devices, Windows should automatically install default drivers. But for specialized peripherals, you may need to download the latest software from the manufacturer’s website.
You can also try uninstalling and reinstalling the device drivers rather than just updating them. This will force Windows to fully reinitialize the drivers as if installing from scratch.
Update USB Controller Drivers
In addition to device-specific drivers, you should also check for any updates to your USB controller driver software. This is the core USB driver that manages all communications with connected USB devices. Keeping this up to date can help resolve code 43 problems.
Change USB Selective Suspend Settings
Another setting that sometimes contributes to code 43 errors is USB selective suspend, which allows the computer to temporarily shut off power to unused USB ports to save energy. Disabling this can improve device compatibility and recognition in some cases.
To do this, open Power Options, click Change plan settings, Change advanced power settings, then disable the USB selective suspend option.
Unplug and Switch USB Ports
If you suspect power delivery issues, try plugging the USB device into a different port on your computer. Also, unplug all unnecessary USB devices to free up more power for the port in question. This may provide a quick fix in cases of underpowered or overloaded USB hubs.
Update BIOS/Firmware
Outdated system BIOS or firmware could also potentially contribute to USB compatibility and recognition problems. Check the support site for your computer or motherboard to see if updated BIOS/firmware is available. Flashing the BIOS can clear up low-level issues like code 43.
Clean Registry with Registry Editor
You can manually scan through the Windows registry to check for any corrupted entries associated with your USB device. Carefully delete any invalid data that may be interfering with the driver loading process. Be extremely careful when editing the registry.
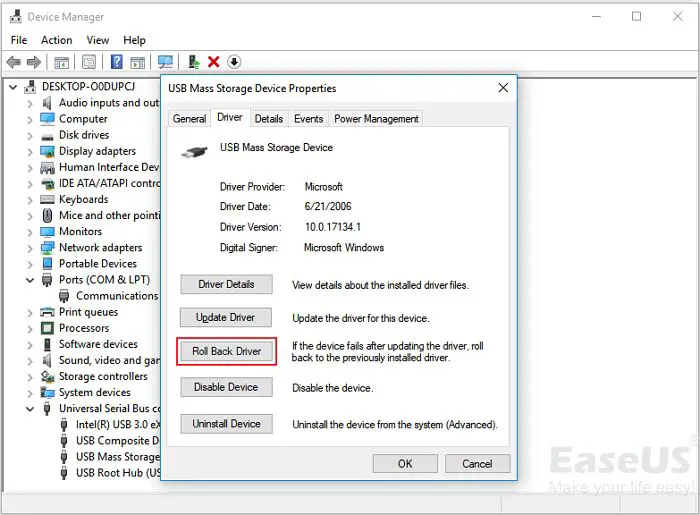
Use Device Manager to Uninstall/Reinstall
Device Manager provides an interface to completely uninstall then reinstall USB device drivers. This forces a fresh driver installation. Access Device Manager, locate the USB device, right-click and select Uninstall. Then reboot the computer and let Windows automatically reinstall fresh drivers.
Check for Physical Damage
Carefully inspect the USB device, port, hub and cables for any signs of physical damage that could cause an internal hardware malfunction. If damage is found, the device may need to be repaired or replaced. This is the likely culprit if code 43 persists after exhausting all other solutions.
Request Manufacturer Support
For proprietary or highly complex USB devices, the best recourse may be to contact the manufacturer’s technical support team. They may have specialized troubleshooting tips for code 43 errors related specifically to their device.
Advanced Solutions for Persistent Code 43 Errors
For difficult code 43 problems that resist basic troubleshooting, there are some advanced solutions to try:
Update BIOS/Firmware
While BIOS updates may seem intimidating, they can fix complex low-level USB issues that cause code 43. Check your motherboard or computer OEM website for a BIOS update utility. Back up your data first before proceeding.
Disable xHCI in BIOS
The xHCI BIOS setting governs USB 3.0 ports and hubs. Disabling xHCI reverts them to older USB 2.0 modes which are sometimes more stable. Try toggling this if USB 3 devices are getting code 43.
Change Power Supply
Some USB devices need up to 900mA power which taxes USB ports. Try a PC power supply upgrade or standalone powered hub specifically designed to provide higher power output. This boosts current to clear up code 43 problems.
Use USB Log Viewer
USBLogView is a free app from NirSoft that monitors and logs all USB device connections, disconnections and errors in Windows. Use its capture feature to hopefully isolate the code 43 and pinpoint causes.
Disable USB Legacy Support
Legacy USB support is for older devices using protocols like USB 1.1. Disabling this via BIOS, Device Manager or registry can resolve conflicts with newer USB standards that trigger code 43.
Try USB Device on Different Computer
To confirm whether the code 43 relates to your specific computer vs the USB device itself, try connecting the device to another computer. If it works fine on a different PC, the issue is with your system. But if it also fails elsewhere, the device is likely defective.
Preventing Code 43 Errors
While not always avoidable, you can take some proactive steps to help prevent code 43 USB errors:
- Install latest device drivers and USB controller drivers
- Connect devices directly to rear motherboard USB ports when possible
- Avoid low quality USB hubs, extension cables
- Use dedicated powered USB hubs for high-power devices
- Update BIOS/firmware on computer
- Disable selective suspend in power settings
- Replace worn out or damaged USB ports
Taking preventative measures will help minimize the chances of encountering this frustrating error.
Conclusion
Code 43 errors indicate Windows was unable to properly load the device driver software for a connected USB device. This prevents proper function and communication. The problem typically originates from outdated/missing drivers, power delivery issues, hardware defects or USB port damage.
Updating drivers, switching ports, cleaning registry, uninstalling/reinstalling drivers and inspecting hardware are good first steps to resolve code 43. For persistent issues, more advanced fixes involve USB troubleshooting utilities, BIOS updates, xHCI toggling and USB legacy disabling. While sometimes tricky, code 43 problems can usually be cleared with sufficient USB debugging and troubleshooting. Being proactive with proper driver management and quality USB hardware also helps avoid the error.