Endpoint detection and response (EDR) refers to a cybersecurity technology that helps detect, investigate, and respond to advanced threats and targeted attacks on endpoints and network devices. EDR provides continuous monitoring and deep visibility into endpoint activity and events in real-time. It enables security teams to identify malicious behavior, unauthorized changes, threat indicators, and anomalies on endpoints. EDR solutions work by deploying lightweight software sensors on endpoints and servers across an organization’s environment. These sensors collect detailed system data, event information, network connections, memory activity, registry changes, and other system level activities. The data is continuously streamed to a central console for analysis, detection, investigation, and response.
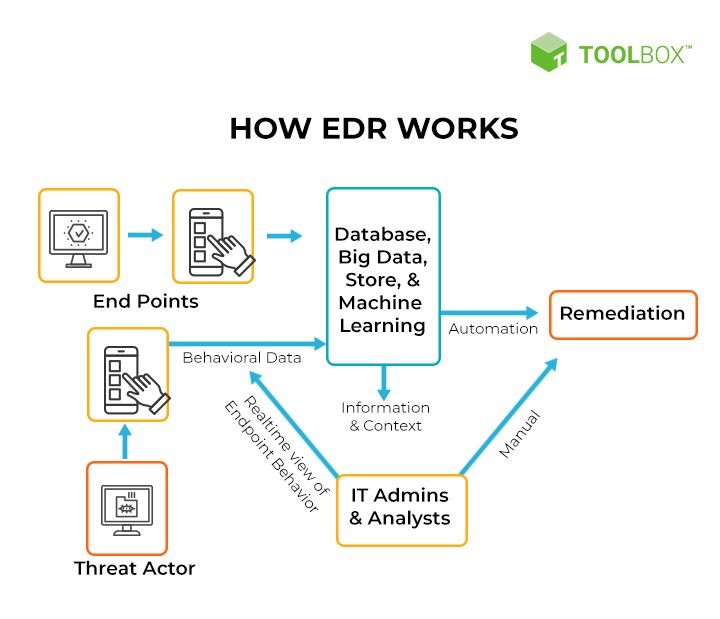
How does EDR work?
EDR solutions typically work in four key stages:
- Data collection: EDR agents or sensors are installed on endpoints and servers to monitor system level activities. They collect detailed telemetry data on processes, network connections, registry changes, memory use, user behavior, and more.
- Advanced detection: The telemetry data is aggregated and analyzed using threat intelligence, behavioral analytics, machine learning algorithms, and other advanced techniques to detect Indicators of Compromise (IOCs), anomalous behavior, and threat patterns.
- Investigation and hunting: Security teams leverage the data collected by EDR to perform investigations. This helps hunt for suspicious activities, understand the scope of attacks, identify compromised systems, and retrace steps taken by attackers across endpoints.
- Response: EDR enables organizations to isolate infected endpoints, kill malicious processes, remove Persistence, delete files, and take other response actions directly from the EDR console. Automated response capabilities are also offered.
By providing continuous visibility and applying advanced analytics, EDR gives organizations the ability to quickly detect, investigate, contain, and respond to advanced threats that may evade traditional security defenses.
What are the key capabilities of EDR solutions?
Here are some of the major capabilities provided by EDR solutions:
- Real-time endpoint visibility: Continuous monitoring of detailed system-level events and activities across endpoints provides complete visibility into what is happening.
- Advanced threat detection: Behavioral analytics, machine learning, and other techniques enable EDR to flag malicious activities, anomalous events, and IOCs associated with advanced threats.
- Attack investigation: Security teams can leverage the collected endpoint data to perform robust attack investigation and uncover the root cause, scope, and impact of security incidents.
- Threat hunting: Proactively hunt across endpoints for signs of compromise, suspicious behavior, or attacker movement to identify ongoing attacks.
- Automated response: EDR allows organizations to contain infected endpoints and automatically neutralize threats with tasks like terminating processes, quarantining files, or isolating systems.
- Forensics data: Detailed historical data enables drilling down on suspicious events to enable forensic investigation and reconstruction of attack activities.
What are the key benefits of EDR solutions?
Here are some of the major benefits provided by EDR solutions for security teams:
- Gain real-time visibility into endpoint activity to rapidly detect security incidents and data breaches.
- Quickly respond to detected threats and prevent damage or data loss.
- Uncover advanced, stealthy attacks that may hide from traditional security tools.
- Streamline threat investigation and hunting workflows to find signs of compromise.
- Reconstruct the timeline of a security breach or attack after detection.
- Proactively hunt for suspicious activities and attacker behavior across endpoints.
- Isolate infected endpoints to prevent threats from spreading across the environment.
- Leverage threat intelligence to identify Indicators of Compromise associated with advanced threats.
- Simplify security operations and enable understaffed teams to handle incidents efficiently.
What types of threats can EDR detect?
Here are some examples of advanced threats and attack techniques that EDR solutions can potentially detect by analyzing endpoint telemetry data:
- Malware and ransomware: Detect known malware signatures and Identify anomalous behavior associated with malware or ransomware activities.
- Fileless attacks: Spot malicious PowerShell scripts, registry changes, WMI activity, and other IOCs of fileless or malware-free attacks.
- Lateral movement: Uncover reconnaissance activities, use of attack tools like Mimikatz, and other lateral movement techniques.
- Command and control: Recognize outbound connections, data exfiltration, and other C2 communications associated with compromised endpoints.
- Suspicious user behavior: Detect abnormal login locations, unusual file access or downloads, suspicious process executions, and more.
- Insider threats: Identify unauthorized or abnormal access to sensitive data and resources by privileged insiders.
- Evasive attacks: Spot use of attack frameworks like Metasploit, Cobalt Strike, and Powershell Empire that are designed to evade defenses.
What are the key components of EDR solutions?
EDR solutions are made up of a few core components working together to provide prevention, detection, investigation, and response capabilities:
- Lightweight endpoint agents: Collect rich data on system activities across endpoints and transmit to EDR server.
- Management console: Centralized dashboard for monitoring, analysis, reporting, administration, and configuration.
- Detection engine: Apply behavioral analytics, machine learning models, heuristics, and intelligence to detect IOCs and threats.
- Threat intelligence: Leverage continuously updated threat feeds and adversary databases to identify new attack patterns.
- Investigation tools: Query interfaces, data exploration tools, and visualization capabilities to enable hunting.
- Response actions: Isolate endpoints, kill processes, quarantine files, roll back changes, and automate other response tasks.
- Forensics and reporting: Retrospective analysis of historical endpoint data to uncover root cause of attacks.
What are some key use cases for EDR?
Here are some of the most common use cases and benefits provided by EDR solutions for security teams:
- Detect ransomware attacks: Spot unusual file encryption activities, file deletion, ransom notes, and other IOCs to catch ransomware.
- Block malware infections: Halt execution of malicious files or processes to prevent malware from infecting endpoints.
- Identify compromised endpoints: Rapidly determine scope of breach by finding other infected or compromised systems.
- Accelerate incident response: Contain attacks faster with capabilities like isolating endpoints and killing processes.
- Streamline threat hunting: Proactively hunt across endpoints to identify hard-to-detect intrusions and attacks.
- Spot insider threats: Detect unauthorized data access, privilege abuse and other risky insider activities.
- Meet compliance mandates: Use endpoint visibility and audit logs to demonstrate compliance with regulations.
What are some key factors to consider when evaluating EDR solutions?
Organizations should consider these important criteria and requirements when evaluating and selecting an EDR solution:
- Detection accuracy: Ability to detect advanced threats and minimize false positives using behavioral analytics.
- Endpoint visibility: Level of telemetry data and endpoint context provided for investigations.
- Threat intelligence: Integration of IOC feeds and adversary databases to detect known threats.
- Incident response: Workflow integration and automation capabilities to streamline response.
- Cloud capabilities: Support for protecting on-prem, cloud, and hybrid environments.
- UI and usability: Intuitive dashboards, visualization tools, hunting interfaces, and workflows.
- Performance impact: Minimal endpoint resource utilization and battery drain.
- Total cost of ownership: Pricing model aligns with business requirements and budget.
Evaluating detection accuracy, level of visibility, ease of use, cloud readiness, and cost structure allows organizations to determine which EDR solution best meets their requirements.
What are examples of leading EDR solutions?
Some of the top EDR solutions offered by leading cybersecurity vendors include:
- CrowdStrike Falcon
- SentinelOne Singularity
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
- Cisco Secure Endpoint
- VMware Carbon Black
- Cybereason Enterprise
- BlackBerry Optics
- Palo Alto Networks Cortex XDR
- Sophos Intercept X with EDR
- Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response
These solutions offer capabilities like behavioral-based threat detection, visibility into endpoint activity, threat intelligence integration, automated investigation and response, and advanced attack containment.
What are the differences between EDR and antivirus software?
There are a few key differences between traditional antivirus (AV) software and modern EDR solutions:
| Antivirus (AV) Software | Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR) |
|---|---|
| Relies on malware signatures and regex patterns to detect known bad files and apps. | Uses advanced behavioral analytics, machine learning, and heuristics to detect malicious activities and anomalies. |
| Limited visibility into endpoint activities beyond scanning files and processes. | Continuously monitors events, changes, and activities at the endpoint level. |
| Alerts on detection of malware based on signatures. | Alerts on suspicious events and threat indicators based on advanced correlation rules. |
| Provides limited forensic data for post-breach analysis. | Collects extensive system-level forensics for hunting and incident investigation. |
| Mainly focused on preventing infections rather than detecting advanced threats. | Aims to rapidly detect, investigate, and respond to sophisticated attacks. |
While AV deals with known bad samples, EDR provides the visibility and analytics to uncover new and advanced attack techniques based on behavior.
How does EDR complement other security tools like SIEM and NGFW?
EDR works synergistically with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) and Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW) solutions to provide broader protection:
- SIEM: EDR provides continuous endpoint data to feed into the SIEM for correlation, alerts, and reporting. The SIEM analyzes network and other security data.
- NGFW: The firewall monitors north-south network traffic between zones. EDR focuses on endpoint events and lateral east-west attacker movement.
Together, EDR, SIEM, and NGFW give broader and more comprehensive visibility across an organization’s environment.
Conclusion
Endpoint detection and response has become a critical capability for securing modern digital environments against sophisticated cyber threats. EDR provides 24/7 visibility into endpoint activities, uses advanced analytics to detect attacks, enables threat hunting across the environment, and facilitates rapid incident response.
By deploying EDR, organizations can spot intrusions early, understand the full scope of a breach, quickly contain attacks, and collect forensic evidence to understand what happened. EDR strengthens enterprise defenses against ransomware, malware, phishing, lateral movement, and many evasive threat vectors.
With capabilities for continuously monitoring endpoint behavior, applying data science for threat detection, speeding up attack investigation, and automating response, EDR solutions provide tremendous value for enhancing the security posture of modern enterprises.