Endpoint threat detection refers to security solutions that monitor computing endpoints like desktops, laptops, and mobile devices to identify and respond to cyber threats. As endpoints have become a key target for hackers, endpoint threat detection has become an important layer of security for organizations.
What are the key features of endpoint threat detection solutions?
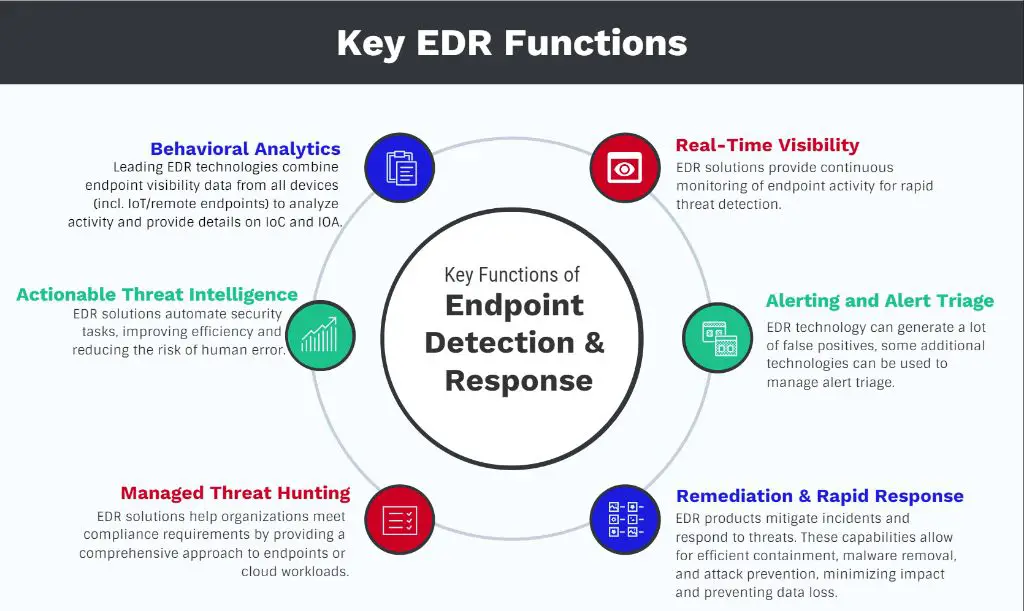
Endpoint threat detection solutions have several key capabilities:
- Monitoring endpoint activity – Solutions continuously monitor endpoints for suspicious events like uncommon processes, registry changes, or network connections that could indicate malware or hacking activity.
- Blocking malicious code – Signatures, heuristics, machine learning, and other techniques are used to identify and block known and zero-day malware.
- Investigating alerts – When a suspicious event occurs, endpoint threat detection tools will flag it for further investigation and provide data like process trees to help understand the scope of an incident.
- Responding to threats – Solutions can quarantine or isolate compromised endpoints, kill malicious processes, or take other actions to remediate threats.
- Reporting – Detailed logs and reports provide visibility into endpoint activity and threats detected across the environment.
How does endpoint threat detection work?
Endpoint threat detection solutions use a few core techniques:
File monitoring – The solution will monitor key areas on endpoints like memory, file systems, and registries for changes that match known indicators of compromise. This allows it to detect threats like ransomware that modify, encrypt, or delete files.
Behavior analysis – By establishing baselines for normal endpoint behavior, the solution can detect out-of-the-ordinary events that could signify an attack. For example, a process launching child processes to spread across a system could be recognized as anomalous behavior.
Machine learning and AI – Advanced techniques like machine learning examine endpoint activity patterns to derive new insights that enable the system to detect never-before-seen threats without relying purely on signatures.
Deception technology – Some solutions plant deceptive items like fake credentials on endpoints. Attempts by malware to access these items reveal its presence.
Threat intelligence – Regular updates on new and emerging threats help endpoint detection stay current on the latest hacking techniques and IOCs.
What are the benefits of endpoint threat detection solutions?
Key benefits that endpoint threat detection solutions offer include:
- Faster threat detection – By monitoring endpoints directly, these solutions can spot in-progress cyber attacks and accelerate incident response.
- Protection for distributed environments – Endpoint security provides protection for devices located outside the corporate network like remote workers and roaming devices.
- Defense against advanced threats – Techniques like machine learning allow endpoint security to detect sophisticated, zero-day malware and hacking techniques designed to evade traditional signature-based defenses.
- Streamlined security operations – By centralizing endpoint monitoring, investigation, and response, security teams can operate more efficiently and with reduced manual effort.
- Threat hunting capabilities – The ability to proactively search across endpoint data enables security analysts to hunt for indicators of compromise and understand the full scope of threats.
What types of threats can endpoint detection solutions detect?
Endpoint threat detection solutions are designed to detect a wide range of cyber threats, including:
- Malware – Malicious software like Trojan horses, spyware, worms, and viruses can be identified by characteristic behavior patterns, suspicious file changes, connections to command and control servers, application hooks, and other indicators.
- Fileless attacks – Malware that operates strictly in memory without installing any files can still be detected via anomalous memory usage, Windows registry modifications, suspicious PowerShell commands, WMI activity, and similar behavior.
- Ransomware – Rapid file encryption, overwriting of the master boot record, changes to file extensions, and communications with command and control servers provide signals to detect ransomware.
- Advanced persistent threats (APTs) – Stealthy, targeted attacks by sophisticated threat actors can be recognized based on subtle suspicious activity across multiple endpoints.
- Lateral movement – Hackers expanding access through a network by pivoting from one compromised machine to another can be detected when they access deceptive credentials planted across endpoints.
- Data exfiltration – Abnormal flows of data off endpoints to external systems can indicate cybercriminals stealing sensitive information.
How do endpoint threat detection solutions fit into the broader security stack?
Endpoint threat detection solutions are a key component of a comprehensive enterprise security program. They complement and interoperate with other security controls:
- Perimeter security (firewalls) – Firewalls filter unauthorized inbound network traffic but cannot see lateral attacker movement once inside the network. Endpoint threat detection provides visibility and defense inside the perimeter.
- Network security – Solutions like network traffic analysis (NTA) examine network activity for anomalies but lack the endpoint context and visibility that endpoint detection can provide when investigating threats.
- Endpoint protection platform (EPP) – Anti-malware/antivirus software blocks known threats. EDR provides additional analysis of suspicious events and automated response capabilities.
- SIEM solutions – Endpoint detection feeds high-fidelity endpoint data like process trees into the SIEM for better monitoring, threat hunting, and correlation across the IT environment.
- Deception technology – The placement of deceptive credentials and assets on endpoints sets traps and improves detection for lateral movement.
What are the key criteria for evaluating endpoint threat detection solutions?
When researching and comparing endpoint detection and response (EDR) products, key evaluation criteria include:
- Detection accuracy – Minimizing false positives and false negatives ensures the solution only triggers alerts for real threats.
- Visibility and profiling – Detailed endpoint process trees, registry activity, file changes, and network connections provide comprehensive visibility and speed threat hunting.
- Incident response – Built-in capabilities like isolating devices, terminating processes, and rolling back changes can accelerate incident response.
- Threat intelligence – Quality threat feeds tailored to the solution provide quick updates on the latest attack techniques and IOCs.
- Cloud infrastructure – Solutions leveraging the cloud for analytics, malware sand-boxing, and collective learning offer better detection of advanced threats.
- Automated response – The ability to automatically implement playbooks and remediation processes reduces the burden on security teams.
Usability, interoperability, impact on endpoint performance, management interface, and total cost of ownership are other key factors to weigh when comparing endpoint detection solutions. Organizations should match solutions against their specific environment, skill sets, and use cases.
What are some leading endpoint threat detection solutions?
Some of the top vendors providing endpoint threat detection and response platforms include:
- CrowdStrike Falcon – Uses indicators of attack, machine learning, and behavioral analysis to prevent ransomware, exploits, command and control communications, credential theft, and lateral movement across endpoints.
- SentinelOne – Behavioral AI examines processes across endpoints in real time to detect and automatically remediate threats like malware and ransomware.
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint – An EDR solution from Microsoft that integrates with the Windows operating system and Microsoft 365 stack to monitor endpoints for IOCs and security configuration issues.
- Cisco Secure Endpoint – Combines anti-malware, firewall, and detection engines supplemented by Talos threat intelligence to detect and block advanced threats on endpoints.
- Cybereason Defense Platform – Behavior-based detection identifies malicious operations being executed across multiple endpoints to uncover sophisticated attacks.
Gartner, Forrester, and other third-party analyst firms publish detailed competitive evaluations of leading endpoint detection and response solutions that organizations can leverage to determine which platform best fits their requirements.
How do you deploy endpoint threat detection?
Key steps for deploying an endpoint threat detection solution include:
- Survey the endpoint environment – Catalog endpoint types, operating systems, geographic locations, and compliance requirements that could impact deployment.
- Evaluate solutions – Test leading solutions in a sandbox environment representing different endpoint types to assess detection accuracy, performance impact, and management overhead.
- Design policies and rules – Configure policies, rules, allow lists, restricted lists, and other parameters to tune detection and minimize false positives based on normal behavior.
- Install agents – Deploy small-footprint software agents to endpoints to monitor activity and communicate with the vendor cloud or on-premises console.
- Integrate and enable features – Connect the endpoint detection system with other security tools like the SIEM via APIs. Enable relevant response capabilities.
- Baseline activity – Allow the system to learn patterns of normal behavior and fine-tune detection rules during an initial learning period.
- Investigate alerts and tune – As the system generates alerts, investigate to identify false positives and further optimize policies and rules.
IT and security teams should ensure proper endpoint detection coverage for the highest risk systems and gradually expand across lower risk endpoints. Ongoing monitoring, response processes, and tuning will optimize alerting and allow the solution to take more automated actions over time.
What are the limitations of endpoint threat detection?
Some potential limitations to consider include:
- Encryption can limit visibility – Widespread use of full disk or file encryption on endpoints could impact the ability of solutions to inspect activity and detect threats.
- Compatibility issues – Solutions may have limited visibility or lack behavioral understanding on endpoints running niche operating systems or proprietary software.
- Detection gaps – Skilled attackers may still find ways to evade detection or exploit blind spots in rules and analytics.
- Resource intensive – Heavy endpoint monitoring could strain resources on underpowered endpoints and interfere with performance.
- False positives – Misconfigured rules and poor analytics can lead to numerous erroneous alerts wasting security team time.
- Limited response capabilities – EDR tools have limited built-in response options compared to having skilled incident handlers perform guided investigation and containment.
To address these potential limitations, organizations should adopt solutions designed for their specific environment, continuously tune detection, pursue ongoing endpoint security hardening, and ensure skilled resources are available to investigate alerts.
Conclusion
Endpoint threat detection solutions provide 24/7 security monitoring, advanced threat analytics, and rapid incident response directly on the endpoints targeted by attackers. By leveraging capabilities like behavioral analysis, deception technology, and machine learning, EDR enables protection against sophisticated and stealthy threats that might evade traditional perimeter defenses. Organizations should evaluate solutions based on detection accuracy, visibility, automated response, and other criteria that maps to their cyber risk profile and security team expertise. By implementing robust endpoint threat detection and response across an environment, security teams can reduce time to detection, accelerate incident response, and shrink the attack surface targeted by hackers.