SD cards have become an essential storage medium for mobile devices and cameras. But what does the acronym “SD” actually stand for? This article will examine the origins of the technology and explain the meaning behind the letters “SD”.
The goal is to provide a comprehensive overview of SD cards, from their initial development to their current capabilities. We’ll look at the history and evolution of SD cards, explain key terminology related to speeds and storage capacities, and summarize some of their most common use cases today. Whether you’re simply curious what “SD” means or want to better understand this ubiquitous storage format, this guide will unpack the story behind secure digital cards.
SD Stands for Secure Digital
SD stands for Secure Digital, referring to the secure digital storage provided by these cards. When SD cards were first introduced in 1999 by SanDisk, Panasonic, and Toshiba, the SD acronym was chosen to highlight the secure and digital nature of this new flash memory card format [1].
At the time, SD cards offered more security features compared to earlier storage formats like CompactFlash. The SD specification includes cryptographic security protocols to protect copyrighted data. This made SD cards well-suited for securely storing and distributing copyright-protected material like music, movies, and games [2].
The “digital” portion of the name refers to SD cards using digital storage rather than analog storage like magnetic tape. As a flash memory card without any moving parts, the SD format provided digital storage designed for the new mobility and portability needs of digital cameras, mobile phones, and other consumer electronics [3].
In summary, the “Secure Digital” name represents the digital security advantages these flash memory cards offered when first introduced to the market in the late 1990s and how they enabled secure mobility of digital content.
[1] https://www.quora.com/What-does-SD-in-SD-card-mean
[2] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wpFGhpEQozY
[3] https://mytechhubgh.com/tech-out-loud-what-is-the-meaning-of-sd-card/
Origins in 1999
In 1999, SanDisk, Panasonic (Matsushita), and Toshiba jointly developed and agreed to market the Secure Digital (SD) memory card. The SD card was derived from the earlier MultiMediaCard (MMC) format, but with improved capacity and performance. It was designed to provide a compact, affordable, and portable method for storing digital content on devices like camcorders, digital cameras, handheld computers, and audio players.
The first SD cards held up to 2 GB of data and offered transfer speeds suitable for recording video like the MiniDV format common at the time. The group of SanDisk, Panasonic, and Toshiba would continue to collaborate and release updated versions of SD cards over the next two decades to achieve faster speeds, higher storage capacities, and better durability. SD cards remain a widely used format today across consumer electronics and computing devices.
Designed for Mobility
SD cards were specifically designed with mobility and portability in mind. As digital cameras, mobile phones, and other portable electronics started gaining popularity in the late 1990s and early 2000s, the need emerged for a small removable storage medium that could meet the demands of these on-the-go devices.
CompactFlash cards were one of the dominant removable storage formats at the time, but they were larger in physical size and didn’t have the best reliability for mobile use. SD cards were created as a replacement that overcame these limitations. Companies like Panasonic, SanDisk, and Toshiba worked together to develop the SD standard with a focus on miniaturization, durability, and seamless user experience across different devices.
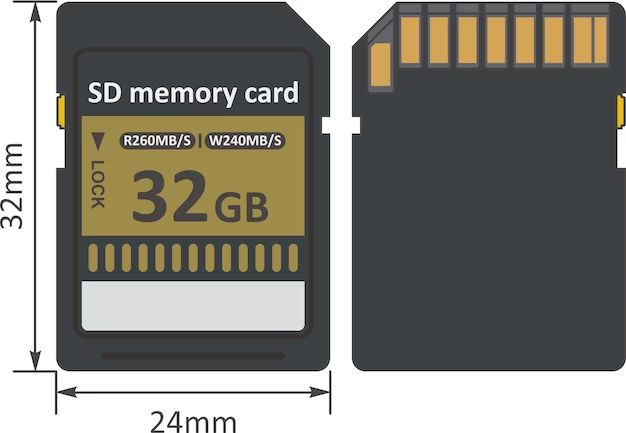
The small physical size of SD cards, reaching just 32 x 24 x 2.1 mm for the standard version, made them perfect for integrating into portable electronics where compactness was key. Their solid state construction with no moving parts also made them more shock and vibration resistant compared to hard disk solutions. All of these design factors enabled SD cards to provide removable storage optimized for mobility and portability.
Digital Security Features
SD cards have built-in security features to allow for secure storage of data through encryption. One of the main security methods used is the SD Security specification, which was introduced in SD cards in 2001. The SD Security specification uses a cryptographic processor built into the SD card to encrypt contents stored on the card. This allows sensitive data like financial information, medical records, or proprietary software to be stored securely.
The cryptographic processor uses a minimum 128-bit key to encrypt data on the SD card. This key is created randomly each time the encryption is initialized on the SD card. The encrypted data cannot be accessed without the correct key to decrypt it. In addition to encryption, the SD Security system also utilizes access control with passwords, allowing users to restrict access to certain data on the card.
Another common encryption method used is CPRM, or Content Protection for Recordable Media. This is a type of DRM (digital rights management) encryption that is applied to certain media files like audio tracks or videos. It allows content creators to apply usage rules and restrict unauthorized copying. The encryption binds the content to the SD card it is placed on, preventing copying.
Overall, the encryption capabilities of SD cards allow for secure portable storage and transfer of sensitive data. Properly encrypted SD cards are very difficult for unauthorized parties to hack into or decrypt without the password or keys. This makes them well-suited for safely storing and transporting important information.
Speed Class Ratings
SD cards are given speed class ratings that indicate their minimum guaranteed speeds. The speed class is represented by a number between 2 and 10. A higher number means a faster card.
SD Speed Class 2 cards have a minimum write speed of 2 MB/s. Class 2 cards are sufficient for standard definition video recording but too slow for HD video.
Class 4 cards have a minimum speed of 4 MB/s. They support 720p HD video recording but may be too slow for 1080p Full HD video.
Class 6 cards have a minimum speed of 6 MB/s and support 1080p HD video recording. Class 10 cards are even faster with a 10 MB/s minimum and support 4K video recording. SD Cards Explained – SDHC vs SDXC and Speed Ratings
The newest speed class for SD cards is Video Speed Class for 4K and 8K video recording. V6 can handle 4K video while V90 is optimized for 8K.
Faster write speeds allow you to take photos rapidly in burst mode without any buffer lag. Higher speeds also help when transferring files to and from the memory card.
Storage Capacities
SD cards are available in a wide range of storage capacities, from just a few megabytes up to multiple terabytes for high capacity versions. The storage capacity determines how much data you can save on the card.
The original SD card standard supported capacities up to 2GB. The SDHC (Secure Digital High Capacity) standard increased that to 32GB. Then SDXC (Secure Digital eXtended Capacity) expanded capacities even further, supporting up to 2TB.
Now there are also SDUC (Secure Digital Ultra Capacity) cards that can store a massive 2TB to 128TB. However, these ultra high capacity cards are expensive and require compatible devices.
For most consumer uses, SD cards in the 16GB to 512GB range offer ample storage. A 16GB card can hold around 4,000 photos or a few hours of HD video. A 512GB card provides capacity for over 100,000 photos and days of video.
When choosing an SD card, it’s important to consider the storage capacity you need for your particular use case, along with speed rating and other factors.
Sources:
https://www.autopia.org/forums/hot-tub/102738-sd-card-storage-capacities.html
https://storables.com/data-storage/sd-cards/how-important-are-sd-cards/
Durability
SD cards are designed to be quite durable and withstand a variety of environmental factors. According to this StackExchange discussion, SD cards generally have a longer life expectancy compared to earlier card formats like MMC. The SD Card Association has standardized durability tests that cards must pass, including tolerance for extreme temperatures, humidity, mechanical shock, and more.
That said, SD cards can still wear out eventually with prolonged use. As explained in this Raspberry Pi SD card guide, factors like high temperatures and humidity can still degrade SD cards over time. And constantly writing and rewriting data to the card will also contribute to eventual failure. But overall, SD cards are designed to withstand typical usage in cameras, phones, and other mobile devices.
Use Cases
SD cards are widely used in portable consumer electronic devices that require removable data storage. Some of the most common use cases include:
Photography and Videography: SD cards are widely used in digital cameras and camcorders to store photos and videos. The cards allow capturing high resolution images and HD video which require significant storage capacity. Photographers and videographers rely on SD cards for portable storage while working in the field. Source
Mobile Phones: Many smartphones have SD card slots to augment internal storage. Users can store music, videos, photos, apps and other data. The cards provide a convenient way to expand storage as needed. Some phones even allow apps and OS files to be stored on the SD card. Source
Gaming Devices: Handheld gaming devices like Nintendo Switch use SD cards to store downloaded games, save game progress and store media files. The cards enabletransporting games and data to other devices. Some digital cameras also have basic gaming capabilities via SD cards. Source
Computers: SD card slots are common on laptops and desktop computers. The cards provide removable storage for media files, documents, backups and more. SD cards offer a way to easily transfer files between devices. Adapters allow using the cards with devices that only have USB ports. Source
Conclusion
To summarize, SD stands for Secure Digital, which refers to the digital security features and performance capabilities built into these storage cards. When the SD format was introduced in 1999, it offered a major step up from previous storage cards in terms of mobility, speed, capacity, and durability. The cryptographic security protections make SD cards resistant to hacking or data theft. Speed class ratings allow users to choose an SD card optimized for their use case, whether 4K video recording or fast action photography. With storage capacities now reaching 1TB in a chip the size of a fingernail, SD cards provide a compact yet powerful data storage solution for consumer electronics and mobile devices. After over 20 years on the market, SD cards continue to deliver digital security and solid performance that makes the “SD” abbreviation an enduring fit.