The APFS (Apple File System) format is the default file system for solid-state drives and flash storage in Mac computers running macOS High Sierra or later. APFS replaced the older HFS+ (Hierarchical File System Plus) format, offering improvements in scalability, encryption, and space efficiency.
Quick Overview of APFS
Some key things to know about APFS:
- Released in 2017 with macOS High Sierra.
- Replaced the older HFS+ file system on Macs.
- Optimized for solid-state drives and flash storage.
- Offers strong encryption, space efficiency, snapshots, and cloning.
- Only compatible with macOS High Sierra and later.
- Cannot be read by Windows or other operating systems.
Key Features and Benefits of APFS
APFS introduces several major new features and improvements over the previous HFS+ file system:
Space Efficiency
APFS utilizes free space much more efficiently than HFS+, allowing storage to be used in a more optimized way. It uses space sharing and cloning to save storage space.
Snapshots
APFS supports snapshots, which are read-only instances of the file system frozen at a point in time. Snapshots allow for backups and versions without duplicating files.
Rapid Cloning and Copying
APFS makes copying and duplicating data nearly instantaneous with shared extents and clones. This makes duplicating large files or even whole drives much faster.
Strong Encryption
FileVault encryption is deeply integrated into APFS, providing safe and secure full disk encryption. Data is encrypted using advanced AES-XTS or AES-CBC algorithms.
Crash Protection
The file system has added checksums to better detect and prevent data corruption. Metadata is also duplicated to aid in recovering from power outages or crashes.
Scalability
APFS scales well with larger storage capacities. It supports drives up to 9 quintillion bytes in size, far exceeding the limits of HFS+.
When is APFS Used on Macs?
Here is an overview of when APFS is used as the file system on Macs:
- The default file system for all SSDs and flash storage running macOS High Sierra or later.
- Used automatically when formatting SSDs or flash storage with Disk Utility.
- Optional for hard disk drives (HDDs), but may offer some benefits.
- Used for iPhones, iPads, Apple Watches, and Apple TVs running the latest OS versions.
- Not used on Macs still running pre-High Sierra versions of macOS.
Essentially, Apple switched to using APFS for all internal solid-state Mac storage with High Sierra in 2017. HDD Macs can still use HFS+, but APFS is recommended for improved features. Older macOS versions do not support APFS.
Converting an Existing HFS+ Drive to APFS
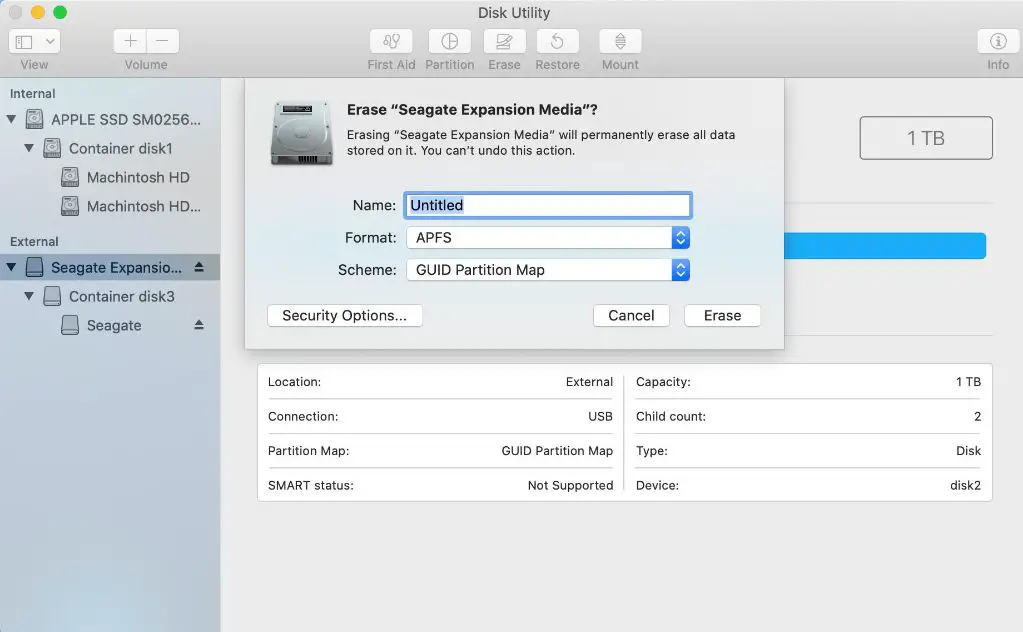
It is possible to convert an existing HFS+ formatted drive to APFS without losing data using Disk Utility. Here is how to convert an HFS+ drive to APFS:
- Backup the HFS+ drive before converting, just to be safe.
- Open Disk Utility on the Mac.
- Select the HFS+ volume you want to convert.
- Click “Erase” in Disk Utility.
- Choose “APFS” as the format and specify a name.
- Allow the conversion process to complete, which may take some time.
- The drive will now be formatted as APFS and retain all data.
Converting is a seamless process and causes no data loss. But backups are still a good idea just in case. Once converted, the drive will no longer be mountable on operating systems that do not support APFS.
Creating New APFS Drives and Volumes
It is straightforward to create new APFS formatted drives and volumes using Disk Utility on Macs running High Sierra or later. Here is how to create a new APFS drive or container:
- Open Disk Utility on your Mac.
- Select the internal drive or external drive you want to format.
- Click “Erase” in the toolbar.
- Choose “APFS” as the format.
- Give the drive a name and complete the process.
Once formatted as APFS, you can also easily add new partitions and volumes to the drive. Just select the APFS container, click “+” to add a new volume, give it a name, and set the desired capacity. The process takes just moments, and you can create as many APFS volumes as needed.
Compatibility with macOS Versions
It’s important to note APFS compatibility depends on your Mac’s macOS version:
| macOS Version | APFS Compatible? |
|---|---|
| macOS High Sierra 10.13 | Yes |
| macOS Sierra 10.12 | No |
| OS X El Capitan 10.11 | No |
| OS X Yosemite 10.10 | No |
| OS X Mavericks 10.9 | No |
Only Macs running macOS High Sierra 10.13 from 2017 or later can access and boot from APFS drives. Older versions of macOS do not support APFS at all. So you must upgrade to High Sierra or newer to use APFS.
Compatibility with Other Operating Systems
APFS drives can only be read by macOS High Sierra and later. No other operating systems support accessing or booting from APFS at this time:
- Windows – No support for APFS. Cannot access drives.
- Linux – No support currently. Work is underway.
- Older Mac OS – HFS+ only. No APFS support.
- iOS/iPadOS – APFS is used, but cannot access Mac APFS drives.
For cross-platform compatibility, HFS+ is still the best choice. But on Macs, APFS offers significant advantages and is the default since High Sierra.
APFS Limitations and Downsides
While APFS has many benefits over HFS+, it also comes with some limitations to be aware of:
- No support on non-Apple operating systems like Windows and Linux.
- Cannot be accessed on older macOS versions pre-High Sierra.
- Lacks some admin features like disk repair tools compared to HFS+.
- No RAID support currently for multi-disk APFS configurations.
- Potential compatibility issues with some third party utilities or bootable disks.
For these reasons, some Mac users may still opt to stick with HFS+ on HDDs for maximum compatibility. But for SSDs and flash storage, APFS is ideal.
What Data is Stored on APFS Drives?
APFS manages the underlying storage on a drive, storing all file data, metadata, directories, and more. Here are some examples of data stored on an APFS formatted drive:
- All user documents, photos, videos, music, and downloads.
- Installed applications and program files.
- The operating system itself (for internal SSDs).
- Configuration files and settings for apps and services.
- System logs, caches, and databases used by macOS.
- File attributes like permissions, creation dates, and ownership.
Essentially, APFS manages everything on the drive it is formatting. This includes both user data and all system files needed to run macOS on an SSD or bootable storage device.
How APFS Improves Space Efficiency
APFS makes much better use of available storage space compared to HFS+ in several ways:
Space Sharing
With APFS, free space is shared and tracked between volumes on the same physical drive. HFS+ partitions have fixed allocations, leading to stranded space.
Snapshots
File snapshots use space efficiently, storing only changed blocks vs full copies. Snapshots don’t duplicate unchanged data.
Clones
APFS clones use shared extents to instantly duplicate files, directories, or volumes without using more space for the copies.
Compression
Transparent compression built into APFS helps reduce the space used by files. This compression happens invisibly at the file system level.
Deduplication
Identical blocks of data are only stored once, then referenced between files. This deduplication further optimizes space usage on APFS.
Together, these APFS capabilities allow for much more efficient use of drive space compared to the older HFS+ file system on Macs.
How APFS Handles Encryption
APFS supports new advanced encryption technologies to keep data secure:
AES-XTS
APFS uses AES-XTS symmetric encryption, which is optimized for storage devices. It utilizes 128-bit or 256-bit encryption keys for robust protection.
Per-File Encryption
In APFS, individual files are encrypted with their own keys. Previous systems encrypted whole volumes with one key.
Improved Encrypted Performance
APFS caches keys in RAM, allowing the fastest encrypted performance for smartphones and Macs with fast storage.
Secure Key Management
Encryption keys are tightly managed by a hierarchal key system. The highest level keys are stored in Effaceable Storage.
Seamless Integration with FileVault
APFS works hand-in-hand with FileVault for easy full-disk encryption on Macs.
Together, these advances make APFS encryption more robust, granular, and efficient compared to previous HFS+ implementations.
How APFS Supports Snapshots
APFS supports lightweight snapshots, which work as follows:
- Snapshots are read-only instances of the file system frozen in time.
- They do not make full copies of files, only changed blocks.
- Snapshots persist alongside main file system, using minimal space.
- Many snapshots can be kept, forming a version history.
- Users can browse previous snapshots to restore old states.
Snapshots are a powerful feature of APFS for creating backups and versions to revert to at any time. They save storage space while allowing prior states to be easily accessed.
How APFS Enables Fast Cloning
APFS supports nearly instant file and volume cloning. Clones work as follows:
- Clones duplicate files, folders or volumes almost instantly.
- They reference the same data blocks as source until changed.
- Metadata is replicated, but data blocks are shared between clone and source.
- Modifications in clone or source diverge to separate data going forward.
- Great for fast copying large files, folders or whole drives.
Clones enable incredibly fast duplication by only copying references to existing data. This makes backing up disks or duplicating large amounts of data far faster than before.
How APFS Checks and Repairs File System Errors
APFS includes several features to detect and repair errors in the file system:
- Metadata is checksummed to detect corruption.
- Critical metadata is replicated across the volume.
- Journaling logs all operations so they can be replayed if needed after a crash.
- Snapshots allow rolling back to prior good state if corruption is detected.
- fsck_apfs tool can scan and repair certain APFS filesystem problems.
While not as full-featured as repair tools for HFS+, APFS provides underlying data protection and options to recover from disk errors.
How APFS Improves Performance
APFS improves performance in several key ways:
- Efficient snapshotting reduces file copy times.
- Fast clones copy and duplicate data nearly instantly.
- Shared free space avoids lengthy allocations and indirections.
- Space efficiency reduces the disk areas needed to be accessed.
- Cached metadata in RAM allows fast directory lookups and access.
Together these APFS capabilities can provide noticeable performance benefits for real-world operations like booting, file copying, duplicating, backups, and more.
Conclusion
The new APFS file system offers major improvements over the older HFS+ in terms of space efficiency, performance, snapshots, cloning, and encryption. It is the ideal modern file system for Macs with solid state drive storage running macOS High Sierra or later.
While APFS is not cross-platform compatible, it provides the best experience on modern Macs. The space savings, encryption, improved reliability, and new features make APFS the right choice as the default file system for SSDs on current Macs.