RAID, which stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks, is a data storage technology that combines multiple disk drives into one logical unit. The main goals of RAID are to provide increased data reliability and/or increased input/output performance. One of the key features of RAID is redundancy, which allows data to be recovered if one of the disks fails. There are different RAID levels that provide different combinations of performance, capacity and redundancy.
When it comes to RAID with only two drives, the main consideration is redundancy to protect against drive failure. The most common RAID types to provide redundancy with two drives are RAID 1 and RAID 10. In RAID 1, data is mirrored between the two drives. In RAID 10, data is striped and mirrored. We’ll discuss the pros and cons of each level for a two drive configuration in this article.
What is RAID?
RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks. It is a data storage technology that combines multiple disk drive components into a logical unit for the purposes of data redundancy, performance improvement, or both (RAID definition).
A RAID system consists of two or more drives working together in unison. The different drives contain duplicate copies of the same data. If one drive fails, the RAID system can instantly failover to one of the surviving drives without any interruption in service. This provides fault tolerance and protects against data loss.
RAID can provide increased storage capacities, speed, and redundancy compared to single drives. There are different RAID levels or configurations that each offer their own benefits. Some focus on improved performance, while others focus on increased fault tolerance.
RAID 0
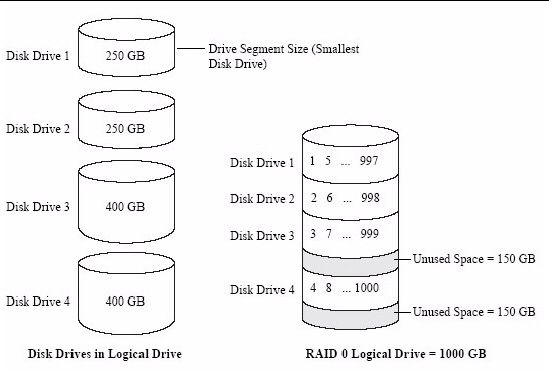
RAID 0, also known as disk striping, is a RAID configuration that splits data evenly across two or more drives with no parity or redundancy (Source: https://www.techtarget.com/searchstorage/definition/RAID-0-disk-striping). The benefit of RAID 0 is improved disk performance and access speeds since data can be read and written simultaneously across multiple drives. However, RAID 0 provides no fault tolerance because if one drive fails, all data across the array will be lost. As such, RAID 0 is generally not recommended in mission-critical environments where uptime and data integrity are paramount.
With RAID 0, the storage capacity equals the total capacities of all the drives in the array. For example, two 1TB drives configured as RAID 0 will provide a total of 2TB storage. However, this comes at the cost of redundancy. RAID 0 is commonly used in non-critical storage environments where performance is more important than data protection, such as in video editing or gaming systems.
RAID 1
RAID 1, also known as disk mirroring, is a RAID configuration where data is written identically to two separate drives (Wikipedia, 2022). This creates an exact copy or mirror of the data across the two drives. RAID 1 provides full redundancy by duplicating all data from one drive to a second drive. If either drive fails, the data can still be accessed from the other non-failed drive. This ensures high availability and fault tolerance. The main advantages of RAID 1 are increased read performance, complete data redundancy, and easy recovery from drive failure. The disadvantage is that only 50% of total capacity is usable for storage, since the same data is written twice. RAID 1 is best suited for mission critical data that requires high availability and cannot tolerate any data loss. It provides the highest level of redundancy but at the cost of usable storage capacity. RAID 1 with two drives, called mirroring, is the recommended RAID level when redundancy is the top priority and there are only two drives available (Prepressure, 2022).
RAID 5
RAID 5 is a type of RAID configuration that utilizes data striping with distributed parity. This means that data is split up into blocks and stripes are written across multiple disks in the array, while parity information is also calculated and written across the disks (Source). The parity information allows for fault tolerance, as if one disk fails, the missing data can be recreated from the remaining data and parity information. At least three disks are required for RAID 5.
The main benefits of RAID 5 are that it provides fault tolerance while also providing more usable disk space compared to mirroring techniques like RAID 1 or RAID 10. Since parity information needs to be calculated and written, write speeds are slower compared to RAID 0 striping, but read speeds can be fast since data is striped across multiple disks (Source). A drawback is that rebuilding an array after failure can be slow since parity needs to be recalculated.
RAID 10
RAID 10, also known as RAID 1+0, is a RAID configuration that combines disk mirroring and disk striping to protect data. It requires a minimum of four disks (What is RAID 10 (RAID 1+0)?).
RAID 10 works by creating a stripe of mirrors. It first mirrors pairs of drives to create two identical copies of the data. Then it stripes data across these mirrored pairs. This results in both high performance and redundancy (RAID 10 & Why Should I Use It?).
The key advantage of RAID 10 is that it can survive multiple drive failures as long as no more than one drive fails in each mirrored pair. This makes it a great choice when redundancy and performance are both critical.
RAID 6
RAID 6, also known as double-parity RAID, is a type of RAID that uses double distributed parity to provide fault tolerance for disk failures (Source: [https://www.techtarget.com/searchstorage/definition/RAID-6-redundant-array-of-independent-disks]). This means that RAID 6 can sustain up to two disk failures without losing data.
Unlike RAID 5 which uses a single parity stripe, RAID 6 uses two parity stripes distributed across different disks. This provides an extra layer of redundancy (Source: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Standard_RAID_levels]). If one disk fails, the first parity stripe can be used to reconstruct the lost data. If a second disk fails, the second parity stripe kicks in.
RAID 6 requires a minimum of 4 drives to implement (two for data, two for parity), but it is recommended to use at least 6 drives for the best performance and protection (Source: [https://recoverit.wondershare.com/windows-tips/what-is-raid-6.html]). The more drives added, the more distributed the parity becomes.
Best RAID for 2 Drives
When it comes to choosing the best RAID level for redundancy with only 2 drives, RAID 1 is the clear choice. As explained in the Selecting the Best RAID Level guide from Oracle, “A RAID 1 array is built from two disk drives, where one disk drive is a mirror of the other (the same data is stored on each disk drive).” (1)
RAID 1 provides full data redundancy by writing all data to both drives simultaneously. If one drive fails, the other contains an exact copy of the data. This makes RAID 1 the go-to RAID level when maximizing fault tolerance with just two drives. The downside is that you lose 50% of the total disk capacity by mirroring the drives. However, given only two drives, RAID 1 gives the best combination of redundancy and storage utilization.
Other RAID levels like RAID 0 provide no redundancy at all, while more advanced options like RAID 5 and 6 require a minimum of 3 drives. For 2 drive configurations focused on redundancy, RAID 1 is the clear winner.
Implementation
Setting up RAID 1 is a straightforward process in modern operating systems like Windows 10/11 and Linux distributions. The basic steps involve:
1. Accessing the RAID configuration utility in the OS (e.g. Storage Spaces in Windows or mdadm in Linux).
2. Selecting the two drives to add to the RAID 1 array.
3. Choosing RAID 1 as the redundancy level.
4. Initializing and formatting the RAID 1 array.
The process takes just a few minutes and only requires a few clicks in the RAID utility (see this guide for step-by-step instructions). The OS will handle most of the complexity behind the scenes.
In terms of performance, RAID 1 provides excellent read speeds since data can be read simultaneously from both disks. However, write speeds are slower as data has to be written twice. Overall, a 2-drive RAID 1 array can achieve speeds of 150-300 MB/s depending on the drive types used.
Regarding cost, RAID 1 requires a minimum of 2 drives so there is a higher upfront cost. However, it provides excellent redundancy against drive failure. If one drive fails, the system continues operating normally using the second drive. RAID 1 is ideal for mission critical data that cannot have any downtime.
Conclusion
In summary, the best RAID level for redundancy with two drives is RAID 1. This level mirrors the data across both drives, providing fault tolerance in case one drive fails. The trade-off is you lose 50% of total capacity. RAID 0 provides no redundancy but maximizes capacity and performance. RAID 5 requires at least 3 drives. RAID 10 provides redundancy but requires 4 drives. RAID 6 also requires more drives. For a two drive system where redundancy is important, RAID 1 is the optimal choice. Just be aware it halves your total usable space.