Malware detection and prevention is a critical component of any organization’s cybersecurity strategy. With the proliferation of sophisticated cyber threats, it’s no longer enough to rely solely on traditional signature-based antivirus solutions. More advanced threat detection capabilities are needed to identify and stop zero-day exploits, fileless attacks, polymorphic malware and other evasive threats designed to bypass traditional defenses.
This is where Microsoft 365 Defender comes in. Microsoft 365 Defender is a unified, cross-product threat detection and response solution available in Microsoft 365. It combines capabilities from multiple Microsoft security products, including Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, Microsoft Defender for Office 365, Microsoft Cloud App Security and Microsoft Defender for Identity. Together, these Defender solutions provide robust malware detection across endpoints, identities, email, collaboration tools, cloud apps and more.
But with multiple components involved, which Defender solution or capabilities within Microsoft 365 Defender are most effective at detecting different types of malware threats? This article will examine the malware detection capabilities of Microsoft 365 Defender components to help identify which tools are best suited for finding malware across different parts of an organization’s digital estate. Analysis of key features and use cases provides guidance on optimizing Microsoft 365 Defender deployment for comprehensive malware detection and response.
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
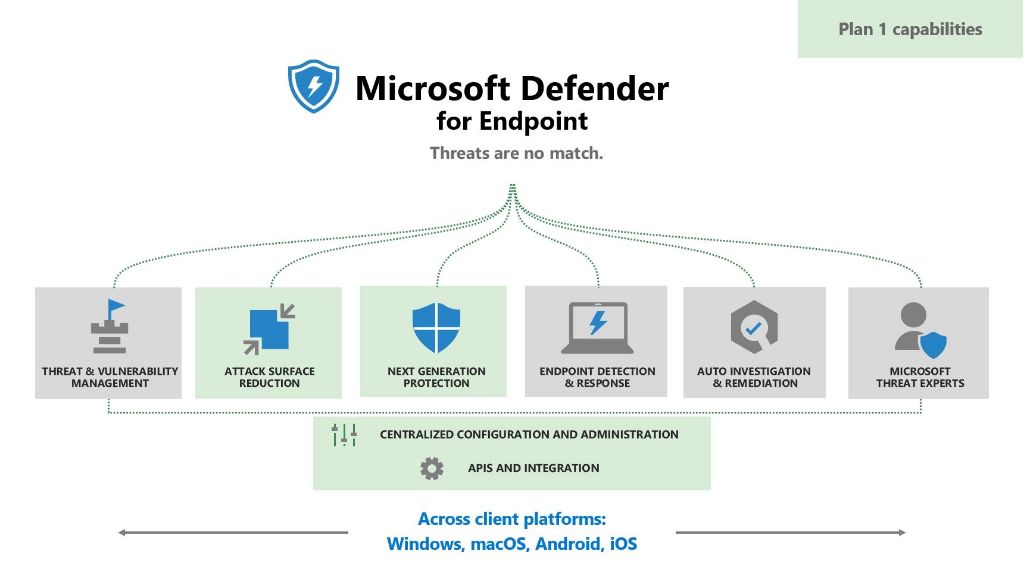
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, formerly known as Microsoft Defender Advanced Threat Protection (ATP), is focused on protecting organizational networks and endpoints, including servers, desktops, laptops and mobile devices. It combines capabilities like behavioral analysis, machine learning and automation to detect and respond to advanced malware and other cyber threats on endpoints.
Some of the key malware detection capabilities provided by Microsoft Defender for Endpoint include:
– File scanning and detection – Defender for Endpoint includes a next-generation protection antivirus engine that scans files and processes on endpoints in near real-time to detect malware. Signatures, heuristics, behavioral analysis and machine learning models are leveraged to identify malicious files and processes.
– Behavioral analysis and anomaly detection – Defender for Endpoint uses advanced behavioral techniques to monitor processes, registry, file system, memory and network activity on endpoints. This allows it to detect and block malware based on suspicious or known malicious behavior, even for new and unknown malware variants.
– Attack surface reduction rules – Predefined rules can automatically block malware infection vectors like executable files from email, browsers or removable media. This prevents malware from even reaching the endpoint.
– Machine learning protection – Trained machine learning models leverage artificial intelligence to augment malware detection based on likelihoods and statistical models predictive of malware. This provides protection against malware that may otherwise fly under the radar.
– Automated investigation and response – Security teams save significant time because Defender for Endpoint can automatically investigate suspicious activities, anomalies and potential malware infections then take action to neutralize the threat across endpoints.
Use Cases
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint is a robust solution optimized for detecting malware threats on endpoints. Key use cases include:
– Protecting endpoint devices – Defender for Endpoint should be deployed to all endpoint devices like laptops, desktops and servers to maximize malware detection. Its combination of signature-based scanning, behavioral monitoring, machine learning and other techniques make it well suited as a first line of defense against endpoint-based malware.
– Detecting advanced malware and evasive threats – Defender for Endpoint specialized capabilities excel at identifying sophisticated malware designed to avoid detection by traditional antivirus products. Things like zero-day vulnerabilities, PowerShell or fileless malware, attacks utilizing legitimate Admin tools and other advanced threats are more readily detected.
– Automating investigation and remediation – The automated investigation and remediation capabilities streamline the malware response process across endpoints by quickly identifying infected devices and cleaning up threats with just a few clicks.
Microsoft Defender for Office 365
Microsoft Defender for Office 365 focuses on securing email and collaboration platforms like Exchange, SharePoint, OneDrive and Microsoft Teams against malware and other advanced threats. It combines automation, machine learning, heuristics and sandboxing to detect malicious content delivered through email or collaboration tools.
Malware detection capabilities provided by Defender for Office 365 include:
– Safe Attachments – Email attachments are detonated in a virtual environment to detect malicious behaviors. Machine learning models identify suspicious characteristics, while sandboxing executes attachments to uncover malicious actions. This allows even unknown malware and zero-day threats to be identified in attachments.
– Safe Links – URLs in emails and collaboration tools are inspected in real-time to check for malicious sites, which are blocked. Malware detected on sites through machine learning and reputation data is blocked when users click on links.
– Anti-phishing protection – AI models in Defender for Office 365 analyze the content of emails and sites to detect phishing campaignslaunching malware. Impersonation and domain spoofing designed to steal credentials via malware links are also identified.
– Content scanning and filtering – Emails and collaboration files are scanned for malware signatures, malicious links and known threats. Custom content filters can be implemented to block emails or files with specific malware indicators.
– Automated investigation and response – Just like Defender for Endpoint, Defender for Office 365 can perform automated investigation of malware detected in content and take response actions like quarantining malicious emails or putting users with compromised accounts under temporary access restrictions.
Use Cases
Defender for Office 365 is optimized for finding malware delivered through software-as-a-service platforms from Microsoft. Ideal use cases include:
– Securing Office 365 – Defender for Office 365 should be enabled to maximize malware detection across Exchange, SharePoint, OneDrive and Microsoft Teams. Automated capabilities reduce the burden on IT teams.
– Blocking malware downloads – Malicious links and attachments containing malware downloads can be blocked before reaching users’ inboxes. Defender for Office 365 prevents email and collaboration tools from becoming infection vectors.
– Countering business email compromise – Sophisticated email threats like CEO fraud, credential phishing and BEC schemes distributing malware are detected using AI and automation in Defender for Office 365.
– Monitoring insider threats – Unusual and potentially malicious files uploaded by compromised insider accounts can be detected by content scans and anomaly detection powered by machine learning models.
Microsoft Cloud App Security
Whereas Defender for Office 365 focuses on Microsoft’s collaboration platforms, Microsoft Cloud App Security provides malware detection across a vast array of third-party cloud applications like Salesforce, AWS, Box, ServiceNow and thousands more. API connections integrate with cloud apps to gain visibility into malware threats.
Malware detection capabilities enabled by Microsoft Cloud App Security include:
– Anomaly detection – Sophisticated machine learning models detect anomalies and outliers in user activities, data transfers and app configurations that may indicate malware operations.
– Third-party app connectors – Out-of-the-box connectors integrate directly with many popular cloud apps to import event logs and scan for malware indicators or compromised accounts.
– Automated threat response – Custom playbooks can be configured to automatically respond to malware detections by containing impacted cloud accounts, revoking permissions or taking other response actions.
– App permissions – Granular visibility into app permissions helps identify and revoke unnecessary access rights that could be exploited to spread malware to cloud data or apps.
– Session monitoring – User sessions across cloud apps can be recorded and analyzed to detect abnormal behavior or privileges escalation that may signal malware activity.
Use Cases
Microsoft Cloud App Security is ideal for these situations:
– Shadow IT discovery – Unknown cloud apps acting as malware vectors can be discovered through Microsoft Cloud App Security’s network traffic analysis capabilities.
– Securing cloud access – The solution provides malware detection for cloud access and activities across various IaaS, PaaS and SaaS environments.
– Detecting compromised accounts – Anomaly detection can spot compromised or hijacked accounts being utilized to propagate malware within cloud apps.
– Monitoring privileged users – Activities by admins and privileged users with access to huge amounts of data can be monitored closely for anomalous behaviors indicating potential malware operations.
Microsoft Defender for Identity
Microsoft Defender for Identity leverages Active Directory and other organizational signals to detect sophisticated identity-based threats and lateral movement techniques aimed at spreading malware across a network. Behavioral analytics spot anomalies associated with identity exploitations and compromised credentials.
Malware detection capabilities offered by Microsoft Defender for Identity include:
– Behavioral analytics – Advanced behavioral profiling of user accounts detects anomalous activity that doesn’t match normal baseline patterns, which may indicate malware utilizing compromised credentials.
– Privileged access alerts – Machine learning models flag unusual spikes in privileged account usage, which could signify an attacker utilizing elevated access to spread malware laterally across systems.
– Lateral movement alerts – The solution looks for telltale tactics like Pass-the-Ticket, Pass-the-Hash, suspicious VPN connections and other techniques used by malware to move within a network.
– Honeytoken accounts – Fake accounts and data act as traps to detect malware attempts to access and exfiltrate sensitive information through stolen credentials.
– Investigation and hunting tools – Security teams can investigate anomalies and search for suspicious patterns or entities impacted by potential malware using powerful analytics and visualization tools.
Use Cases
Microsoft Defender for Identity is most applicable for these use cases:
– Detecting identity-based attacks – Malware often gains access through compromised credentials and Defender for Identity’s behavioral models excel at detecting compromised accounts.
– Stopping lateral movement – Behavioral analytics can detect malware’s lateral transitions within the network enabled by credential theft attacks and quickly cut off access.
– Securing Active Directory – Defender for Identity should monitor AD and domain controllers closely since compromise of these critical identity stores can facilitate rapid malware spread.
– Protecting privileged access – Anomaly detection can spot privileged account misuse associated with malware seeking elevated permissions to access sensitive systems and data.
Conclusion
In summary, Microsoft 365 Defender provides multiple capabilities that can detect malware threats across different parts of an enterprise environment. Key takeaways for which Defender solutions excel at finding malware include:
– Microsoft Defender for Endpoint provides robust malware detection on endpoints through signature scanning, behavioral analysis, machine learning and other leading techniques. It should be a foundational tool to stop endpoint malware infections.
– Microsoft Defender for Office 365 uses automation, heuristics and sandboxing to find malware in email, collaboration platforms and SaaS apps. It’s ideal for blocking malware downloads through emails or files.
– Microsoft Cloud App Security leverages anomaly detection and app permissions to spot malware operations across various cloud environments, making it well suited for securing cloud apps and access.
– Microsoft Defender for Identity detects identity-based reconnaissance and lateral movement tactics often associated with malware using behavioral analytics and privileged access monitoring. It complements the other solutions by identifying compromised accounts.
Of course, the capabilities of Microsoft 365 Defender are most effective when used together. Orchestrating incident response, sharing signals and unifying alerts across endpoints, identities, cloud apps, email and collaboration tools amplifies malware detection and gives comprehensive visibility into malware operations across digital estates.
By understanding the malware detection strengths of Microsoft 365 Defender components, organizations can optimize use of these Defender solutions and configure Microsoft 365 Defender for end-to-end security against constantly evolving malware threats.