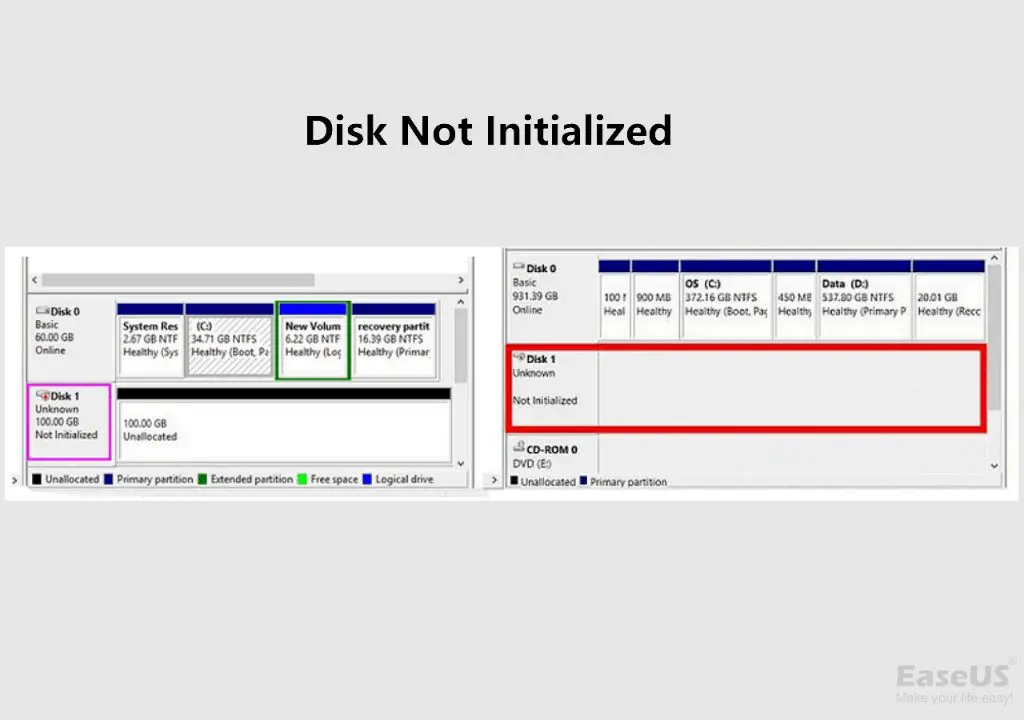
Disk initialization is a process that prepares a new disk drive for use with Windows. When you first connect a brand new disk to your computer, Windows will detect the disk but it will be listed as uninitialized in Disk Management. Before the disk can be formatted and have a drive letter assigned, it must first be initialized. Initializing the disk writes partition information to the drive and creates the partition table so that the operating system recognizes the disk format and can manage the partitions and data on the disk.
When Disk 0, the system drive, is uninitialized on a Windows 10 computer, it usually indicates a problem or incomplete setup. Disk 0 contains critical Windows system files and needs to be initialized for the OS to start up properly. This article provides an overview of disk initialization in Windows 10, examining the causes and solutions for an uninitialized system drive, the options between MBR and GPT, and steps to initialize Disk 0 or any drive using the tools built into Windows.
What is Disk Initialization?
Disk initialization is the process of preparing a new disk drive for use in Windows. During initialization, Windows will write specific structures to the drive that allow the operating system to recognize it and allocate disk space for partitioning and formatting.
There are two main partitioning schemes used for disk initialization: MBR (Master Boot Record) and GPT (GUID Partition Table).
MBR is the older legacy method that has been around since the early days of PCs. MBR partitions are limited to 2TB in size. MBR also only supports up to 4 primary partitions per disk.
GPT is the newer standard introduced with 64-bit versions of Windows. GPT supports larger partition sizes over 2TB and allows for unlimited partitions on a single disk. GPT also provides better security through the use of unique disk identifiers.
For most recent PCs, especially if you want to utilize the full capacity of newer large drives, GPT is typically recommended over MBR for disk initialization and partitioning.
When is Disk 0 Uninitialized?
Disk 0 can become uninitialized during the initial setup of a new PC. When installing Windows for the first time, the operating system may fail to recognize and initialize the main internal drive. This leaves disk 0 in an unknown and unallocated state.
Another common cause is replacing the motherboard on a PC. If you swap out the old motherboard for a new one, Windows may not automatically detect disk 0, leaving it uninitialized. This typically occurs because new motherboards utilize different SATA controllers and drivers compared to the previous board.
Finally, connecting an external drive to a Windows PC for the first time can result in the drive showing up as uninitialized. This is because the drive has not yet been assigned a file system or mapped to a drive letter. To use new external drives, Windows requires users to first initialize the disk properly through Disk Management.
Sources:
https://www.stellarinfo.co.in/blog/disk-0-unknown-not-initialized/
https://www.easeus.com/resource/disk-unknown-not-initialized.html
Consequences of Uninitialized Disk
An uninitialized disk can lead to several problems that prevent you from properly accessing and using the drive. Here are some of the main consequences of having an uninitialized disk in Windows 10:
The disk will not show up in File Explorer. Without being initialized, Windows does not recognize the drive and therefore it will be hidden from view in File Explorer and other parts of the operating system. You will not be able to view, open, copy, move, or access files on the uninitialized disk (Source).
You cannot store data on the disk. Since Windows cannot interact with an uninitialized disk, it is not possible to read or write data to it. Any attempt to save files to the disk will result in errors. The disk is essentially unusable for file storage until it is initialized (Source).
Disk errors may occur. If you try to access an uninitialized disk, Windows can prompt disk read or write errors, I/O device errors, or other disk-related issues. This is because the operating system lacks the necessary setup on that disk to properly communicate with it.
Initializing Disk 0 in Windows 10
There are a few different ways to initialize Disk 0 in Windows 10:
Using Disk Management
The easiest way is to use the built-in Disk Management utility. Here are the steps:
- Open Disk Management (right-click the Start menu and select “Disk Management”).
- Right-click on Disk 0 and select “Initialize Disk”.
- Select the disk partition style – MBR or GPT.
- Click “OK” to confirm.
Disk Management will now initialize the disk and allow Windows to access it
(Source).
diskpart command
Diskpart is a command line tool that can also initialize disks. To use it:
- Open the Command Prompt as Administrator.
- Type “diskpart” and press Enter.
- Type “list disk” to display all disks.
- Select the target disk with “select disk 0” (replace 0 with the disk number).
- Type “clean” to erase and prepare the disk.
- Type “create partition primary” to create a primary partition.
- Type “format fs=ntfs quick” to quick format the partition.
- Type “assign” to give the volume a drive letter.
- Type “exit” to close diskpart.
The disk will now be online and accessible in Windows
(Source).
During Windows installation
If the disk is uninitialized during a fresh Windows install, you can initialize it then:
- Boot from the Windows installation media.
- On the “Where do you want to install Windows?” screen, select the uninitialized disk.
- Click “Drive options (advanced)” at the bottom.
- Select the disk and click “New”. Choose MBR or GPT.
- Click “Format” to quick format the partition.
- Click “Next” to continue the installation.
The installer will initialize the disk 0 and install Windows on it
(Source).
MBR vs GPT for Disk 0
The two main partitioning schemes for hard disks are Master Boot Record (MBR) and GUID Partition Table (GPT). MBR is older and more compatible while GPT is newer with some advantages.
MBR was introduced back in 1983 with a maximum partition size of 2TB. However, modern large hard drives are larger than 2TB which MBR cannot handle (https://www.diskgenius.com/how-to/mbr-vs-gpt.php). MBR also only supports 4 primary partitions and does not have backup partition tables.
GPT was designed as the successor to MBR in more modern systems. It supports huge partition sizes exceeding 2TB and up to 128 partitions on a drive. GPT also stores multiple backup copies of the partition table for redundancy (https://www.alphr.com/mbr-vs-gpt/).
For Disk 0, GPT is generally recommended for UEFI-based systems while MBR is required for legacy BIOS. Converting between the two involves backing up data, wiping the drive, and restoring partitions. However, switching from MBR to GPT may require a reinstall of Windows.
Troubleshooting Uninitialized Disk
If you see the error “disk unknown, not initialized” in Disk Management, there are several troubleshooting steps you can take to try and initialize the disk:
Check Connections
First, check the physical connections from the uninitialized disk to your computer. Make sure the power and data cables are properly plugged in at both ends. If it’s an external drive, try connecting it to a different USB port as well.
Update Drivers
Outdated, corrupt or missing drivers can sometimes cause disks to show up as uninitialized. Visit your motherboard or disk drive manufacturer’s website to download the latest drivers. Install the drivers and reboot your PC to see if that fixes the problem.
Use Diskpart
You can try using the Diskpart command line tool to clean and reformat the disk, which may allow Windows to initialize it. Be warned this will erase all data on the disk.
3rd Party Tools
If the above steps don’t work, you may need data recovery or partition management software to try and recover data or fix errors on the disk so that Windows can initialize it. Some options to try are EaseUS Partition Master, AOMEI Partition Assistant or Stellar Data Recovery.
With patience and trying the right troubleshooting steps, you should be able to get your unknown or uninitialized disk working again in Windows.
When to Initialize a Disk
There are a few key situations when you’ll need to initialize a disk in Windows 10:
- New PC build – When assembling a PC from scratch and installing a fresh copy of Windows, all new blank hard drives will need to be initialized before they can be used. This assigns them a file system so Windows can access and manage the storage space.
- Adding a new drive – If you install an additional internal hard drive or SSD, Windows will see this as an unknown disk that needs to be initialized before it can save files. The same applies when hot-swapping an external drive into your system for the first time.
- After replacing motherboard – If the system motherboard is replaced, Windows will no longer detect the boot drive properly. You’ll need to initialize it to make the drive accessible again. This should only be done as a last resort, as initializing erases all data.
In these situations where Windows cannot recognize the disk, initializing allows the OS to detect it and assign it a drive letter so it can be used as storage. The initialization process essentially prepares a blank slate for the drive to be formatted and partitioned.
Citations:
According to Microsoft, “If the disk is listed as Offline, first select and hold (or right-click) the disk, and then select Online.” (Source)
As 4DDiG explains, initializing a disk “erases all its data and partitions when changing it from offline to online state.” (Source)
Initializing External Drives
The process for initializing external drives like USB hard drives and SSDs is very similar to initializing internal disks in Windows 10. However, there are a couple additional steps involved.
First, external drives must be connected and powered on so they are detected by Windows. Next, you need to take ownership of the drive if it’s brand new or was erased. To take ownership, right-click the disk, choose Properties, and click the Security tab. Then click Advanced and the Change button to take ownership of the disk.
Once you’ve taken ownership, you can right-click the disk in Disk Management and choose Initialize Disk just like with an internal drive. This will allow you to select either MBR or GPT partitioning. Then you can create new volumes if needed.
According to Microsoft’s documentation, some external USB drives cannot be initialized if the hardware is incompatible with Windows initialization [1]. In these cases you may need to initialize the disk on another OS first before using it with Windows.
Overall the process is straightforward. Just be sure the drive is connected and powered on, take ownership if it’s blank, then initialize as MBR or GPT before formatting volumes as needed.
Conclusion
In summary, disk initialization is the process of preparing a new disk for use by configuring it with a partition style like MBR or GPT. Disk 0 specifically refers to the main system disk that contains the operating system. Properly initializing Disk 0 is critical because if it is left uninitialized, Windows will not be able to save data or boot up properly.
When Disk 0 is uninitialized in Windows 10, it is usually the result of connecting a brand new drive that has never been used before. Windows will detect the disk but not be able to interact with it until it has been initialized. The consequences of an uninitialized Disk 0 include inability to install programs, save files, or boot into Windows.
Initializing Disk 0 can be done through Windows Disk Management or by using diskpart commands. You must choose between MBR or GPT partition style based on your specific needs. MBR is legacy but compatible with older systems, while GPT enables larger partitions and better security.
If you are still having trouble initializing Disk 0, it may be due to disk errors, connection issues, or hardware problems. However, properly initializing system disks is a requirement before using them. Overall, correct disk initialization allows Windows to fully leverage and interact with storage drives as needed.