There are a few common reasons why your BIOS may detect your solid state drive (SSD) but not recognize it as a bootable drive.
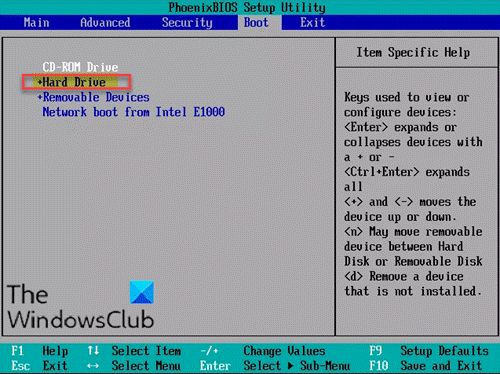
The SSD is not set as the first boot device in BIOS
The most likely culprit is that the SSD simply is not set as the first boot device in your BIOS settings. When you start up your computer, the BIOS checks the boot order and tries to boot from the first device in that list. If your hard drive or another device is set before your SSD, it will boot from that device instead.
To fix this:
- Access your BIOS settings (typically by pressing F2, F10 or Delete during startup)
- Find the boot order section
- Move your SSD to be the first boot device
- Save changes and exit BIOS
Now when you restart, the BIOS should detect your SSD as the primary boot drive and start booting from it.
Boot mode is not set properly
Another potential issue is that the boot mode for the SSD is not set correctly in BIOS. SSDs typically need to be set to AHCI mode, while old hard drives use IDE mode.
To check this:
- Enter BIOS settings
- Find the section related to SATA or onboard devices
- Locate the setting for your SSD’s SATA port and make sure it is set to AHCI mode
- Save changes and restart
Setting the proper AHCI mode Should allow the BIOS to detect your SSD as a bootable drive.
Drive is not partitioned and formatted
In order for a drive to be seen as bootable, it needs to contain a partition with an operating system installed. If your SSD is blank or unpartitioned, the BIOS will not detect it as a bootable device.
You can check if your SSD just needs to be partitioned and formatted using Disk Management in Windows:
- Go to Search, type diskmgmt.msc and open Disk Management
- See if your SSD shows up as an unallocated drive
- If so, you need to create a new partition on it to be able to install an OS
- Right-click the unallocated space and create a new simple volume
- Format this partition with NTFS file system
Once partitioned and formatted, you can install Windows or another OS to the SSD which should then allow it to be detected as a bootable drive.
SSD is faulty or disconnected
If your SSD is not being detected properly at all in BIOS, there could be a hardware issue with the drive itself or its connection.
Try the following troubleshooting steps:
- Check SSD power and data connections
- Try connecting the SSD to another SATA port
- Try using a different SATA cable
- Check for loose cables or any damage to connectors
- Reset CMOS to undo any improper BIOS settings
If the drive still is not recognized, it is likely damaged or outright failed and needs to be replaced.
Wrong boot mode for UEFI/GPT system
On newer systems using UEFI and GPT for booting, you need to have UEFI mode enabled rather than legacy BIOS mode.
To switch to UEFI:
- Access BIOS settings
- Find the boot mode option
- Switch from legacy/BIOS to UEFI
- Adjust boot order if needed
- Save and restart
With UEFI properly enabled, your SSD should be detected as a UEFI bootable device.
SSD missing system partition
For an SSD to be bootable in UEFI mode, it must contain a special UEFI system partition with boot files. If your SSD is missing this partition, the BIOS will not detect it as bootable.
You can add the partition using the following steps:
- Use disk management to shrink volume on SSD to create unallocated space
- Create new partition with size of 100-500MB
- Format the partition with FAT32 file system
- Set partition type to EFI system partition
This will add the required system partition so your SSD can boot in UEFI mode.
Incompatible firmware
In rare cases, an SSD may have firmware that is not compatible with your computer’s BIOS. This can prevent the BIOS from properly detecting and booting from the SSD.
To fix this, you would need to update the firmware on the SSD itself. Refer to your SSD manufacturer’s instructions to update the firmware using their tools.
Conclusion
In summary, these are some of the common reasons why your BIOS may detect an SSD but not boot from it:
- SSD not set as first boot device in BIOS
- Incorrect boot mode set in BIOS for SSD
- SSD not partitioned and formatted
- Faulty or disconnected SSD
- Legacy vs UEFI boot mode mismatch
- Missing EFI system partition on SSD
- Incompatible firmware needing update
Carefully checking each cause and trying the appropriate solutions should help you get your SSD recognized properly as a bootable drive by the BIOS.
Why can a BIOS detect but not boot from an SSD?
There are a few main reasons why a BIOS may detect an SSD but not boot from it:
- The boot order is incorrect – A different hard drive or device is listed first in the boot order.
- The SSD’s controller mode is incorrect – It needs to be set to AHCI mode instead of IDE.
- The SSD is not partitioned and formatted – The BIOS can’t boot from a blank/unallocated drive.
- There is a hardware issue – Faulty cables, connectors, SSD damage, etc.
- Incorrect boot mode – UEFI versus legacy/BIOS modes don’t match.
- On UEFI systems, the SSD is missing its EFI system partition.
- The SSD has incompatible firmware that the BIOS cannot properly detect.
How can I fix my BIOS not detecting my SSD as a bootable drive?
To get your BIOS to properly recognize your SSD as bootable, try these troubleshooting steps:
- Check that the SSD is set as the first boot device in BIOS settings.
- Confirm the SATA controller mode for the SSD port is AHCI, not IDE.
- Make sure the drive is partitioned/formatted if currently blank.
- Try different SATA ports, cables, reset CMOS to defaults.
- If using UEFI, enable UEFI boot mode and create EFI system partition.
- Update SSD and motherboard firmware/BIOS to latest available.
In most cases, this will resolve the BIOS detection issue and allow proper booting from the SSD.
What should I do if my SSD is not detected in BIOS at all?
If your BIOS doesn’t detect your SSD at all, try the following troubleshooting steps:
- Check SSD power and data connections are firmly attached.
- Try connecting the SSD to a different SATA port and cable.
- Verify the SATA controller is enabled in BIOS.
- Look for any signs of physical damage to the SSD or cables.
- Update SSD firmware and motherboard BIOS to the latest available.
- Reset BIOS to default settings to undo any settings causing detection issues.
- If still not detected, the SSD itself has likely failed and needs replacement.
This will help identify any connection problems or incompatible issues causing the SSD to not be detected at all within BIOS.
Additional Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some additional troubleshooting tips for further diagnosing an SSD not being detected as a bootable drive:
Verify drive health using manufacturer tools
Use the SSD maker’s own drive utilities to run tests on the health of the drive. Tools like Samsung Magician can check for errors and do low-level formatting if needed.
Update motherboard drivers and BIOS
Get the latest chipset, SATA and other drivers for your motherboard to improve compatibility with your SSD. Also update the BIOS to the newest available version.
Try booting with CSM/legacy mode
If UEFI boot is not working properly, try disabling it and booting in legacy CSM mode to see if the SSD is detected normally.
Clear CMOS to reset BIOS
Resetting the CMOS will clear any improper BIOS settings that may be interfering with proper SSD detection and boot.
Check for loose cabling
Loose SATA cables can cause intermittent connection issues. Reseat cables firmly to ensure a tight connection.
Test with external dock or enclosure
Try connecting the SSD externally using a USB dock or enclosure to isolate the issue being with the drive itself versus something on the motherboard.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is my SSD detected in BIOS but not in Windows?
If your SSD shows up in BIOS but not within Windows, typical causes include:
- The drive is not partitioned and formatted properly
- Outdated storage drivers in Windows
- Drive letter not assigned in Disk Management
- Damaged partition table or file system
- Failed SSD controller or other hardware fault
How do I get Windows to detect my SSD?
If Windows is not detecting your SSD, try the following:
- Ensure the SATA controller drivers are up to date
- Check for the SSD in Disk Management and initialize if blank
- Assign a drive letter if missing
- Scan for new hardware changes in Device Manager
- Disconnect and reconnect the SSD SATA cable
Why does my SSD work in one computer but not another?
Some potential reasons an SSD may work on one PC but not another include:
- Driver conflicts or issues on one machine
- Different BIOS/firmware incompatibility
- UEFI versus legacy boot mode mismatch
- Lack of an EFI system partition required for UEFI
- Bad SATA port or cable on one computer
- Insufficient power supply on one machine
How can I tell if my SSD is dead or faulty?
Signs your SSD may have completely failed include:
- Not detected at all in BIOS or OS
- Detected but all data corrupted or inaccessible
- BSOD errors referencing the drive
- Failed initialization/formatting
- Overheating/burnt smell from drive
- Failed drive diagnostic/health checks
- Mechanical sounds like clicking or grinding
If experiencing any of those issues, especially combined with SMART errors, the SSD is likely faulty and needs to be replaced.
| Scenario | Potential Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| SSD not listed first in boot order in BIOS | Boot order incorrect | Re-order so SSD is first in boot sequence |
| BIOS mode set to IDE/Legacy instead of AHCI | Incorrect SATA mode | Switch mode to AHCI for SSD compatibility |
| SSD not partitioned or formatted | Blank/unallocated drive | Create partition, format with NTFS |
| Loose cables, faulty ports, physical damage | Hardware issue | Reseat connections, test different ports/cables |
This table summarizes some common scenarios, causes and solutions for an SSD not being detected as bootable.
Conclusion
Troubleshooting an SSD that is detected in BIOS but not bootable requires verifying settings like boot order and SATA mode, checking for hardware issues, and ensuring the drive is partitioned and formatted correctly. On UEFI systems the SSD also needs a proper EFI system partition.
Following the step-by-step guides outlined in this article should help identify and correct the underlying problem. In most cases, this will resolve the bootability issue and get your SSD running as the primary boot drive.