RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a data storage technology that uses multiple hard drives to increase performance and/or provide fault tolerance. There are several levels of RAID that offer different combinations of performance, capacity, and redundancy. RAID 6 is one of the most robust and secure RAID levels, making it a popular choice for mission-critical storage needs.
What is RAID 6?
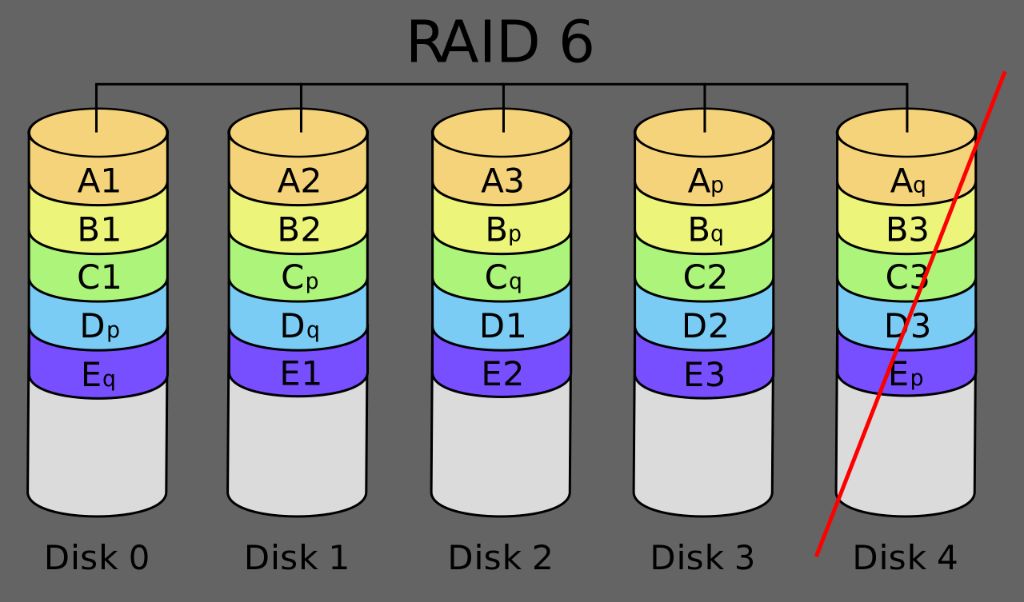
RAID 6 provides block-level striping with double distributed parity. This means the data is broken down into blocks that are striped across multiple drives. Parity information is calculated and written across different drives as well. RAID 6 uses at least four drives, with two drives storing parity information. If any two drives fail, the storage array will still be operational thanks to the dual parity.
How does RAID 6 provide fault tolerance?
RAID 6 can sustain up to two drive failures without losing any data. Here’s how it works:
- Data is striped across multiple drives at the block level
- Parity information is calculated and written across different drives
- Dual parity provides redundancy – the parity blocks are stored on different drives
- If one drive fails, the parity blocks on the other drives can reconstruct the lost data
- If two drives fail, the dual parity mechanisms still allow for data recovery
By distributing parity across multiple drives, RAID 6 can withstand multiple drive failures. The dual parity provides an extra layer of redundancy compared to a single parity scheme like in RAID 5.
What are the advantages of RAID 6?
Here are some of the key benefits of using RAID 6:
- Excellent fault tolerance – The dual parity providing by RAID 6 means it can handle up to two drive failures without data loss. This makes it much more robust than a single parity solution.
- Rebuilding drive replacements is faster – With single parity RAID 5, rebuilding a failed drive requires reading data from all the remaining drives. But with RAID 6, there is less load on each drive since parity data is spread across multiple disks.
- Higher storage efficiency than RAID 1 – Unlike mirroring in RAID 1, parity doesn’t require full duplication of data. So the total capacity in a RAID 6 is much higher for the number of disks used.
- Good performance for read and small writes – Small random reads and writes will be distributed across multiple spindles for enhanced parallel performance.
In summary, the excellent fault tolerance and rebuild performance make RAID 6 well-suited for mission critical storage needs where downtime is unacceptable.
What are the disadvantages of RAID 6?
There are a few potential downsides to using RAID 6:
- Lower write performance – The parity calculations can impact write speeds, especially for large contiguous writes. RAID 10 or RAID 50 may provide faster write performance.
- Higher cost per TB – Because of the dual parity overhead, the cost per TB is higher than single parity or non-redundant options. You need a minimum of 4 drives as well.
- Increased rebuild times – If more than 2 drives fail before a rebuild, there is risk of data loss. Rebuilding dual parity is also slower than single parity configs.
- Complexity – Managing and monitoring dual parity solutions requires more advanced technical skills.
While RAID 6 is slower at large writes compared to RAID 10 or RAID 50, the substantial fault tolerance advantages often make it a preferred choice for critical data protection for many organizations.
When is RAID 6 better than RAID 10?
RAID 10 utilizes mirroring, while RAID 6 uses parity. Here’s a comparison of the two options:
| RAID 10 | RAID 6 | |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum Drives | 4 | 4 |
| Fault Tolerance | 1 drive per mirror | Up to 2 drives |
| Storage Efficiency | 50% | N-2 drives |
| Read Performance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Write Performance | Excellent | Good |
| Rebuild Time | Faster | Slower |
The decision between RAID 10 vs RAID 6 depends on your priorities:
- If maximum performance is needed, RAID 10 is better because read/write speeds are excellent.
- When cost per TB is most important, RAID 6 provides much better efficiency.
- For critical data that needs redundancy, RAID 6 offers far superior protection surviving up to 2 drive failures.
- If faster rebuilds are vital, mirrored RAID 10 rebuilds drives faster than dual parity RAID 6.
Overall, RAID 6 is preferable for most scenarios where fault tolerance is critical and cost is a factor. But RAID 10 surpasses RAID 6 in performance and faster rebuilds.
How does RAID 6 compare to RAID 5?
RAID 5 was once the most common choice for redundant storage. But RAID 6 has surpassed RAID 5 in popularity due to its superior fault tolerance. Here’s a rundown of how the two compare:
| RAID 5 | RAID 6 | |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum Drives | 3 | 4 |
| Fault Tolerance | 1 drive | Up to 2 drives |
| Storage Efficiency | N-1 drives | N-2 drives |
| Read Performance | Very good | Excellent |
| Write Performance | Good | Good |
| Rebuild Time | Faster | Slower |
The main advantages of RAID 6 over RAID 5:
- Dual parity provides fault tolerance for up to 2 drive failures.
- The load is distributed across more drives during rebuilds for faster recovery.
- Larger drive sizes have increased likelihood of rebuild failures on RAID 5.
The popularity of large drives over 8 TB has increased the chance of failure during RAID 5 rebuilds. Combine this with the need for higher fault tolerance, and RAID 6 becomes the better solution in most cases.
How does RAID 60 compare to RAID 6?
RAID 60 combines the straight block-level striping of RAID 0 with the distributed dual parity of RAID 6. This provides excellent performance while maintaining fault tolerance. Here’s a quick look at how RAID 60 and RAID 6 stack up:
| RAID 6 | RAID 60 | |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum Drives | 4 | 8 |
| Fault Tolerance | 2 drives | 2 drives per array |
| Storage Efficiency | N-2 drives | N-2 drives |
| Read Performance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Write Performance | Good | Excellent |
The advantages of RAID 60 over RAID 6:
- Significantly faster write performance due to RAID 0 striping.
- Much higher throughput for large sequential reads and writes.
- Array can sustain up to 2 drive failures in each mirrored set.
RAID 60 combines the performance of RAID 0 with the fault tolerance of RAID 6. It’s ideal for applications that demand speed, capacity, and redundancy.
What are real-world use cases for deploying RAID 6?
Here are some examples of systems where RAID 6 provides significant advantages over other RAID levels:
- Database servers – RAID 6 offers excellent read speeds for the mostly small, random I/O typical of busy databases. And the dual parity gives robust data protection.
- File servers – File storage requires high capacity and reliable redundancy. RAID 6 is scalable and can tolerate multiple drive failures.
- Media servers – Storing large volumes of media files demands significant capacity. RAID 6 provides ample space without sacrificing redundancy.
- Virtualization – High amounts of mostly read I/O favors RAID 6. And redundancy is critical for maintaining virtual machines.
- Backup storage – Backup repositories need plenty of fault-tolerant capacity. RAID 6 fits the requirements well.
Any application that demands a balance of performance, capacity, and robust data protection can benefit from deploying RAID 6 storage.
Conclusion
RAID 6 provides an excellent combination of storage efficiency, performance, and fault tolerance. The dual parity mechanism allows it to withstand up to two drive failures. This high level of redundancy makes RAID 6 ideal for mission-critical data that cannot afford loss. Compared to RAID 5, RAID 6 offers massively superior protection thanks to the second parity drive.
The lower storage overhead of parity compared to mirroring also gives RAID 6 better capacity and cost efficiency than RAID 10 in most cases. But RAID 10 does outperform RAID 6 when it comes to faster rebuilds or maximizing performance. Fortunately, RAID 60 delivers the best of both worlds by marrying RAID 0 striping with RAID 6 parity.
For highly demanding storage needs that require speed, capacity, and resilience, RAID 6 checks all the boxes. The performance is excellent for reads and small random writes, there is built-in redundancy to survive dual drive failures, and storage efficiency is high. Thanks to these well-rounded capabilities, RAID 6 remains a staple choice for critical server and enterprise storage where downtime is unacceptable.