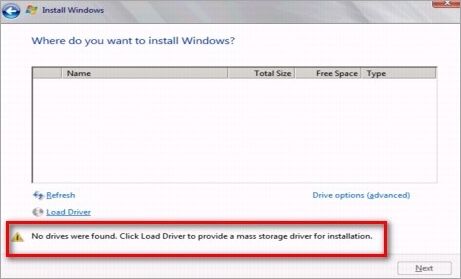
There are a few common reasons why your hard drive may not be detected during Windows 10 installation:
Faulty or unplugged SATA cable
If the SATA cable connecting your hard drive to the motherboard is loose, damaged, or unplugged, Windows will not be able to detect the hard drive. Make sure both ends of the SATA cable are securely plugged in – one end to the motherboard SATA port, and the other end to the back of the hard drive.
Troubleshooting steps
- Physically inspect the SATA cable and connections.
- Try using a different SATA cable if you have a spare.
- Plug the hard drive into a different SATA port on the motherboard.
Hard drive not powered on
Hard drives need power from the PSU in order to function. Make sure the power cable running from the PSU to the hard drive is securely plugged in at both ends. Some modular PSUs require you to plug in additional power cables.
Troubleshooting steps
- Check the hard drive power cable connections.
- Try using a different power cable if you have a spare.
- Plug the hard drive power connector into a different port on the PSU.
Hard drive not enabled in BIOS
For the motherboard and OS to be able to access the hard drive, it needs to be enabled in BIOS first. Enter your system BIOS and make sure the hard drive is listed under the “Boot” or “Storage” sections. If not, you may need to enable it manually.
Troubleshooting steps
- Boot into BIOS and look for the hard drive.
- If not listed, look for a setting like “Storage Configuration” to manually enable it.
- Save changes and exit BIOS to reboot.
Failed or malfunctioning hard drive
If the hard drive itself is damaged or malfunctioning, it won’t be detectable during Windows installation. Typical signs include the BIOS not detecting the drive, the drive not spinning up, or the system freezing when attempting to access it.
Troubleshooting steps
- Listen for hard drive spin-up sounds on boot.
- Check if the drive is detected in BIOS.
- Try the drive in another system if possible.
- Run the manufacturer’s diagnostic software.
- Consider replacing the faulty hard drive.
Incompatible hard drive
Very rarely, a hard drive may be incompatible with the motherboard hardware or BIOS version. For example, some newer NVMe drives may not be detect on older systems. Make sure your hard drive meets the system requirements.
Troubleshooting steps
- Verify the hard drive is supported by the motherboard.
- Check for BIOS updates that improve hardware support.
- Try updating the storage controller drivers.
Loose component or connector
It’s worth inspecting the physical hard drive itself in case anything is loose. This includes the SATA and power connectors attaching to the drive, or even an internal component that may have come undone.
Troubleshooting steps
- Visually inspect the hard drive for any internal damage or loose parts.
- Check the SATA and power connectors are securely attached.
- Reseat the hard drive in the bay.
- Consider hard drive replacement if internal damage found.
Corrupted Windows installation
If this issue only started happening after a partial or failing Windows installation, then file corruption could be preventing Windows from detecting the hard drive correctly. A clean reinstall should resolve this.
Troubleshooting steps
- Back up any data and do a fresh Windows install.
- Delete all existing partitions during Windows setup.
- Perform a full format on the hard drive.
Damaged system files or registry
A previously faulty or incomplete Windows installation can also cause registry or system file errors that prevent proper hard drive detection. Startup repair or system restore may fix the corrupted files.
Troubleshooting steps
- Run sfc /scannow to check system file integrity.
- Perform a system restore to undo registry changes.
- Use startup repair to fix boot issues.
Driver conflicts or issues
Outdated, corrupted or misconfigured drivers can potentially lead to hard drive detection issues in Windows. Update chipset, SATA and storage drivers to latest available versions.
Troubleshooting steps
- Update SATA, chipset and storage drivers.
- Uninstall/reinstall storage controller drivers.
- Check for updated driver versions from manufacturer.
Insufficient power supply
If the computer power supply unit (PSU) is underpowered, weak, or failing, it may not provide enough steady power to operate the hard drive. This can cause intermittent detection issues.
Troubleshooting steps
- Confirm PSU wattage meets system power requirements.
- Try a higher wattage PSU if available.
- Test system voltage levels in BIOS or using multimeter.
- Consider replacing old or low-quality PSU.
Loose or faulty power, SATA cables
Defective power or data cables can cause faulty hard drive connections resulting in detection issues. Inspect cables for damage and ensure firm connections.
Troubleshooting steps
- Inspect SATA and power cables for damage.
- Reconnect cables at both ends.
- Try new cables if available.
- Check cable connections inside computer case.
BIOS misconfiguration
Incorrect or outdated BIOS settings may prevent proper initialization and detection of the hard drive at boot. Restore BIOS defaults or update to latest version.
Troubleshooting steps
- Reset BIOS to default settings.
- Update to the latest stable BIOS version.
- Verify boot mode (UEFI vs. Legacy) is correct.
- Enable hot-swap if SATA controller supports it.
Faulty SATA controller
A damaged or malfunctioning SATA controller on the motherboard can lead to hard drive detection issues. This may require motherboard replacement if confirmed to be faulty.
Troubleshooting steps
- Try a different SATA port if available.
- Update SATA controller drivers.
- Disable/re-enable SATA controller in BIOS.
- Test hard drive on another system.
- Replace faulty motherboard if needed.
Disabled drive in Disk Management
Hard drives must be online and partitioned in Disk Management for Windows to fully detect them and install. Make sure the disk does not show as Offline or Not Initialized.
Troubleshooting steps
- Check disk status in Disk Management.
- Online the drive if shown as Offline.
- Initialize the disk if unallocated.
- Create a partition and format if necessary.
System BIOS needs update
An outdated system BIOS that lacks full support for a newer hard drive can cause intermittent detection issues. Check the manufacturer website for the latest BIOS version.
Troubleshooting steps
- Identify current BIOS version.
- Check manufacturer website for updates.
- Flash latest stable BIOS version.
- Enable AHCI mode if available.
Hardware incompatibility
Rarely, a hard drive may be partially incompatible with the specific motherboard or chipset in use, causing sporadic detection. Check for compatibility issues.
Troubleshooting steps
- Verify hard drive and motherboard compatibility.
- Update motherboard BIOS, chipset drivers.
- Disable unnecessary storage options in BIOS.
Non-system hard drive
Drives only containing data and not the operating system typically won’t be detected until after the OS loads. This is normal for secondary non-boot drives.
Troubleshooting steps
- Check if drive appears in BIOS boot menu.
- Verify if visible in File Explorer after boot.
- Ensure cables are connected if newly added.
Conclusion
Hard drives not showing up during Windows installation is a common problem with various potential causes. Carefully inspecting connections, troubleshooting in the BIOS, updating drivers/firmware, and testing components can help isolate the issue. Replacing defective cables, drives, PSUs or motherboard may be required in some cases. Always backup data first, and use tools like Disk Management for further diagnosis.
| Potential Cause | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|
| Faulty SATA cable | Inspect connections, try new cable |
| Hard drive not powered on | Check power cable connections |
| Drive not enabled in BIOS | Enter BIOS and enable drive |
| Failed or dead drive | Listen for spin sounds, test in another system |
| Loose component or connection | Reseat connectors, check for internal damage |
| Corrupted Windows installation | Clean install Windows, delete partitions |
| Damaged system files or registry | Run Startup Repair, system restore, chkdsk |
| Driver conflicts or issues | Update SATA, chipset drivers |
| Insufficient PSU power | Test PSU wattage, try new PSU |
| BIOS settings misconfigured | Reset BIOS, update BIOS version |
| Hardware incompatibility | Verify support, update motherboard drivers/BIOS |