Quick Overview
There are a few common reasons why Windows may not detect a hard disk drive (HDD):
- The HDD is not properly connected or has become unplugged.
- The HDD is damaged or malfunctioning.
- The HDD is not getting power.
- There is an issue with the HDD controller or cables.
- The HDD is not recognized in the BIOS.
- There are driver issues in Windows.
- The HDD has not been partitioned and formatted.
The most common solutions are to check the physical connections, try connecting the HDD in another computer, check for issues in the BIOS, update drivers, or reformat the HDD. Read on for more detailed troubleshooting steps.
Check Cabling and Connections
The first thing to check is whether the HDD is properly connected. Here are some steps:
- Turn off the computer and unplug it from power.
- Open the computer case and check that the SATA data and power cables are firmly plugged into the HDD and motherboard.
- If using an external enclosure, plug the power adapter in and use a different USB port or cable.
- Reseat the cables by unplugging and plugging them back in. Ensure the connectors are securely inserted straight into the ports.
- Inspect the SATA cables for any bent pins or damage. Try swapping in a known good SATA cable if possible.
- Plug the computer back in, restart it, and see if Windows detects the HDD.
Loose, damaged, or unplugged cables are common reasons for disks not being detected. Reseating connections will often fix connectivity issues.
Check for HDD Damage or Malfunction
If drive cables are connected but Windows still does not detect the HDD, the drive itself may be damaged or malfunctioning. Here are some troubleshooting tips:
- Listen closely to the HDD when starting up the computer. Make sure you can hear the disk spinning up and that there are no unusual sounds like grinding or whistling.
- Check the HDD status lights if applicable. The activity light should briefly flash on power-up. Lights should not indicate an error code.
- Check S.M.A.R.T. status using the HDD utility software or disk manager. This can reveal underlying problems with the drive.
- Run the HDD maker’s diagnostic software. Tests can identify bad sectors or internal hardware failure.
- Try connecting the HDD externally through USB or in another computer. If it is still not recognized, the drive itself is likely faulty and may need to be replaced.
Malfunctions can prevent an HDD from being usable. Always backup important data in case a disk is failing.
Confirm the HDD is Receiving Power
Hard disk drives require power from the PSU to operate. Issues like a loose power connector, bad cable, or inadequate wattage can prevent spin up. Check these items:
- Make sure the HDD power cable is firmly connected to the back of the drive and to the PSU.
- Try swapping the HDD power cable with a spare to rule out damage.
- Check that the PSU is switched on and functional. Test with a voltmeter if possible.
- Use a PSU calculator online to confirm your power supply wattage is adequate for the system.
- Try eliminating unnecessary system components to reduce power load as a test.
Without the proper power delivery, an HDD will fail to start up and be detected. Test with another PSU if still having issues.
Verify HDD Controller and Ports
Problems with the motherboard’s HDD controller or a damaged port can show as a disk not detected. Things to verify:
- Inspect motherboard SATA ports for any bent or missing pins.
- Try plugging the HDD into a different SATA port if available.
- Test with a different SATA cable to rule out a damaged cable.
- Update motherboard drivers, chipset, and BIOS to latest available versions.
- Try the HDD in another computer or external enclosure for comparison.
- Swap in a known good HDD to test if the same port/controller works.
This can determine if the issue is with the specific HDD or controller hardware. External enclosures usually have their own controller.
Check for HDD in BIOS
The next step is to verify that the BIOS detects the HDD on boot up:
- Enter the system BIOS, typically by pressing F2, F10, or Delete during boot up.
- Check that the HDD is listed on the hardware/device summary screen.
- If not listed, the drive is not being detected at a pre-boot hardware level.
- Enable “Auto” for the SATA mode instead of IDE/RAID modes (common mistake).
- Update to the latest BIOS version in case this corrects detection issues.
If the BIOS sees the drive, the issue lies with Windows. If not, the problem is hardware related.
Update or Reinstall HDD Drivers
With disk connectivity and controllers ruled out, driver problems within Windows may be preventing detection:
- Open Device Manager and expand the Disk Drives section. The HDD should be listed here.
- If the HDD shows here but not in Windows Explorer, try updating the Standard AHCI SATA Controller drivers.
- Reinstall or rollback the HDD driver from Device Manager.
- Uninstall the HDD driver completely, reboot and let Windows reinstall it automatically.
- Use a tool like Snappy Driver Installer to update all drivers, focusing on chipset and storage drivers.
Modern HDDs typically use generic Windows drivers. Reinstalling these often resolves conflicts.
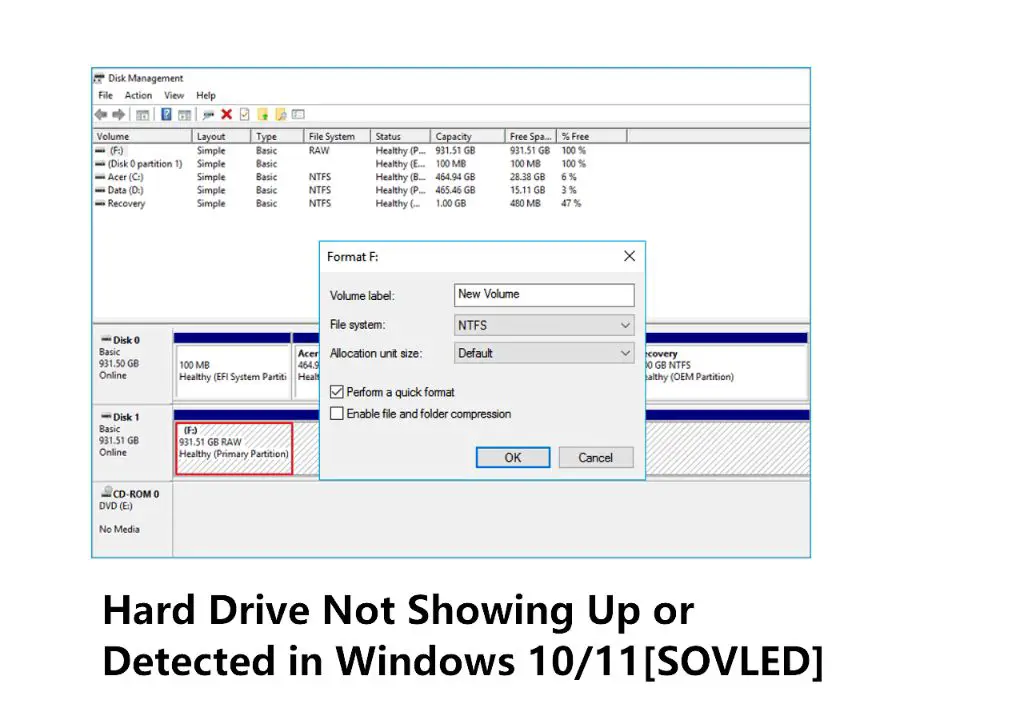
Initialize and Format HDD
For new HDDs or ones moved from another system, detection may fail because Windows has not prepared the disk:
- Use Disk Management to locate the new disk. Right-click it and select Online to activate it.
- To make the disk usable, right-click it and choose Initialize Disk.
- Select a partition table like GPT or MBR depending on the size.
- Right-click each new volume and choose Format to create filesystem.
After following these steps to initialize and format, the HDD should show up as a usable drive letter in File Explorer.
Additional Troubleshooting Tips
A few other things to check if Windows is not detecting the hard drive:
- Make sure no removable HDD bays or disabling hotkeys like FN+F9 are in use.
- Boot into safe mode to load generic drivers instead of third party ones.
- Check for updated firmware for the HDD and install if available.
- Try removing other recently added hardware in case of conflicts.
- Check if the HDD is properly mounted if this is a new installation.
Also verify that the BIOS is set to boot the correct HDD if Windows loads but the boot drive is not found.
When to Replace the Hard Drive
If you have exhausted all other troubleshooting steps, the HDD may need to be replaced:
- Hardware diagnostics show read/write errors or bad sectors.
- The HDD makes abnormal spinning, clicking or scratching noises.
- Drive does not spin up properly or powers up very slowly.
- Extensive bad sector counts that keep growing.
- The drive is very old or has exceeded manufacturer lifespan.
- Obvious physical damage like dents, cracked circuit board.
Typical signs of an HDD reaching end of life. Data should be backed up and migrated to a new replacement drive.
Conclusion
Windows failing to detect an internal or external hard drive is a common problem with several potential causes. Start troubleshooting by checking the physical connections, trying another PC or enclosure, looking for issues in the BIOS, and confirming the HDD has power. Updating drivers, initializing the disk, or even replacing the drive may be needed if those steps do not resolve the detection problem. Backing up important data provides a contingency plan if the HDD ends up needing replacement due to a hardware failure.