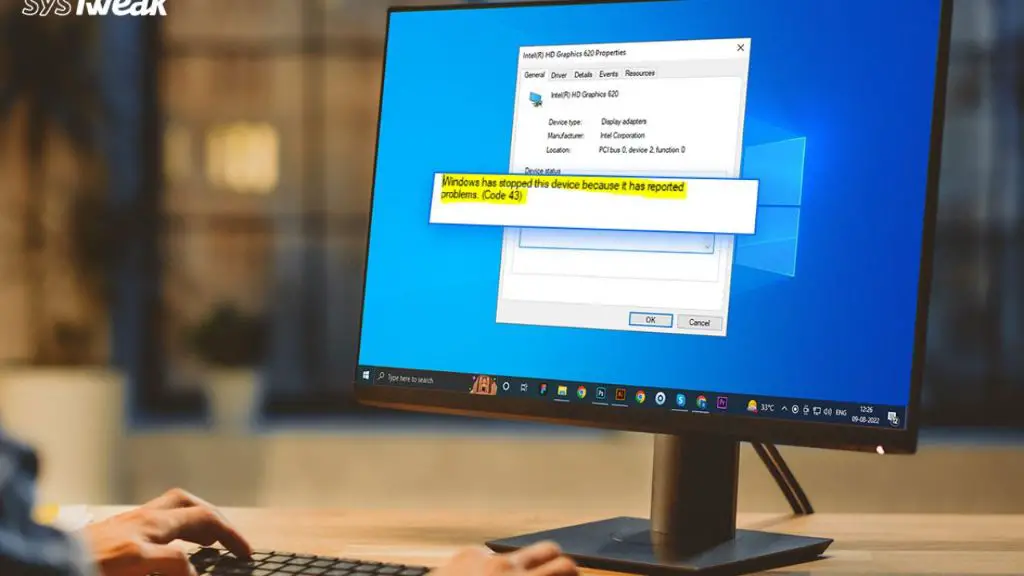
Device code 43 errors in Windows are frustratingly vague, often leaving users puzzled as to why a device has suddenly stopped working. This error simply states “Windows has stopped this device because it has reported problems” without providing any real indication of what has gone wrong or how to fix it.
What causes code 43 errors?
There are a few potential causes of the code 43 error in Windows:
- Outdated, corrupt or missing drivers
- Hardware problems with the device itself
- Incompatible hardware/software
- Power supply issues
- Windows registry problems
By far the most common cause of the code 43 error is driver related. Every hardware device requires a driver to function properly in Windows. If the driver becomes outdated, corrupted or goes missing, Windows will no longer be able to communicate with the device, leading to the code 43 error.
How to fix a code 43 error
There are a number of steps you can take to try and resolve a code 43 error:
- Update or reinstall device drivers – Make sure you have the latest manufacturer drivers installed for the device. Reinstalling the drivers often fixes code 43 errors.
- Try uninstalling device in Device Manager – Uninstall the device then scan for hardware changes to reinstall drivers.
- Plug device into a different USB port – Sometimes switching the port it is plugged into resolves code 43.
- Disable USB selective suspend – This setting can sometimes cause code 43 errors for USB devices in Windows.
- Update Windows – Install the latest Windows updates which may contain fixes for hardware/driver issues.
- Remove duplicate devices – Duplicate devices with code 43 errors can cause conflicts in Device Manager.
- Use the Device Cleanup Tool – Runs diagnostics and fixes device problems like code 43.
- Check for overheating – Overheating components can lead to code 43 failures. Ensure proper airflow.
- Update BIOS/Firmware – Outdated system BIOS or device firmware can result in code 43.
- Try a different cable – Faulty USB or other cables can cause devices to fail with code 43.
- Test hardware in another machine – Helps determine if the issue is with the device itself or your specific machine.
If the above steps do not resolve the code 43 error, the device itself may be defective and need replacing. Contacting the device manufacturer for support is recommended if all troubleshooting steps fail.
Why fixing code 43 errors is important
It’s important to take the time to properly diagnose and fix code 43 errors for a few reasons:
- Failed devices are unusable – Code 43 prevents you from using the full features and functions of your hardware.
- Causes performance issues – Code 43 errors can lead to freezes, crashes, slowdowns and other problems.
- Can indicate larger hardware failure – Often a precursor to complete device failure.
- Data loss concerns – Failing devices have a greater risk of data loss or corruption.
- Permanent damage possible – Allowing hardware problems to persist risks permanent component damage.
- Errors may recur – Device will likely stop working again even after rebooting.
Quickly resolving code 43 errors helps restore full functionality, improves system stability, protects your data and reduces the chances of permanent hardware damage. Ignoring the issue likely means an essential device becoming completely non-functional in the future.
Helpful tips for troubleshooting code 43
Follow these tips when attempting to diagnose and fix a Windows code 43 error:
- Don’t assume it’s a driver issue – While the most common cause, hardware and compatibility problems can also be at fault.
- Update all system drivers – Updating chipset, motherboard and other drivers may help, not just the device drivers.
- Research your specific device – Manufacturer forums and support sites often have specialized troubleshooting tips.
- Test with bare essential peripherals – Remove other USB devices and peripherals to isolate potential conflicts.
- Scan for malware – Malware that modifies system files can cause code 43 failures.
- Inspect physical components – Check for damage, wear & tear, debris blocks or frayed cables.
- Check System Log – Detailed error info may be logged about device failure events.
- Consider system restore – Restore to earlier restore point before code 43 occurred if needed.
- Backup data – Always backup data before making repairs in case hardware fails completely.
Troubleshooting code 43 thoroughly step-by-step helps identify the cause and prevents wasted time trying ineffective solutions repeatedly. Pay close attention to any patterns and test devices/configurations systematically.
Helpful utilities for fixing code 43 errors
Specialized utilities that can aid in resolving code 43 errors include:
- Device Manager – Manage installed devices and update or reinstall drivers.
- Device Cleanup Tool – Scan for issues with USB and other devices and apply fixes.
- DISM Tool – Repair damaged system files that may cause hardware failures.
- SFC Scanner – Scans Windows system files and replaces corrupted files.
- Driver Verifier – Stresses drivers to identify issues causing code 43 errors.
- Windows Troubleshooting – Built-in Windows troubleshooters diagnose many device issues.
- Windows Update – Provides the latest driver and Windows updates.
- System Restore – Reverts system configuration changes that caused code 43.
- Clean Boot – Boots Windows with minimal services and drivers enabled for testing.
Leveraging tools like these that are included in Windows or provided by device manufacturers streamline troubleshooting code 43 errors rather than resorting to guesswork.
When to reinstall Windows to fix code 43
Reinstalling Windows is sometimes necessary to resolve a persistent code 43 error, when:
- All drivers and Windows updates have been applied without success.
- Device works on another computer system but still has code 43 on your machine.
- System Restore does not resolve the error.
- DISM, SFC and other troubleshooting have failed.
- Windows system files are corrupted.
- A Windows update or configuration change caused the error.
- Multiple devices began failing with code 43 around the same time.
Before reinstalling Windows:
- Backup important data.
- Research if similar configurations have issues.
- Determine if BIOS, firmware or hardware updates are available.
- Weigh if upgrading hardware components may help.
- Consider advanced troubleshooting like clean boot testing.
Reinstalling Windows should be a last resort after all other options have been exhausted. Code 43 errors originating within Windows itself will require a reset of the operating system to overcome.
Steps for a trouble-free Windows reinstall to fix code 43
Follow these best practices when reinstalling Windows to resolve code 43 problems:
- Backup data and settings.
- Research most stable Windows version for your hardware.
- Download latest media creation tool and updates.
- Disconnect unnecessary peripherals and drives.
- Perform clean install on system drive only.
- Install chipset/motherboard drivers if needed.
- Reinstall device drivers.
- Set BIOS to optimized defaults.
- Install latest Windows updates.
- Restore data and settings.
Preparation is key – installing Windows with only the target device connected improves stability. Slowly add peripherals back one at a time after verifying operation first. This isolates any new conflicts or issues.
Potential pitfalls when reinstalling Windows for code 43
Avoid these mistakes when reinstalling Windows to fix code 43 problems:
- Not backing up data.
- Installing before updating BIOS and firmware.
- Retaining old configuration files.
- Connecting peripherals too soon.
- Installing unnecessary software initially.
- Allowing Windows to install drivers automatically.
- Rushing – take time to thoroughly test stability.
- Not testing extensively before restoring data.
- Restoring data before applying all Windows updates.
- Not checking for updated drivers before migrating data back.
Rushing the process risks reintroducing problems like code 43 after Windows is installed. Take a methodical approach to give each component a fresh start.
When to replace hardware causing code 43 errors
Replacing faulty hardware is sometimes the only way to permanently resolve a code 43 error. Consider hardware replacement if:
- Device functions normally on other systems.
- All drivers, Windows and BIOS updates have been applied.
- Clean Windows install does not fix code 43 with device.
- Device has physical damage or deterioration.
- Code 43 returns quickly after fixing or persists across Windows reinstalls.
- Manufacturer troubleshooting and support is unsuccessful.
- Device fails diagnostics testing.
Prior to replacing hardware:
- Confirm warranty or return policies of device.
- Research compatible replacement options.
- Determine if used/refurbished models are acceptable.
- Backup data and export settings.
- Uninstall device drivers and remove from Windows.
Properly removing failing devices before replacement helps ensure a smooth transition to the new hardware.
Typical hardware that may need replacement due to code 43
Some types of devices more prone to code 43 failures include:
- USB and Bluetooth adapters
- Webcams
- Card readers
- Capture cards
- TV tuners
- Drawing tablets
- Touchscreen monitors
- KVM switches
- Docking stations
External devices with more components and circuitry tend to fail more often from wear and tear or power issues. Internal hardware like video cards, network adapters and hard drives can also cause code 43 errors when malfunctioning.
Signs hardware should be replaced due to code 43
Indications hardware failure is causing persistent code 43 errors:
- Device not recognized or drops connection intermittently.
- Overheating, unusual noises or smells from device.
- Cracked, bent or otherwise damaged device.
- Code 43 recurs immediately upon reconnecting device.
- Device fails diagnostic suite.
- Same device works on multiple other systems.
- Issues began after electrical storm, power surge or outage.
- Device has exceeded expected lifespan.
Code 43 often stems from components simply wearing out. Power spikes or prolonged uptime accelerating demise. Visible damage also indicates replacement need.
Top tips to avoid code 43 hardware errors
You can help prevent code 43 failures by:
- Buying quality, name brand hardware from reputable sources.
- Only using required device drivers from manufacturer.
- Keeping devices in temperature controlled environment.
- Not moving devices excessively when in use.
- Unplug devices safely using “Eject” options.
- Using surge protectors and UPS battery backups.
- Dusting computer and devices regularly.
- Updating drivers, firmware and BIOS promptly.
- Disconnecting devices during electrical storms.
- Avoiding excessive manual configuration changes.
Carefully handling hardware and providing clean, stable operating conditions goes a long way toward avoiding code 43 failures down the road.
Conclusion
Windows code 43 errors can stem from multiple causes but nearly always indicate a significant underlying hardware, driver or system problem requiring immediate attention. While frustratingly vague, code 43 should not be ignored as it is the symptom of a larger issue needing repair.
Thoroughly troubleshooting code 43 by updating drivers, testing configurations, isolating conflicts and researching manufacturer fixes allows correcting the problem without replacing hardware unnecessarily. However, some code 43 failures do ultimately require replacing worn or damaged devices.
Carefully evaluating the error details, troubleshooting methodically and being prepared for a Windows reinstall or hardware replacement provides the best chance of swiftly resolving code 43 issues and restoring normal device functionality.