Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts files on your computer and demands payment to decrypt them. If your computer becomes infected with ransomware, you may wonder if resetting your PC will remove the malware and decrypt your files. Here is a quick overview of how resetting your PC affects ransomware.
TL;DR: Reset usually removes ransomware, but doesn’t decrypt files
Resetting your PC will typically remove ransomware, as it erases everything and reinstalls Windows. However, resetting will not decrypt your encrypted files. You’ll need your backup or the ransomware decryption key for that. Resetting is one way to clean the ransomware infection, but not to get your original files back.
What happens when you reset your PC?
When you reset your Windows PC, it reinstalls a clean copy of the operating system and removes all of your personal files, apps, and settings. This process does the following:
- Wipes the hard drive and repartitions it
- Reinstalls a fresh copy of Windows
- Removes all installed programs and drivers
- Erases all user files and accounts
- Resets all settings back to default
Essentially, resetting gives you a brand new Windows installation. This clean slate approach will eliminate any malware, including ransomware, that was present on the old OS.
Does a reset remove ransomware?
In most cases, yes, resetting your PC will remove any ransomware that was installed on it. Here’s why:
- The reset wipes the entire hard drive, erasing any ransomware files.
- Reinstalling Windows means there is no malware left over from the previous OS.
- With a clean OS install, there is no way for dormant ransomware files to persist.
- The ransomware won’t have registered itself in the new Windows registry.
Since the reset process erases everything and starts fresh, it eliminates any ransomware that was present on the computer before. Most forms of ransomware end up getting wiped out.
Exceptions where ransomware may persist
In some cases, ransomware may still affect a reset PC in the following scenarios:
- The ransomware has infected the computer’s UEFI or BIOS firmware – resetting the OS won’t touch this
- It is present on other connected drives that are not erased during reset
- It has infected system files on a backup drive that are restored after reset
- The malware reinfects from its original source after the reset completes
These cases are less common, as most ransomware resides solely in the main OS. But they illustrate how resetting may not always completely eliminate ransomware.
Will resetting decrypt ransomed files?
Unfortunately, while resetting removes the ransomware infection itself, it does not restore access to any files encrypted by the ransomware.
Encrypted files remain encrypted even after the associated ransomware is gone. Resetting the PC has no effect in decrypting them. This is because the encryption process is irreversible without the right decryption key.
To regain access to ransomed files, you either need:
- The secret key and decryption tool from the ransomware operators
- A backup copy of the files from before they were encrypted
- A decryption tool for that specific ransomware strain (if available)
Resetting alone won’t restore your files. It only removes the malware that encrypted them in the first place.
Should you reset your PC after a ransomware attack?
Resetting your PC is generally recommended after a ransomware infection, but there are some caveats:
- Pros: Removes all ransomware files and gives you a clean system.
- Cons: Doesn’t decrypt files and you lose all user data.
- Ideally: Decrypt files from backup first before resetting.
If you don’t need anything from the PC, resetting provides a quick and thorough way to wipe the ransomware. But if you need certain files, work to restore from backup before resetting.
When resetting makes sense
Resetting your PC is smart after ransomware if:
- You have backups of your important files.
- The infection is severe and persists through antivirus scans.
- You want to start fresh rather than try to disinfect drive.
- You use the PC for testing or non-essential purposes.
For minimal or non-critical PCs, resetting often makes more sense than spending time scrubbing ransomware. Just be sure you don’t need anything off the drive first.
When to avoid resetting
You may want to avoid resetting your PC if:
- You need files stored on the PC that are not backed up.
- You use specialized software that would be difficult to reinstall.
- You have no way to restore applications or operating system licenses.
- There are application settings you want to preserve.
In these cases, it may be better to thoroughly scan and clean the PC to remove ransomware instead of wiping everything.
Steps to reset your Windows PC
If you decide that resetting your PC is the best solution after ransomware, here are the steps to reset in Windows:
Windows 11
- Go to Windows Settings > System > Recovery.
- Under Advanced startup, click Restart now.
- After restarting to Diagnostic Mode, select Troubleshoot > Reset this PC.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to reinstall Windows.
Windows 10
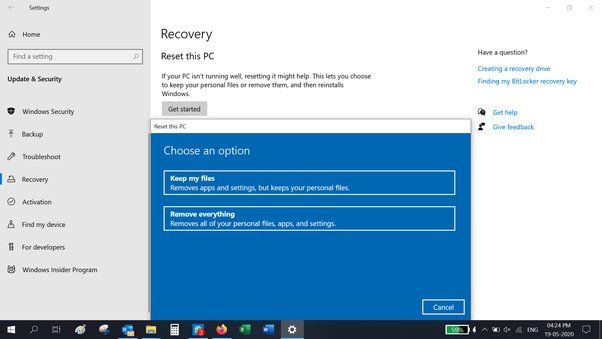
- Open the Start menu and go to Settings > Update & Security > Recovery.
- Under Reset this PC, click Get Started.
- Choose either Keep My Files or Remove Everything before confirming the reset.
- Windows will reinstall itself and restart when finished.
This will completely reset Windows and reinstall a clean copy of the OS. Be sure to backup any needed files first.
What to do after resetting your PC
Once you successfully reset your PC, there are a few important steps:
- Reinstall any essential software programs.
- Restore your files from a recent backup.
- Update Windows, software, and security programs.
- Change all passwords that were used on the infected PC.
- Be vigilant about not downloading suspicious files or visiting risky sites.
Resetting gives you a malware-free PC, but you’ll need to set it up again properly to avoid another infection. Be cautious and don’t restore any files that may be infected.
Other options for ransomware removal
Resetting is one option for dealing with ransomware, but there are other ways you may be able to remove an infection while keeping your files and settings:
- Antivirus software – Run scans to detect and quarantine ransomware.
- Anti-ransomware software – Specialty software focuses specifically on ransomware.
- System restore – Roll back your PC state to before the infection happened.
- Manual removal – Using anti-malware tools to manually delete ransomware.
In some cases, these methods can remove the ransomware without resetting the entire PC. However, resetting often provides the most thorough cleaning.
Key takeaways on resetting your PC for ransomware removal
Here are some key points to remember:
- Resetting removes ransomware infections and wipes the system clean.
- However, resetting does not decrypt any files already encrypted.
- Back up important files before resetting, if possible.
- Reset works best when you don’t need to save anything from the infected system.
- Alternative removal options may work if you need to preserve data or software.
- Always be vigilant about backups and cybersecurity hygiene to limit ransomware impact.
The bottom line
Resetting your PC will wipe ransomware off your system by reinstalling Windows. But encrypted files will remain locked unless decrypted via backup, ransom payment, or security tools. Resetting removes the infection but does not get your original files back. Work to restore critical files from backup first before resetting, if you have that option available.