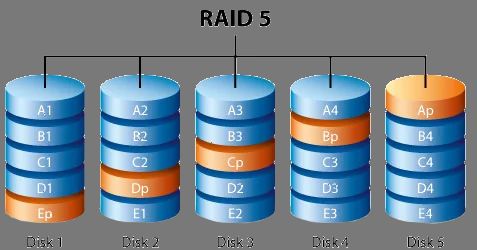
When you have a RAID 5 array running out of space, one option is to add a larger hard drive to expand capacity. But can you safely add a larger drive to an existing RAID 5 array without losing data? Here we’ll look at the factors to consider when adding a new, bigger drive to RAID 5.
Quick Answers
Here are the key points about adding a larger drive to RAID 5:
- Yes, you can add a larger drive to an existing RAID 5 array.
- The new drive must be equal to or larger than the existing drives.
- The array will rebuild and restripe data to use the new drive’s capacity.
- This process can take hours or days, depending on the array size.
- It’s best to add drives one at a time to avoid overly long rebuild times.
- Always back up your RAID array before making changes.
Can You Add a Bigger Drive to RAID 5?
The short answer is yes, you can safely add a larger hard drive to an existing RAID 5 array. RAID 5’s distributed parity design allows you to increase storage capacity this way.
When you add the new drive, the RAID controller will rebuild the array to stripe data across all drives, including the new larger drive. This provides more overall capacity while retaining the same RAID 5 level of redundancy.
Requirements for the New Drive
However, there are some specific requirements for the new drive you add to RAID 5:
- The new drive must be equal to or larger than the existing drives in capacity. You cannot add a smaller drive to RAID 5.
- The new drive should be the same interface type and rotational speed as existing drives. Mixing drive types can cause performance issues.
- Aim to add drives of the same model as existing ones when possible.
As long as you choose a drive that meets these requirements, it can be successfully added to RAID 5 for more storage space.
The RAID 5 Rebuild Process
When you add the new physical drive and initiate the RAID rebuild, here is what happens:
- The RAID controller detects the new drive and verifies it matches requirements.
- The controller begins rebuilding the array across all disks, including the new one.
- Data is recalculated and striped across the larger set of drives.
- The controller recomputes parity and writes it to the new drive.
- When finished, the array is rebalanced and has more overall capacity.
This rebuild process can take substantial time depending on the size of your RAID 5 array. Rebuilding a 6TB five-disk RAID 5 with a new 8TB drive could take over 6 hours, for example. The larger your array, the longer an add/rebuild takes.
Benefits of the Rebuild Process
While lengthy, the rebuild provides two key benefits:
- Full integrity check: Rebuilding RAID 5 recalculates all parity and data, ensuring there are no latent inconsistencies or errors.
- Easy capacity increase: After rebuild, all available space on the new drive is added without altering existing data.
So in exchange for the rebuild time, you gain increased storage along with a full scan and integrity check of the array.
Adding Multiple Drives to RAID 5
For larger capacity increases, you may want to add several new drives at once. Is this possible with RAID 5?
Yes, you can add multiple new drives to RAID 5 in the same rebuild process. However, there are a few caveats:
- Each new drive must still meet the minimum size and type requirements.
- Adding too many drives significantly extends the rebuild time, impacting performance.
- It’s best to add no more than 1 or 2 new drives at once to limit rebuild time.
Staggering drive additions in phases helps minimize disruption. Add one drive, let it rebuild, then add another. This keeps rebuild times manageable.
Example Adding Two 8TB Drives to RAID 5
Here’s a step-by-step example of expanding a RAID 5 by two drives:
- Start with a 3 drive RAID 5 array with 6TB drives, total 12TB capacity.
- Backup the RAID array before making changes.
- Add one new 8TB drive and start a RAID 5 rebuild. Wait for rebuild to complete.
- The array now has 16TB capacity with the first new drive added.
- Now add the second 8TB drive and start another rebuild.
- After the second rebuild, the array has 24TB capacity across 5 drives.
This staged rebuild keeps the system running while minimizing disruption. Avoid adding more than 2 drives at once to limit rebuild times.
RAID 6 Considerations
The above guidance applies to both RAID 5 and the similar RAID 6 standard. RAID 6 simply has an extra parity drive, but otherwise supports drive additions the same way.
With RAID 6 you can safely add larger drives one or two at a time just like RAID 5. The rebuild process occurs identically. RAID 6 may have slightly longer rebuild times due to the extra parity calculation.
When to Choose RAID 6 Over RAID 5
Given the choice, RAID 6 is generally preferable to RAID 5 today since it offers an extra fault tolerance. The advantages of RAID 6 include:
- Allows two drive failures without data loss instead of just one.
- Better suited for larger drive capacities where rebuild times are longer.
- Parity drives spread write load compared to just one in RAID 5.
For most uses today, the advantages of RAID 6 make it a better choice over RAID 5 if available. But both work well for expanding array capacity when needed.
Steps to Add a Drive to RAID 5 or RAID 6
If you’ve decided to add a new drive to your RAID array, here are the steps to follow:
- Select a new drive that matches or exceeds the size and type of existing drives.
- Backup your RAID array before making any changes!
- Physically install the new drive in the server or external enclosure.
- Using the RAID management interface, add the new drive to the array.
- The system will begin the RAID rebuild process.
- Wait for the rebuild to fully complete before accessing the array.
- The additional capacity from the new drive will now be available.
Take care when adding new drives to avoid errors. And give the rebuild time to complete fully before resuming normal operations.
Pitfalls to Avoid
While adding a larger drive to RAID 5 is possible, there are some potential mistakes to avoid:
- Adding small capacity drives – Never add a smaller drive or rebuilding fails.
- Incompatible drive types – Mixing SSD and HDD drives causes performance problems.
- Incomplete rebuilds – Aborted or paused rebuilds can lead to data inconsistencies.
- Multiple drive failures during rebuild – More than one fault during rebuild may cause data loss.
As long as you add compatible larger drives and give rebuilds time to complete, the process is straightforward. But small mistakes can lead to trouble, so take care.
Do’s and Don’ts
Here are some best practices when adding drives to RAID 5 or 6:
Do:
- Add drives one at a time to limit rebuild times.
- Use matching drive models and types as current drives.
- Allow rebuilds to complete fully before accessing array data.
- Back up the RAID before making any changes.
Don’t:
- Add smaller capacity drives.
- Mix drive types like SSD and HDD.
- Interrupt or pause a rebuild process.
- Try to use the array before a rebuild finishes.
Alternative Ways to Expand RAID 5
While adding drives is the main method to expand RAID 5, there are a couple other options:
Larger Drive Swap
You can replace existing drives one-by-one with larger drives, allowing a rebuild after each swap. All data is retained. This gradually grows capacity over time.
New RAID Array
Build an entirely new RAID 5/6 array with larger drives, then migrate data over from the old array. This quickly gets you more capacity but requires migrating data.
Adding new drives is usually simpler than these alternatives. But the other methods can work if adding drives isn’t an option.
Key Considerations
Here’s a quick summary of the key points when adding drives to RAID 5 or 6:
- Yes, you can safely add larger drives.
- Add one drive at a time and wait for rebuilds.
- New drives must meet minimum size and type requirements.
- Give the RAID controller time to fully rebuild the array.
- Capacity is added after the rebuild finishes.
- Always backup the array before making changes!
As long as you follow best practices, expanding RAID 5 or RAID 6 with new drives is straightforward. Just be patient during the rebuild process and avoid mistakes like adding undersized drives.
Conclusion
While the rebuild process takes time, adding larger drives to RAID 5 or RAID 6 is an effective way to increase array capacity when needed. By following the proper steps and practices outlined here, the procedure can be completed smoothly without issues. Just be sure to backup important data first!
With the guidance provided in this article, you should now have a solid understanding of how to successfully add a new larger hard drive to your existing RAID 5 array. Take it slow, allow time for rebuilds, and double check compatibility. Expanding capacity this way can extend the useful life of a RAID 5 or 6 array while retaining existing data safely.