Browsing history refers to a log of websites and pages that have been visited in a web browser such as Safari on a Mac computer. History is recorded automatically as users navigate the web. There are a few reasons why someone may want to delete their browsing history:
- Privacy – To prevent others from seeing which sites they have visited.
- Security – To remove traces of sensitive sites visited.
- Clutter – To clear old unwanted history that builds up over time.
While history can be deleted, it’s important to note that it may still be possible to recover or restore deleted history data from backup files or other locations depending on the deletion method used. Permanently deleting all traces of browsing history requires overwriting the data.
Checking the History Menu
The easiest way to view your browsing history on a Mac is to open the History menu in your browser. The three most popular browsers on Mac – Safari, Chrome, and Firefox – all have a History menu where you can view visited webpages.
To view history in Safari, click the History menu option in the top menu bar. This will show your recent browsing history organized by date and time. Deleted history may still appear here until it gets purged from your system. You can click “Show All History” at the top to see your full history. Source 1
In Chrome, click the History menu option and then click “History” on the dropdown menu. This will open your full history page showing visited webpages. Deleted items may still show here. Source 2
For Firefox, click the History menu > “Show All History” to view your full history. Recent deleted history can also appear here.
So the History menu in your browser is the first place to check for any deleted history. But it may not show items that were deleted further back in time.
Looking in Recently Deleted
Most browsers on Mac store deleted history items in a “Recently Deleted” folder for a period of time before permanently removing them. This allows users to recover accidentally deleted history if needed. Here are the steps to access these folders in the major browsers:
In Safari:
- Click “History” > “Show All History”
- In the left sidebar, click “Recently Deleted”
You’ll see a list of your recently deleted history items. You can right click on any item to recover it (Cleverfiles.com).
In Google Chrome:
- Click the Chrome menu icon (three dots) > “History”
- On the left sidebar, choose “Recently deleted”
This shows your recently deleted Chrome browsing history. Click an item to restore it (Handyrecovery.com).
In Firefox:
- Click the menu icon (three lines) > “History” > “Recently Closed Tabs”
Here you’ll find your recently closed Firefox tabs. Right-click and choose “Reopen” to restore them (Stellarinfo.com).
Searching Spotlight
One way to find deleted browser history on Mac is by using Spotlight search. Spotlight indexes a variety of data on your Mac, including browsing history from Safari, Chrome, Firefox and other browsers.
To search Spotlight for browsing history, use the following steps:
- Click the magnifying glass icon in the top right corner of the screen or press Command+Space to open Spotlight.
- Type in keywords related to your browsing history like a website name, search term, or keyword.
- Spotlight will display results related to your search terms from your browsing history.
- You can click on a result to open the website again or get more details like the visit date and time.
Keep in mind that Spotlight does not store your full browsing history forever. It will periodically clear out older history data. But searching Spotlight can still reveal websites and searches you may have forgotten about or thought were deleted.
For more targeted searches, you can use commands like these:
- “history:techcrunch.com” – Show history of visits to techcrunch.com
- “search:how to make pasta” – Show search engine queries containing “how to make pasta”
- “images:kittens” – Show image searches for kittens
So using the powerful indexing capabilities of Spotlight can uncover browsing history you thought was lost. Just enter a related keyword or domain and you may be able to rediscover your past browsing activities.
Checking iOS Sync Data
If you use Safari on your iOS devices (iPhone, iPad) as well as on your Mac, your browsing history may be synced across devices using iCloud. When you sync your iOS browsing history to your Mac, it stores a copy of that history locally on your Mac. So even if you delete your browsing history directly on your iOS device, you may still be able to find traces of that history from your synced iOS devices on your Mac. Here’s how to view it:
1. On your Mac, open the Safari app.
2. Click Safari in the menu bar and select Preferences.
3. Go to the General tab.
4. Check the box next to “Show full website address.”
5. Below that, click on “Advanced.”
6. Check the box next to “Show Develop menu in menu bar.”
7. Close System Preferences.
8. In Safari’s menu bar, select Develop > Show Web Inspector.
9. In the Web Inspector window, click on the Storage tab.
10. In the left sidebar, expand the localStorage section.
11. Click on the file named “SafariLocalHistory” to view your synced iOS browsing history.
This will allow you to see websites and URLs that may have been deleted directly on your iPhone or iPad but still exist in your synced history on your Mac.
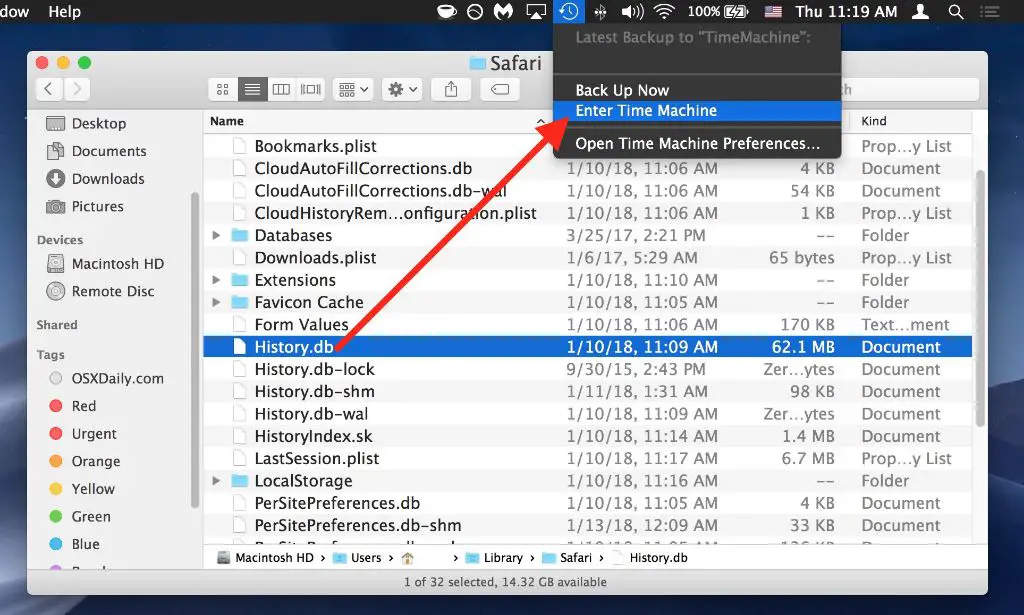
Using Time Machine
Time Machine is Mac’s built-in backup software that can help you recover deleted Safari history. Time Machine takes periodic backups of your Mac’s data, allowing you to restore files and data from an earlier point in time.
Here are the steps to browse Time Machine backups and find deleted Safari history:
- Open Time Machine on your Mac. You can find it using Spotlight or in the Applications folder.
- Once Time Machine opens, you’ll see a timeline on the right showing different backup points. Click back through the timeline to browse older backups.
- When you find a backup point before the history was deleted, click on it. This will open the backup in Finder.
- In Finder, navigate to Users > [Your Username] > Library > Safari.
- Open the History.db file to view the browsing history from that backup date. You can also search for specific sites or terms.
- Copy any history data you need out of this file and into the current version in your user Library folder to restore it.
Using Time Machine this way allows you to recover Safari browsing history that may have been deleted or lost. Just be sure Time Machine backups are active before history goes missing.
Checking Log Files
Browsers like Safari, Chrome, and Firefox store website visit history and cache data in log files on your Mac. These log files can contain detailed records of your browsing history, even if you’ve deleted it from the browser’s history menu.
To access these log files in macOS, you can use the Console app to view logs for different applications and system processes. Some important log files to check for browsing history include:
- /private/var/log/apache2/access_log – Stores visited URLs for Safari.
- /Users/username/Library/Application Support/Google/Chrome/Default/History – Chrome browser history.
- /Users/username/Library/Application Support/Firefox/Profiles/profile folder/places.sqlite – Firefox history and bookmarks.
You can also use the log show command in Terminal to output logs chronologically. Pass the --last 1h flag to view only the last hour of logs.
Using Third-Party Tools
If the previous methods don’t work, your best option is to use a purpose-built Mac history recovery application. These tools are designed specifically to dig deep and recover deleted browser history from your Mac.
Here are some top recommendations:
iBoysoft Mac Data Recovery – Scans your entire Mac drive and reliably recovers deleted Safari, Chrome, Firefox and other browser history. Easy to use with a high recovery rate.
Stellar Data Recovery – Advanced scanning recovers lost and deleted browser history on Mac. Has different scan modes for efficient recovery.
These tools utilize advanced scanning algorithms to dig deep and find deleted browser history that is otherwise inaccessible through standard methods. They can recover history even if you emptied the trash, with a high success rate. Just install, scan your Mac drive, and preview recoverable history files.
Permanently Deleting History
Even when you delete your browsing history in Safari or other browsers, traces of that history may still be stored on your Mac in various places like cache files and logs. For example, website data may be cached to speed up loading times. And activity logs created by macOS or security software record events like websites visited.
To permanently delete all traces of your browsing history from the Mac, you need to clean multiple locations. Here are some tips:
- Clear the browser cache – This removes temporary internet files stored by Safari, Chrome etc.
- Delete logs – macOS and security software logs should be cleared.
- Use a privacy cleaner tool – This scans the Mac for any remaining history data like thumbnails.
- Enable private browsing – Using this mode doesn’t store history during that session.
With a multi-pronged approach, you can ensure browsing history is completely deleted from the Mac and can’t be recovered by data recovery software. For maximum privacy, repeat cleaning of cache/logs regularly.
Conclusion
In summary, there are several methods available to recover deleted browsing history on a Mac computer. The History menu in Safari can reveal recently closed tabs and windows. The Recently Deleted folder stores browsing data for 30 days before permanent removal. Spotlight search can uncover traces of websites visited. iOS device sync data may retain browsing information as well. Time Machine backups and log files also provide ways to resurrect deleted history.
While it may be possible to recover browsing records, internet users should exercise caution regarding personal information exposed through search and visit histories. Private browsing modes, settings to clear history, and privacy-focused tools can help prevent tracking of online activity. Overall web safety and security call for responsible handling of sensitive data.