Quick Answer
There are a few potential ways to try to recover a previous version of a file you accidentally saved over, including:
- Use your operating system’s file versioning or backup features (like Windows Previous Versions or Time Machine on Mac) to restore an older version of the file.
- Use backup software like Veeam or Acronis to restore the file from a backup.
- Use file recovery software like EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard or Stellar Data Recovery to scan your drive and recover the older version.
- Check your cloud storage like Google Drive or Dropbox to see if you have an older version stored there.
- If applicable, check your email – you may have emailed the file to someone previously or have an older draft attachment.
The sooner you act, the better chance you have of recovering the unsaved version. Avoid saving new files to that drive to prevent overwriting the deleted data.
What causes files to be overwritten and lost?
Files can easily be overwritten and lost in a few common scenarios:
- Accidentally hitting Save instead of Save As: If you open a file, make edits, and save without realizing you forgot to use Save As, the original will be overwritten.
- Sync errors: If a cloud sync service encounters an error, such as connection issues or a conflicted copy, newer local versions may overwrite cloud versions.
- Saving on exit: Some programs will prompt to save changes when closing a file, which can accidentally overwrite the original.
- Auto-recover files: Apps like Microsoft Office create temporary auto-recover files to try to prevent data loss from crashes. However, recovering from one of these files will replace your original.
- Auto-save features: Some apps like Google Docs automatically save changes as you work, so manual saves will overwrite previous auto-saved versions.
Being attentive when saving files and backing up important documents can help prevent accidental overwriting. Enabling versioning features in apps like Office can also protect against lost changes.
Check Your Operating System’s File History
One of the first things to check when trying to recover an overwritten file is your operating system’s built-in file versioning or backup utilities.
Windows Previous Versions
If you are on Windows, you may be able to use a feature called Previous Versions to restore older copies of files. This allows you to roll back a file, folder, or entire drive to a time before changes were made.
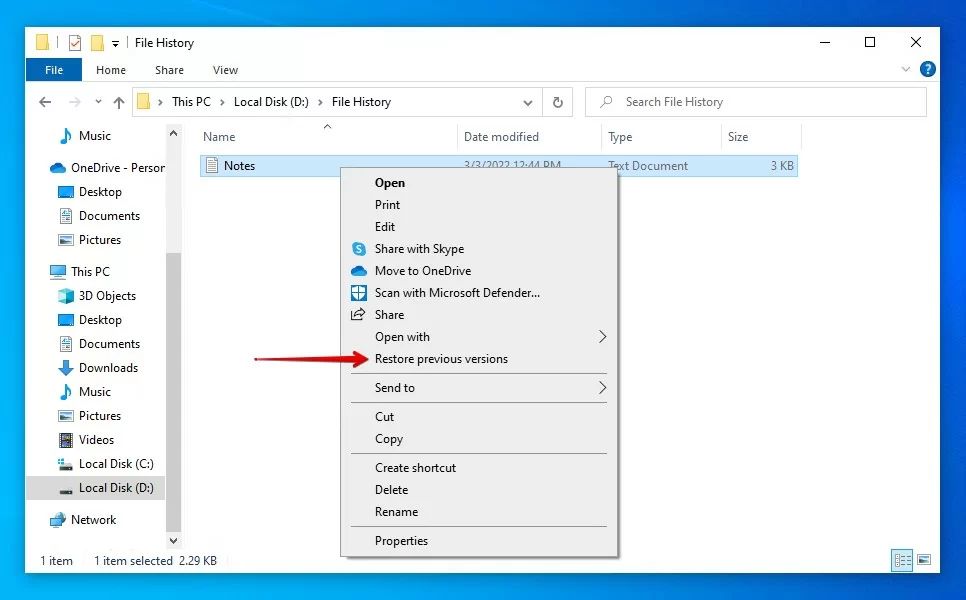
To check for previous versions:
- Navigate to the location of the file in File Explorer.
- Right-click on the file and select ‘Restore previous versions’ from the menu.
- In the file properties window that opens, switch to the Previous Versions tab.
- You should see a list of older versions of that file along with the date they were saved. Select a version to restore.
Previous Versions uses Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) to take snapshots of files at certain points in time as a form of backup. This allows you to restore older “shadow copies” if needed. However, it only keeps snapshots periodically and for a limited time, so older versions may not always be available.
Mac OS Time Machine
On Mac OS, Time Machine offers full backups at specific intervals that you can browse and restore from. To use Time Machine to find a previous version of a file:
- Open the Time Machine interface – you can click the Time Machine icon in the Dock or use the menu bar item.
- Browse through the timeline of file history snapshots to find the version you want to restore.
- Select the file and click Restore to retrieve the older copy, which will be saved back to its original location.
Time Machine needs to have been already configured and actively backing up your Mac to an external drive in order to have file snapshots to restore from. If you did not have it set up before losing the file, Time Machine likely won’t help recover that version.
Other versioning tools
Some other backup tools and cloud services also keep older copies of files that you may be able to restore:
- iCloud – Users can access previous document versions saved to iCloud.
- Google Drive – Offers a revision history showing past versions of Google documents and 30-day backups for other files.
- Dropbox – Maintains 30-day history of deleted and earlier versions of files.
- Box – Retains 30-day simple file versioning with Box file streaming.
If you use one of these services for the lost file, check to see if they have a copy you can roll back to. But be aware that they have time limits on how far back versions are stored.
Use Backup Software to Restore
Backup software that creates system images or full disaster recovery backups provide another option for retrieving previous copies of your files. They can restore entire partitions or drives to a time before the file was overwritten.
Some popular backup utilities to try:
- Veeam Agent – Allows recovery of previous versions of files, folders, or entire volumes from image backups.
- Acronis True Image – Can browse and restore from file versions in full system backups.
- Macrium Reflect – Restores previous file versions and folders from image backups.
- AOMEI Backupper – Has a Previous Version feature to recover older file versions from system backups.
The key when using backup software is having a backup that contains the older version you need. If the backup was done after you overwrote the file, it won’t help get that version back. You will need a system restore point or image backup from before the file was overwritten.
Some backup tools also include standalone disk imaging capabilities that may be able to restore older copies of files and folders without a full system backup.
Use File Recovery Software
If system backups and version histories don’t have the older file version you need, the next option is dedicated file recovery software. These tools scan your drives and attempt to retrieve deleted files that have not yet been completely overwritten with new data.
Some top file recovery programs include:
- EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard – Allows finding and restoring previous versions of overwritten or deleted files.
- Stellar Data Recovery – Scans and can recover previously saved over files.
- Disk Drill – Has Quick and Deep scan options to restore lost file versions.
- Recuva – Ability to restore prior versions of damaged or overwritten documents.
File recovery has the best success right after data loss occurs and before continuing normal system use that could further overwrite the file. For the best results:
- Stop using the device with the lost file immediately after realizing the overwrite occurred.
- Use recovery software to scan the drive from another computer.
- Search recovered files and restore the needed version to another drive.
Advanced recovery software may provide additional options like targeted deep scanning for office documents or certain file types that can help improve your chances.
Check Cloud Storage
Next, check any cloud storage services you use for storing your files. Some key services to check include:
Google Drive
Google Drive keeps 30-day revision history for many file types including Google documents, spreadsheets and drawings. You can browse and restore previous versions within that window. It also retains deleted files for up to 25 days for possible recovery.
Dropbox
Dropbox has a 30-day version history and extended deleted file retention of up to 180 days for Dropbox Plus users. You can restore previous copies of overwritten or deleted files within those time periods.
Microsoft OneDrive
OneDrive has a simple File Version History option that retains earlier copies of files for up to 30 days after changes. Users can browse and restore previous iterations.
OneDrive also saves deleted files for an additional 30 days for OneDrive Personal subscribers, just in case.
Other services
Services like Box, iCloud and Amazon Cloud Drive also provide some basic file versioning that you can review and roll back from if applicable. Their retention time frames and features vary.
The benefit of cloud storage is that it offers an off-site backup if you accidentally overwrite or delete a file locally. As long as the cloud copy still exists, you can restore it to your device.
Check Email
Depending on the situation, your email may also house an older copy of the lost file. Some potential email options include:
- Sent attachments – If you previously emailed the file to someone, your email account will have a sent copy.
- Received attachments – Someone may have emailed the missing file version to you previously.
- Drafts – Check for draft emails where you attached the file but didn’t send.
Webmail like Gmail also keep files in your Google Drive account, so even deleted emails may still have recoverable file versions attached if recovery options like “Restore deleted messages” are enabled.
Dedicating some time to thoroughly searching your email can uncover an important missing document in a pinch if all other options are exhausted.
Prevent Files From Being Overwritten
While you hopefully can restore your important overwritten file using one of these methods, it’s always best to try and avoid losing your files in the first place. Here are some tips to help prevent accidental overwrites:
- Be extra cautious when saving: Always double check you are using Save As for important files instead of just Save to avoid overwrites.
- Enable AutoRecover: AutoRecover in Office apps saves regular versions as you work in case of crashes.
- Configure backups: Use comprehensive backup software or system images to protect your files.
- Leverage cloud storage: Cloud services give you an alternate copy if you accidentally overwrite locally.
- Version files: Apps like Word can automatically retain past versions as you edit.
- Limit permissions: Using read-only sharing where possible can help avoid unintentional overwrites.
Getting into consistent habits with your file management and utilizing all backup options available to you minimizes the chances of ever needing to rely on file recovery. But it’s useful to know these options in case of emergency data loss.
Conclusion
When important files are accidentally overwritten, there are often still ways to get them back. Your operating system may have built-in file history or versioning you can leverage to restore previous copies on your local drive. Backup software provides another option to retrieve files from before the overwrite occurred.
Powerful file recovery tools can scan drives and find unsaved information that hasn’t yet been completely written over. Cloud storage services give you an alternate avenue to look for versions stored remotely. And in certain cases, your own email archives could retain an older iteration of the lost data.
While it takes some effort, with the right tools, attention to detail, and prompt action, you can often recover a file assumed to be long gone. Just be sure to be more careful in the future to configure backup systems, enable versioning, and use file management best practices to avoid finding yourself in this situation again down the road.