The ability for software or devices to work across different operating systems and platforms is incredibly important in today’s technology landscape. With so many devices and platforms, users expect their files, apps, and data to be accessible and usable no matter what system they are on. This is where file systems come in. File systems are a core part of any operating system and determine how data is stored, organized and retrieved. Some file systems are designed for specific operating systems while others are made to work across platforms.
When looking at cross-platform ability, the file system is a key consideration. Being able to read, write, and transfer files between different devices and operating systems – whether Windows, Mac, Linux, Android, etc – requires having a file system that has built-in compatibility and support across platforms. The importance of cross-platform file systems is that they allow seamless data sharing and usage across devices, removing frustrating limitations of device-specific file systems. As technology continues advancing, cross-platform file systems will only grow in significance.
What is exFAT?
exFAT (Extensible File Allocation Table) is a file system introduced by Microsoft in 2006 and optimized for flash memory such as USB flash drives and SD cards (Wikipedia). It was designed to replace FAT32 as the preferred file system for flash storage like flash drives and SD cards. exFAT’s main advantages over FAT32 are support for much larger file sizes and better performance for large files and on memory cards.
Some key characteristics of exFAT (Microsoft):
- Supports maximum file size of 16 exbibytes (EB)
- Uses 64 bits to describe file size to enable large file support
- File system optimized for flash memory such as USB flash drives and SD cards
- Lower overhead than NTFS for reading and writing small files, ideal for flash storage
Overall, exFAT was designed by Microsoft as an optimized file system for flash media like USB drives and memory cards where FAT32 was too limited.
What is NTFS?
NTFS (NT File System) is a proprietary file system developed by Microsoft. It is the standard file system for Windows NT, including all modern Windows versions like Windows 10. NTFS was designed for hard disks larger than 32 MB and to overcome limitations of the previous FAT file system (TechTarget).
Some key features of NTFS include:
- Support for larger partition sizes – up to 16 exabytes
- Improved reliability and disk space utilization
- File system journaling to prevent data corruption
- Native encryption and compression
- Advanced security permissions for files and folders
NTFS is the default file system for Windows PCs today, delivering higher performance and stability versus older file systems like FAT32. It offers important features for protecting and organizing data on modern high-capacity hard drives.
Compatibility
exFAT works natively with both Windows and Mac operating systems, making it a convenient choice for cross-platform external storage devices like USB drives or SD cards. According to PCMag, exFAT “works on Windows and Mac right out of the box.”
In contrast, NTFS is natively compatible only with Windows operating systems. Macs can read NTFS drives but need third party software to write to them. Per TWiT, “NTFS isn’t really designed for removable storage.” So for external drives used across Windows and Mac, exFAT offers better cross-platform compatibility.
File Size Limits
Both exFAT and NTFS have much higher maximum file size limits compared to the FAT32 file system. According to the exFAT Wikipedia page, exFAT supports files up to 16 exabytes (EB) in size. The exFAT vs. FAT32 Comparison states exFAT’s maximum file size as 18EB. In contrast, NTFS supports much larger maximum file sizes up to 16 EB or 18 quintillion bytes [1]. Therefore, while exFAT allows significantly larger file sizes than FAT32, NTFS supports even larger maximum file sizes compared to exFAT.
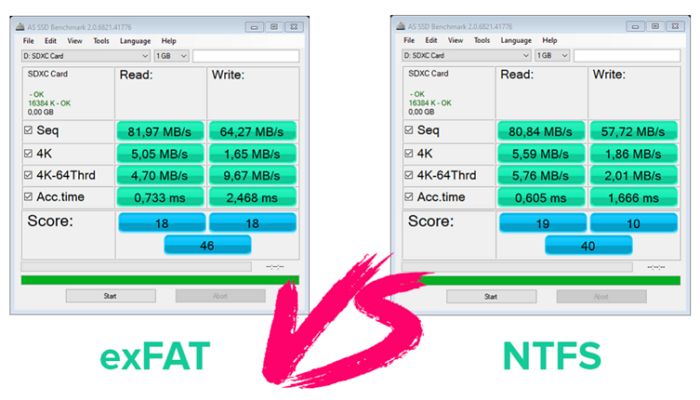
Performance
When it comes to performance, NTFS is generally faster than exFAT for Windows systems, but exFAT is faster on macOS. According to FAT32 vs. exFAT vs. NTFS USB3 Performance Comparison, NTFS delivers up to 68% faster performance than exFAT for file deletion on Windows. However, for macOS, exFAT performs file operations faster than NTFS since Apple specifically optimized exFAT for better performance on macOS.
The reason NTFS is faster on Windows is because Microsoft developed and optimized NTFS specifically for Windows. The file system is tightly integrated with the Windows kernel for better performance. In contrast, exFAT was designed for interchangeability between operating systems rather than performance. So while exFAT works across macOS, Windows, and other systems, it’s not tuned for peak performance on any specific OS.
In summary, for optimal performance on Windows, NTFS is the better choice. But on macOS, exFAT will provide faster file transfers and operations. The performance difference matters most for large files and disk-intensive operations like video editing or managing photo libraries.
Reliability
When it comes to reliability, NTFS generally has the advantage over exFAT. NTFS employs journaling and other features to ensure file system integrity and recoverability in case of corruption or crashes.
As noted in this analysis, exFAT only uses a single file allocation table (FAT) whereas older FAT32 uses two copies for redundancy. This means NTFS has more built-in protection against data corruption.
NTFS also utilizes logging and checkpoints to track system changes. If an unexpected shutdown occurs, NTFS can roll back to a last known good state during the recovery process. exFAT does not have this capability. As one expert pointed out on Super User, NTFS’s journaling helps ensure better protection and recovery from corruption issues.
Therefore, for storage devices where reliability is critical, NTFS is generally the safer choice over exFAT due to its more robust journaling and recovery features.
Security
NTFS supports more robust security features compared to exFAT. Some key differences:
- NTFS allows you to set granular permissions on files and folders, restricting access to specific users or groups. exFAT has no permissions system. All files are accessible to anyone with physical access to the disk.
- NTFS supports encryption at the file system level via the Encrypting File System (EFS). This allows files and folders to be transparently encrypted. exFAT does not support encryption.
- NTFS provides auditing features to track file access and modifications. exFAT does not have auditing capabilities.
- NTFS supports Access Control Lists (ACLs) for even more granular control over file permissions. exFAT lacks ACL support.
In summary, if you need to securely store sensitive data on a drive that will be accessed by multiple users, NTFS is a better choice due to its extensive security mechanisms like encryption and permissions.[1][2]
When to Use exFAT vs NTFS
Both exFAT and NTFS have advantages and disadvantages that make them better suited for certain use cases. Here are some guidelines on when to choose exFAT or NTFS:
Use exFAT for:
- External storage devices under 2TB that will be used with Windows and macOS
- USB flash drives that will transfer files between macOS and Windows devices
- SD cards and other removable media that will be used across operating systems
exFAT has good cross-platform compatibility, and performs well enough for most external storage needs under 2TB. Its lack of journaling and other security features make it less ideal for internal or system drives.
Use NTFS for:
- Internal hard drives on Windows computers
- External hard drives over 2TB on Windows
- Drives that require advanced security features like file permissions and encryption
- Drives where maximum performance and reliability are needed
NTFS is ideal for internal Windows system drives, thanks to features like journaling and access control lists. It can also handle very large partitions over 2TB. But NTFS should be avoided for external drives that will be used across operating systems, due to limited macOS support.
In general, exFAT works best for external storage under 2TB that will be used across Windows and Mac devices. For larger partitions or drives that will be used solely in Windows, NTFS is likely the better choice.
Conclusion
In summary, the key differences between exFAT and NTFS are:
- Compatibility – exFAT is compatible with both Windows and macOS, while NTFS is limited to Windows without additional software.
- File size limits – exFAT supports larger individual file sizes up to 16EB, while NTFS limits individual files to 16TB.
- Performance – NTFS generally has faster read/write speeds while exFAT favors compatibility.
- Reliability – NTFS is more reliable and less likely to be corrupted.
- Security – NTFS has more built-in security features like file/folder permissions.
For storage that will be used across both Windows and Mac computers, exFAT is likely the better choice for its plug-and-play compatibility. For storage that will only be used on Windows machines, NTFS is preferable for its better performance, reliability, and security.
For large media files above 16TB, exFAT is required as NTFS has file size limits. In general, exFAT favors easy cross-platform access while NTFS provides speed and control at the expense of compatibility.