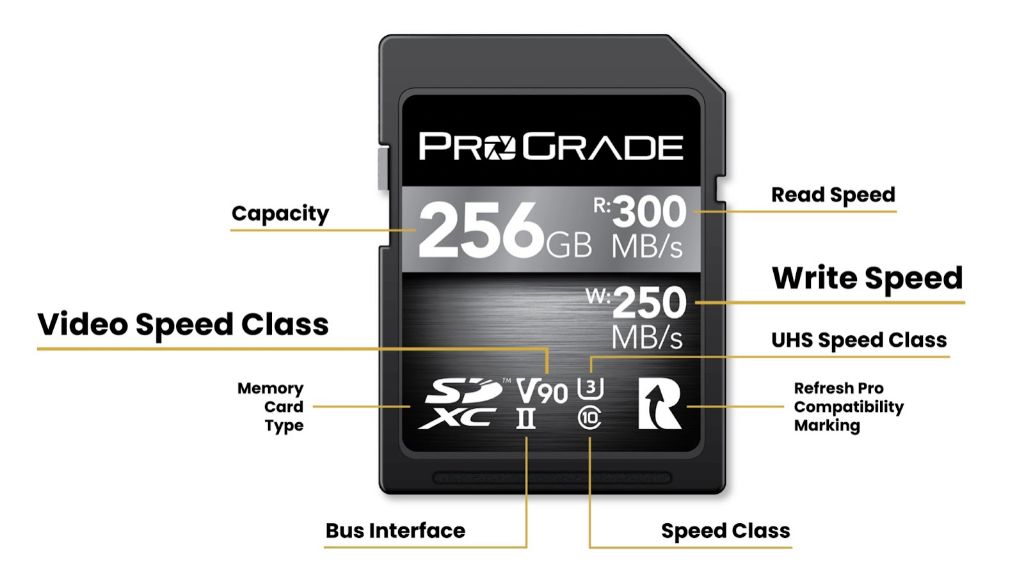
SD cards have different speed classes that denote the minimum guaranteed speeds they are capable of. The speed class gives you an idea of the minimum write and read speeds to expect from that card. With the proliferation of high-resolution photos and 4K video, you need cards with faster write speeds for recording these large files to your device without having to wait for the card to catch up.
What are the different SD card speed classes?
SD cards come marked with speed classes 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, U1, U3, V6, V10, V30, V60, and V90. Each designates a minimum speed guarantee in MB/s as below:
| Speed Class | Minimum Write Speed |
|---|---|
| Class 2 (C2) | 2 MB/s |
| Class 4 (C4) | 4 MB/s |
| Class 6 (C6) | 6 MB/s |
| Class 10 (C10) | 10 MB/s |
| UHS Speed Class 1 (U1) | 10 MB/s |
| UHS Speed Class 3 (U3) | 30 MB/s |
| Video Speed Class 6 (V6) | 6 MB/s |
| Video Speed Class 10 (V10) | 10 MB/s |
| Video Speed Class 30 (V30) | 30 MB/s |
| Video Speed Class 60 (V60) | 60 MB/s |
| Video Speed Class 90 (V90) | 90 MB/s |
The SD Association has standardized these speed classes to help consumers pick the right card for their recording needs. The classes denote the minimum sustained write speed in MB/s that the card guarantees. So a Class 10 card promises a minimum write speed of 10 MB/s, while a UHS Speed Class 3 (U3) card guarantees a 30 MB/s minimum write speed.
Do faster classes mean better performance?
Yes, a faster class card indicates better performance. A higher speed class denotes faster read and write speeds. So a Class 10 card will outperform a Class 4 card. And a U3 class card will be faster than a Class 10 card.
Higher speed cards have faster rated read and write speeds. They can read and write your data much quicker than lower speed cards. This means less waiting when transferring photos, videos and other files to and from the card.
Benefits of higher speed classes
- Faster shooting – Class 10 and UHS cards allow your camera to capture images quicker in burst mode.
- Less shutter lag – Higher speed cards have faster write times so the buffer clears quickly, reducing shutter lag.
- Faster continuous shooting – The faster write speeds help maintain burst mode image capture.
- Quick transfer times – Higher speed cards can read/write your data much faster to computers and other devices.
- Better full HD and 4K video recording – Video Speed Class cards ensure minimum speeds needed for high resolution video capture.
- Smooth video recording – Faster cards allow uninterrupted recording of high bitrate video without frame drops.
Higher speed cards are recommended if you shoot a lot of burst photos, full HD or 4K videos, or use a camera with high megapixels and data write needs.
Do all devices support fast SD cards?
No, the device where the SD card is used needs to be compatible with the speed class. Older devices may not be able to support the high data rates of faster cards. Using a fast card in an incompatible device will restrict the card to lower speeds. The device determines the actual speed, the class only denotes the minimum guaranteed speed.
Factors determining max SD card speed
- Device card slot – The SD card slot needs to support the interface (SDHC, SDXC) for high capacity cards. Older devices may only support up to 2GB cards.
- Card reader/writer speed – Card readers or writers may limit max speeds to below what the card can support.
- USB standard – The USB version (e.g. USB 2.0, USB 3.0) used to transfer data from the card also affects speeds.
- Camera/device specs – The camera image processor and data bus affect its ability to utilize high speed cards fully.
Always check your device specs to ensure compatibility with high speed SD cards to be able to use their full potential. Else the card will be restricted to your device’s max speed support.
Do all Class 10 cards have the same speeds?
No, Class 10 only signifies a minimum 10MB/s write speed. Actual write speeds can vary across Class 10 cards based on:
Factors affecting Class 10 card speeds
- Memory technology – Cards using UHS-I and UHS-II interfaces are faster than plain Class 10 cards using just SDHC or SDXC.
- Brand and model – Due to different controllers and memory technology, write speeds vary across cards of same class.
- Capacity – Generally higher capacity cards are faster as they use more parallel NAND flash memory chips.
- Testing conditions – The test environment like OS, card reader, test software etc. impact measured speeds.
While Class 10 cards from different brands vary in actual speeds, they are guaranteed to deliver at least 10MB/s writes. So they will all outperform Class 4 or Class 6 cards in terms of speed.
Are UHS-I cards faster than Class 10 cards?
Yes, UHS-I cards are faster than regular Class 10 SDHC cards. The Ultra High Speed Phase I (UHS-I) interface allows faster data transfer compared to plain Class 10 cards using just the SDHC specification.
UHS-I cards support up to 104 MB/s transfer whereas Class 10 SDHC are limited to 25 MB/s. So UHS-I cards can reach higher actual write speeds compared to Class 10, though both guarantee 10 MB/s minimum write.
UHS-I also supports advanced memory card architecture enabling faster local data transfer within the card, contributing to the speed gain over Class 10.
Comparison between Class 10 and UHS-I SD cards
| Class 10 SDHC | UHS-I SDHC | |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum write speed | 10 MB/s | 10 MB/s |
| Maximum data bus speed | 25 MB/s | 104 MB/s |
| Interface | SDHC | SDHC, UHS-I |
| Advanced architecture | No | Yes |
The higher interface speed and improved architecture make UHS-I cards faster overall than regular Class 10 cards of same capacity and brand.
Are V30 and V60 cards the same speed?
No, V30 and V60 cards are not the same speed. The V30 and V60 ratings denote minimum write speeds but don’t indicate maximum speeds.
V30 cards guarantee a minimum sustained 30MB/s write speed. V60 cards assure minimum 60MB/s write speeds. Both ratings are for video recording speeds.
But V60 cards used in devices supporting UHS-II and UHS-III interfaces can reach maximum write speeds of 156MB/s or 312MB/s respectively. Whereas V30 cards have upper speed limit of 104MB/s in UHS-I supported devices.
So V60 cards have double the guaranteed minimum speed and also twice the maximum potential write speeds compared to V30 cards. A V60 card will outperform a V30 card from the same manufacturer when used in a compatible device.
V30 vs. V60 speed comparison
| V30 | V60 | |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum sustained write | 30 MB/s | 60 MB/s |
| Maximum interface speed | 104 MB/s (UHS-I) | 156 MB/s (UHS-II) 312 MB/s (UHS-III) |
| Intended use | Full HD, 4K video | 8K video |
While V60 cards assure double the minimum speeds over V30 ones, their maximum potential is even higher in devices supporting UHS-II and UHS-III interfaces.
Do Application Performance Class cards matter?
Application Performance Class is an optional speed rating geared towards apps with sustained random writes like 4K video recording. Cards are assigned classes of A1 and A2 denoting minimum speeds.
The A1 class guarantees a minimum of 1500 read IOPS and 500 write IOPS (4KB random writes). The A2 class assures 4000 read IOPS and 2000 write IOPS.
This speed rating matters for devices like action cams and drones that record high resolution video at high frame rates. It indicates the SD card is optimized for sustained random write performance needed for smooth 4K/8K video capture.
However, the rating is optional and mainly used as marketing. For most users Class 10 or UHS speed ratings are more useful indicators of a card’s capabilities than the application performance class.
When does application performance class matter?
- Shooting high frame rate 4K, 8K video – Minimizes frame drops and stutter.
- Recording video longer than 5 minutes – Prevents slower write speeds over time.
- Using high resolution, high bitrate video modes – Supports large data volumes.
- Capturing fast action like sports, racing etc. – Smoother autofocus and burst shooting.
- Devices with single card slot – Reduces chance of overflow as buffer clears faster.
For typical use cases like photos, full HD video and casual 4K filming, Class 10 or UHS ratings are sufficient. But devices demanding sustained high speed random writes will benefit from application specified A2 cards.
Do all A2 cards have the same speeds?
No, just like Class 10 and V30 cards, A2 cards also differ in their actual maximum speeds depending on factors like:
Why A2 card speeds vary
- Memory technology – UFS 3.0/3.1 cards are faster than those using UFS 2.0/2.1.
- Capacity – 256GB or higher capacity models outperform 64GB/128GB versions.
- Controller and flash – Quality of components impacts max read/write speeds.
- Interface – UHS-II has over double the interface speed of UHS-I cards.
- Testing methods – Tools, card readers and software used affect results.
While guaranteed speeds are similar for A2 cards from different brands, their maximum read and write speeds can vary widely. Checking manufacturer ratings for maximum speeds can help pick the fastest A2 card of a given capacity.
Conclusion
SD card speed classes denote the minimum performance users can expect for that card in capable devices. While classes only specify a minimum speed “floor”, actual speeds can go higher depending on factors like interface, capacity, controller and flash memory.
Newer standards like UHS-II/III and UFS 3.0/3.1 allow substantially higher card speeds compared to older interfaces like SDHC and UFS 2.0/2.1. So two cards of the same speed class can have very different maximum speeds based on the memory technology used.
For best performance, matching your device’s SD card interface with compatible cards that use that interface is recommended. Else the card’s interface will downgrade to your device’s max interface support, not utilizing the card’s full capabilities.
Understanding SD card speed classes and interfaces helps pick cards optimized for your use – whether photos, full HD or 4K/8K video or high resolution modes demanding fast continuous shooting.