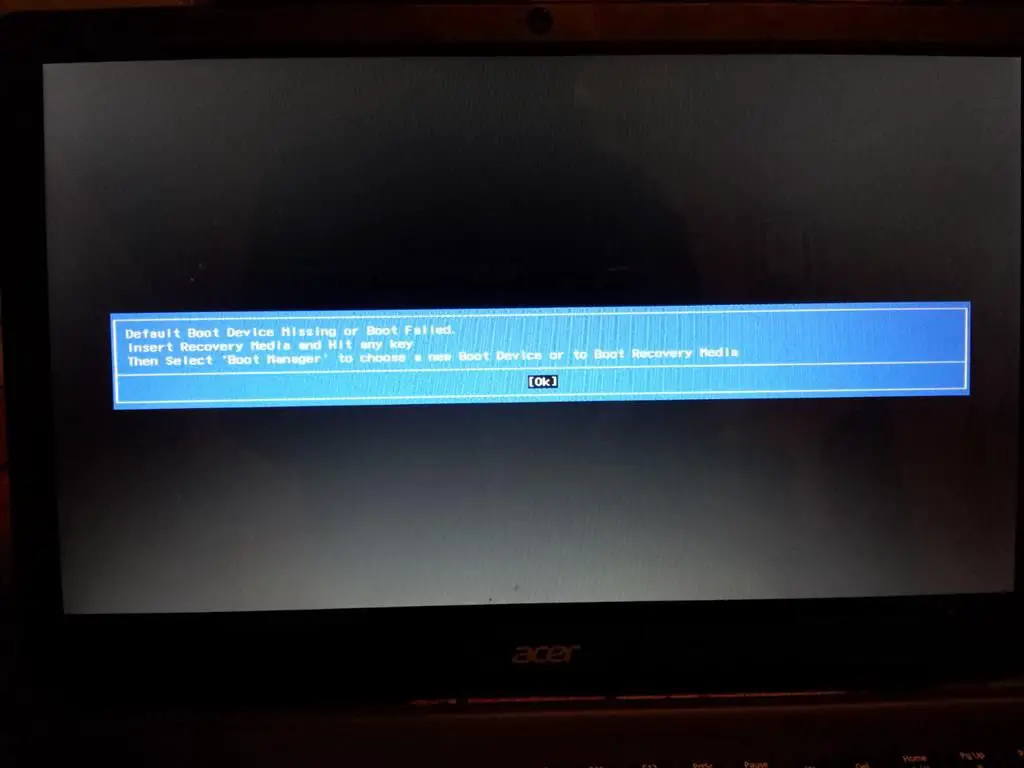
The “no boot device found press any key to reboot the machine” error message indicates that the computer is unable to find a bootable device during the boot process. This usually means that there is no bootable operating system installed on the hard drive or the boot configuration is incorrectly set.
Common Causes of the Error
There are several potential causes for the “no boot device found” error message:
- Hard drive failure – If the hard drive has failed or is corrupted, the computer may not be able to access the boot files and operating system.
- Disconnected or damaged hard drive – If the hard drive is disconnected, loose, or damaged, the computer will not be able to locate the boot files.
- Missing operating system – If the hard drive does not contain an operating system or the main partition has been deleted or corrupted, there will be no boot files to start the system.
- Boot order not set correctly – The BIOS boot order may be configured incorrectly, so the computer tries to boot from the wrong device.
- Damaged bootloader – Issues with the Master Boot Record (MBR) or EFI boot partition can prevent loading the operating system.
- Hard drive not detected – If the BIOS cannot detect the hard drive, it will not be able to boot from it.
Troubleshooting Steps
Here are some steps to troubleshoot the “no boot device found” error:
- Check hard drive connections – Power off the computer, open the case, and check that all hard drive cables are firmly plugged into the motherboard and hard drive.
- Inspect hard drive for damage – Look for any signs of physical damage on the hard drive like scratches or cracks. If the drive is making unusual noises, it may be failing.
- Boot from a different device – Try removing all attached devices except the hard drive and booting the computer. You can also try booting from an external USB drive or bootable CD/DVD.
- Enter BIOS setup – Access the system BIOS, typically by pressing F2, F10, or Delete during bootup. Check that the hard drive is listed in the boot order and set as the first boot device.
- Reset BIOS to factory defaults – Reset BIOS settings to their factory defaults in case they have been modified incorrectly.
- Replace cables and reseat hard drive – Replace any potentially faulty SATA data/power cables connecting the hard drive to the motherboard. Reseat the hard drive firmly.
- Check hard drive partition table – Use disk management or partition software to verify the hard drive has a valid partition table with a detectable file system like NTFS or FAT32.
- Reinstall operating system – If no hardware issues are found, you may need to reinstall your operating system from recovery media or a bootable installer drive.
- Replace hard drive – If all else fails, the hard drive itself may need to be replaced with a new drive that contains an operating system.
Causes Explained
Hard Drive Failure
One of the most common reasons for the “no boot device” message is a hard drive failure. If the hard drive has malfunctioned or is severely corrupted, the computer will not be able to access the critical boot data and operating system files stored on it. Hard drive failures can occur for many reasons:
- Mechanical failure – Disk read/write heads and motors can wear out over time and prevent access to data.
- Electrical failure – Short circuits, failed components, power surges can render a hard drive inoperable.
- Logical failure – File system corruption, failed sectors, viruses can damage the integrity of data on the drive.
- Physical damage – Dropping/impacting a hard drive can damage internal components and heads.
Signs of hard drive failure include the computer failing to boot, unusual beeping sounds, grinding noises from the drive, and obvious physical damage. If the BIOS does not detect the drive at all, it’s highly likely the drive has completely failed or has serious corruption.
Disconnected or Damaged Hard Drive
If the hard drive has become physically disconnected from the motherboard or damaged, this can generate the “no boot device” message:
- Loose cables – Power and data cables that connect the hard drive to the motherboard need to be firmly seated. If vibrations or movement have loosened the cables, it can break the connection.
- Dislodged drive – It is possible for hard drives to become slightly dislodged from their mounting, especially in laptops. This can misalign the connectors between the drive and computer.
- Broken connector – Excessive force or strain on a cable can damage the SATA hard drive connector pins. A broken connector will prevent communicating with the drive.
Carefully reseating cables and the hard drive may help resolve these types of issues. Visually look for any damaged ports or connectors on cables and drives.
Missing Operating System
The boot error can also appear if the hard drive does not contain any operating system at all, or the main system partition has been deleted, corrupted, or otherwise lost. Potential scenarios include:
- New drive – A brand new hard drive that has not had an OS installed on it yet cannot boot.
- Replaced drive – If you replace the original hard drive with a new blank drive, it will not have an OS to boot from.
- Reformatted drive – Reformatting or deleting all partitions causes all data, including operating systems, to be erased.
- OS corruption – A corrupted registry or system files due to viruses, system crashes, or errors can render an OS unbootable.
In these cases, a new OS will need to be installed like Windows or Linux to restore normal boot functionality.
Boot Order Incorrect
The system BIOS checks a defined boot order of devices to load an operating system from. If this order gets changed or configured incorrectly, the BIOS may skip the hard drive entirely during bootup. Common causes include:
- Boot sequence changed – Adding or removing devices like USB drives can alter the boot order set in BIOS.
- Trying to boot from wrong device – The BIOS may be set to check for boot files on a disconnected DVD drive or USB first.
- BIOS reset – Resetting or updating the BIOS may revert the boot order back to factory settings.
- Boot options modified – Advanced BIOS options like UEFI/legacy modes, secure boot, or boot protocols can interfere with bootability if settings are incorrect.
Entering the BIOS setup menu during boot and correcting the boot sequence will typically resolve this problem.
Damaged Bootloader
The bootloader is programming located in specific areas of the hard drive that launches the operating system. If this data gets corrupted or overwritten, the computer will not boot properly. The two main bootloaders used are:
- Master Boot Record (MBR) – Used on older BIOS/legacy systems. The MBR resides at the very beginning of the hard drive.
- EFI System Partition – Newer UEFI systems use the EFI bootloader located on a special partition on the hard drive normally labeled “System”.
Damaging the bootloader can happen due to:
- Virus infection – Viruses and malware sometimes specifically target and overwrite the MBR/EFI bootloader code.
- Accidental deletion or overwrite – Deleting all partitions or repartitioning the drive incorrectly can erase the bootloader location.
- Drive errors – Bad sectors where the bootloader resides can corrupt the data.
- Incorrect BIOS mode – Trying to boot EFI with legacy BIOS or vice versa often results in unbootable systems.
Typically requires advanced recovery methods to rebuild or replace damaged bootloader data.
Hard Drive Not Detected
If the BIOS cannot detect the physical hard drive hardware, it will not be able to access it to boot an operating system:
- Disconnected drive – A loose cable or connection issue can prevent the hard drive from being detected.
- Disabled in BIOS – Hard drive interfaces like SATA can sometimes be disabled in BIOS, hiding the drive.
- Failed controller – The disk controller that manages the hard drive may have failed.
- Incompatible storage drivers – An incorrect driver, improper AHCI/RAID mode, or other disk mode may hide the hard drive.
Reseating connections, enabling the SATA interface, updating BIOS and chipset drivers may help get the hard drive detected again so it can boot.
Recovering from the Error
Here are some options for recovering from the “no boot device found” error if troubleshooting does not resolve it:
Reinstall Operating System
If the hard drive is functional, reinstalling the operating system fresh is usually the quickest way to restore bootability:
- Boot from recovery media or a bootable USB installer drive.
- Erase or reformat the internal hard drive partitions.
- Clean install the OS to the internal drive, including bootloaders.
- Reboot and the computer should load the new OS.
Replace Hard Drive
For defective hard drives that cannot be repaired, replacement is required:
- Physically install a new internal SATA hard drive or SSD.
- Partition and format the new drive using another computer or external adapter if needed.
- Install the operating system to the new drive with bootloaders.
- Swap recovered data backups if needed.
The computer should now boot properly from the new hard drive.
Send for Professional Repair
For advanced troubleshooting like corrupted bootloaders, boot issues, or physical damage, a computer repair shop may be required:
- Repair technicians can analyze hardware issues and attempt data recovery from damaged drives.
- They have access to advanced diagnostic tools, partition editors, and boot repair software.
- Physical damaged components like connectors or controller boards can be replaced.
- A repair shop can properly install and configure new hard drives.
While costly, a professional repair ensures the computer boots correctly and avoids making novice mistakes.
Preventing the Error
You can take proactive measures to help prevent the “no boot device found” error:
- Regularly backup critical data and operating systems.
- Keep BIOS firmware, drivers, and OS updated.
- Use protective cases for laptop hard drives.
- Carefully handle hard drives when transporting or installing them.
- Use surge protectors and UPS battery backups.
- Monitor hard drives for early failure warning signs like bad sectors.
- Avoid questionable downloads or sites that could contain malware.
Conclusion
The “no boot device found” error indicates the computer cannot find a bootable operating system on storage devices during system initialization. It is most often caused by hard drive issues like corruption or hardware failure. Checking connections, troubleshooting the hard drive, replacing cables, correcting boot order in BIOS, reinstalling operating systems, replacing the hard drive, and professional repair are common solutions. With proper care and maintenance, the error can often be prevented by protecting hard drives from damage and keeping firmware and software updated.