Expandable storage has long been a popular feature on Android phones, allowing users to increase the storage capacity of their devices using external SD cards. While some Android phones in recent years have dropped support for expandable storage, many models still retain the ability to use SD cards.
There are several reasons why Android users may want to expand their phone’s internal storage capacity with an SD card. As camera resolutions and video quality continue to improve on smartphones, media files take up more and more space over time. Games and apps are also increasing in size. This can quickly eat into the finite internal storage on a phone. An SD card provides a convenient way to add substantial additional storage, often hundreds of gigabytes extra, while retaining the same phone.
Using an SD card allows users to store more photos, videos, music, apps and files. It provides flexibility to manage which data is stored internally vs externally. One can keep frequently accessed apps on the faster internal storage, while relegating media files and backups to the removable SD card. Overall, expandable storage is a simple way for Android users to customize their phone’s storage capacity as per their needs.
What is an SD Card?
An SD card, or Secure Digital card, is a small removable flash memory card used for storing photos, videos, music, and other files on devices like digital cameras, smartphones, and tablets. The name ‘Secure Digital’ comes from the encryption technology originally used to protect the stored data.
SD cards were first introduced in 1999 by Panasonic, SanDisk and Toshiba as an improvement over MultiMediaCards (MMC). They offered greater storage capacity and speed compared to previous formats like CompactFlash. Over the years, SD cards have evolved to support higher data transfer speeds and increased storage capacity up to 2 terabytes.
There are several types of SD cards available today, categorized by their physical dimensions. The most common are:
- SD – original size
- miniSD – smaller size
- microSD – smallest size often used in smartphones and tablets
SD cards are also given speed classes which signify their minimum guaranteed transfer speed. Common speed classes are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 with higher numbers indicating faster read/write speeds. Newer SD cards support ultra high speeds over 100MB/s.
Overall, SD cards provide a convenient way to add more storage space to devices and transfer files between gadgets. Their small size and plug-and-play functionality have made them a ubiquitous standard for removable storage.
SD Card Specifications
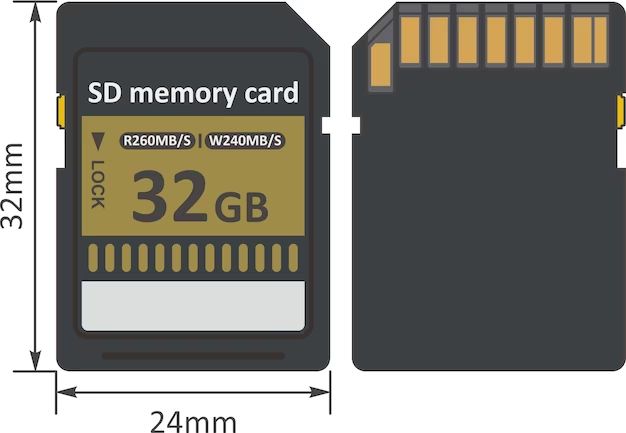
SD cards have specific physical dimensions and capacities that determine compatibility and performance. The physical size of SD cards is 32 mm × 24 mm × 2.1 mm (1.26 in × 0.94 in × 0.083 in), weighing around 2 grams. The storage capacities range from 4GB to 2TB for SDXC cards.
There are also speed classes that indicate the minimum guaranteed speeds. The main classes are 2, 4, 6, 10 for the minimum write speeds in MB/s. UHS speed classes U1 and U3 further subdivide those for SDHC and SDXC cards. All SD cards are backwards compatible with devices that support lower speeds.
In summary, key SD card specifications involve the physical size, storage capacity ranges, speed classes denoting minimum write speeds, and backwards compatibility across types and speeds (CDW).
Max SD Card Size for Android
Theoretically, the maximum SD card size for Android devices is 2TB based on the SDXC standard. However, there are some practical limitations:
Android 4.4 KitKat and older only officially support up to 32GB SD cards, though some devices may unofficially support larger. Android 5.0 Lollipop and newer support SDXC cards up to 2TB (Source).
Many Android phones have model-specific limitations, capping support below 2TB. For example, the Galaxy S21 lineup only supports up to 1TB (Source). Older devices may have even lower limits, like 256GB.
There are few 2TB SD cards on the market, and compatibility cannot be guaranteed. 1TB cards are more common among higher capacity offerings.
In summary, while 2TB is theoretically possible, real-world limits are lower. Check your Android version and specific phone model specs to determine the maximum supported capacity.
Tips for Choosing an SD Card
When shopping for an SD card for your Android device, here are some tips to ensure you choose the right one:
Stick to Known Brands
It’s generally best to choose an SD card from a well-known brand like SanDisk, Samsung, Sony, or Kingston. Lesser-known brands may be cheaper but are more likely to result in performance or reliability issues down the line (CNET).
Choose Appropriate Speed Class
Pay attention to the SD card’s speed class rating, which indicates the minimum write speed it supports. For 4K video recording, look for UHS Speed Class 3 (U3) or Video Speed Class 30 (V30) cards. For full HD video and burst photo shooting, UHS Speed Class 1 (U1) or Class 10 cards should suffice (Kingston).
Balance Price and Performance
Higher speed cards usually cost more. Consider how you plan to use the card and choose the least expensive option that meets your performance needs.
Consider Application Needs
If you plan to store a lot of apps or games on the SD card, focus on capacity over speed. But for 4K video recording, higher speeds are essential.
How to Insert an SD Card
Inserting an SD card into your Android device is a straightforward process. Here are the steps to follow:
First, locate the SD card slot on your device. This is typically on the side or bottom edge of the phone. The slot may have a cover that you need to open to access it. Be gentle when opening the cover.
Once the slot is accessible, take your SD card and orient it properly before inserting. SD cards have a beveled edge that matches the shape of the slot. Line this edge up and gently slide the card into the slot until it clicks into place.
It’s important to insert the card correctly without forcing it. If you have the wrong orientation or are pushing too hard, you may damage the card or slot. Take care to align the card properly and apply gentle, even pressure to insert it fully.
After the card clicks into place, you should get a notification that new storage has been detected. Your Android device will automatically mount the SD card and make it available for use. The card is now ready to store your files, photos, videos, and apps.
How to Move Apps to SD Card
Moving apps to your SD card can free up internal storage on your Android phone. Here are a few ways to move apps to SD card:
First, you need to enable the ability to move apps to SD card in your phone’s settings. Go to Settings > Apps & notifications > Advanced > Special app access > Storage access. Enable “Allow access to manage all files” for the apps you want to move.
You can then use your phone’s built-in App Manager to move apps. Go to Settings > Storage > Internal Shared Storage > Apps. Tap the app you want to move, then select “Change” and choose your SD card. Repeat for each app.
Some apps like SD Card Manager and Link2SD allow you to move apps in bulk. These tools are useful if you have many apps to move.
You can also move apps individually by going into the app’s info screen. Tap & hold the app icon, tap the “i” icon, select Storage, then change the storage location to your SD card.
Moving apps to SD can help free up internal storage and allow you to install more apps. Just make sure your SD card has enough space for the apps you want to move.
SD Card Maintenance
Proper maintenance is essential to ensure your SD card continues functioning at optimal performance. Here are some tips for maintaining SD cards:
Always safely eject the SD card before removing it from your device. Simply pulling out the card without ejecting can lead to file corruption or data loss. Use your device’s settings to eject the SD card.
Regularly back up important data from the SD card to another storage device or the cloud. This protects your data in case the card becomes corrupted or damaged. Schedule regular automatic backups.
If you encounter a corrupted SD card, first try reformatting it through your device’s settings. This erases the card and creates a new filesystem, potentially fixing software corruption issues. If errors persist, the card may be physically damaged and need replacement.
Upgrade to a newer, higher-capacity SD card as your storage needs increase over time. Newer SD card versions offer faster speeds and greater durability. Check your device specifications to ensure compatibility with the latest standards.
By following these SD card maintenance tips, you can ensure optimal performance and longevity for your valuable data. Remember to format your card regularly, safely eject it, keep it protected, and upgrade when needed.
Sources:
https://butterflycoins.org/topics/650c8e78f79a415125079623
https://www.remosoftware.com/info/sd-cards-explained
SD Card Security
Keeping your SD card and your data secure is important. Here are some tips for SD card security:
Set up encryption – Enabling encryption on your SD card adds an extra layer of security to protect your information if your phone is lost or stolen. Many Android devices allow encrypting external SD cards in the security settings.
Beware public computers – Avoid accessing files on your SD card when connecting your phone to a public computer. Only use trusted devices to help prevent malware infections.
Enable permissions – Set up individual app permissions for reading/writing to the SD card to limit exposure. Disable permissions for apps that don’t need access.
Use antivirus – Install a highly-rated antivirus app on your Android device to scan your SD card and protect against malware. ESET provides top antivirus apps for Android.
Future of Expandable Storage
Despite some manufacturers recently removing microSD card slots from their devices, demand remains strong for expandable storage on Android phones. Many budget and mid-range devices continue offering SD card support as a key feature.
According to an Android Central reader poll in late 2022, over 80% of respondents said expandable storage was an important factor when purchasing a new phone. Comments on Reddit and Quora also indicate microSD is still preferred for storing photos, videos, and large apps.
Manufacturers are expected to release SD cards with 2TB and higher capacities in the coming years. This will enable even more onboard storage for media collections and game apps. Speeds are also increasing, with UHS-III microSD cards now reaching sequential read speeds over 400MB/s.
For phones without expandable storage, consumers rely more on cloud backups and streaming services. However, limited connectivity and privacy concerns remain challenges. High-capacity internal storage is another alternative but often costs much more compared to microSD cards.
Overall, expandable storage looks to have an ongoing role in the Android ecosystem, especially for budget-conscious consumers and heavy media users. Faster SD cards with higher capacities will likely meet demand for the foreseeable future.