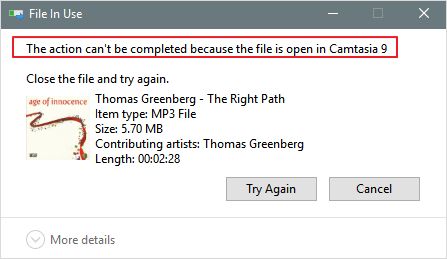
There are a few common reasons why you may be unable to delete a file on your computer:
The file is in use or open
If a file is currently open or in use by an application, you will not be able to delete it. This is because the operating system cannot delete a file that is being accessed. To resolve this, close any programs that may be using the file before attempting to delete it.
You don’t have permissions
On Windows, Mac, and Linux operating systems, files and folders have permissions settings that control which users can access, modify, or delete them. If you try to delete a file but get an “access denied” error, it likely means your user account does not have delete permissions for that file.
To fix this, you need to either change the file permissions to allow your account delete access, or delete the file while logged into an administrator account that has full permissions.
The file is read-only
Making a file read-only prevents it from being modified or deleted. If you try deleting a read-only file, you’ll get an error. To make the file deletable, you need to remove the read-only attribute.
On Windows, right-click the file, select Properties, uncheck Read-only, and click OK. On Mac, use the Get Info window to uncheck Locked.
The file is corrupted
If a file has become corrupted or damaged, trying to delete it may result in errors. Use your operating system’s disk repair and file restore tools to fix the corruption first. On Windows, run CHKDSK. On Mac, run Disk Utility’s First Aid.
The file is located on a read-only drive
Drives can sometimes be set to read-only mode which prevents deleting files. This is common with CD/DVD drives and some external drives. You’ll need to change the drive permissions back to read/write to allow file deletion.
You don’t have enough space on the drive
Deleting a file requires free space on the drive to perform the delete operation. If your drive is completely full, the OS may not let you delete anything until you free up space.
Delete unneeded files to free up space on the drive, then try again. You can also try deleting the file from Safe Mode which requires less free space.
The file is hidden or system protected
Some special hidden or system files are protected from accidental deletion. You may need to unhide the file and disable system protection first before you can permanently delete it.
The file deletion is being blocked by security software
Antivirus software, firewalls, and other security programs can sometimes block file deletion to protect your system. Add an exception for the file in your security software before trying to delete it.
The file path is too long
Operating systems have a maximum file path length. If the full path to the file exceeds that limit, you may get errors when trying to delete it. Shorten the file path by moving it closer to the root directory.
How to Fix “Unable to Delete File” Errors
Here are some step-by-step guides to help you troubleshoot and fix errors when attempting to delete files in Windows, Mac, and Linux operating systems:
Windows File Deletion Troubleshooting
- Close any programs that may be using the file you want to delete.
- Confirm you have permissions to delete the file and folder it is contained in.
- Uncheck the Read-only attribute on the file’s Properties if set.
- Run a disk check and repair any errors using CHKDSK.
- Make sure the drive has enough free space to delete the file.
- Disable any security software that could be blocking the deletion.
- Try deleting from Safe Mode if normal deletion fails.
Mac File Deletion Troubleshooting
- Close any application using the file.
- Check that the file/folder permissions allow your user to delete it.
- Uncheck Locked in the file Get Info if enabled.
- Repair disk errors and permissions using Disk Utility.
- Ensure there is sufficient free space on the drive.
- Add an exception for the file to any security software.
- Try deleting in Recovery Mode if standard deletion does not work.
Linux File Deletion Troubleshooting
- Close any open programs accessing the file.
- Verify your user has permissions to delete the file.
- Use chmod to remove the read-only file attribute if set.
- Check and repair the filesystem using fsck.
- Delete other files to free up space if the disk is full.
- Disable AppArmor or SELinux restrictions if applicable.
- Try deleting from a live CD/USB if you still cannot delete.
Best Practices to Avoid “Unable to Delete File” Errors
Here are some tips to prevent running into file deletion issues in the future:
- Close files/programs properly after use so they fully release the file.
- Don’t store files in system directories which have restricted permissions.
- Be careful applying read-only statuses to files you may later want to edit or delete.
- Regularly check your disk health and repair any corruption issues.
- Maintain sufficient free disk space for proper system operation.
- Exclude specific files from antivirus/security scanning if needed.
- Avoid excessively long file paths that exceed the OS limit.
Recovering Deleted Files
If you find a file is already deleted but you needed it, there are still options to try recovering it:
- Restore from backup – Restore the file/folder from a recent backup copy if available.
- Use file recovery software – Applications like Recuva and Disk Drill can scan the drive and recover deleted files.
- Find copies in other locations – The file may exist in other places like email attachments, network drives, or cloud storage.
- Retrieve from the Recycle Bin – On Windows, the Recycle Bin holds deleted files for a period of time before final deletion.
- Undelete on Linux – The extundelete utility can recover deleted Linux files immediately after deletion.
The sooner you attempt recovery, the higher your chances as portions of the file are overwritten over time. Try to recover deleted files as soon as possible.
Conclusion
Being unable to delete a file can be frustrating, but is usually caused by one of several common issues like permissions errors or file corruption. Following troubleshooting steps for your operating system can typically resolve “Access denied” or other errors encountered when trying to delete stubborn files. Taking preventative measures like maintaining disk health can help avoid these problems developing in the first place. And if you find yourself needing to recover a deleted file, utility and recovery software provide options to attempt restoring lost files if backups are not available.