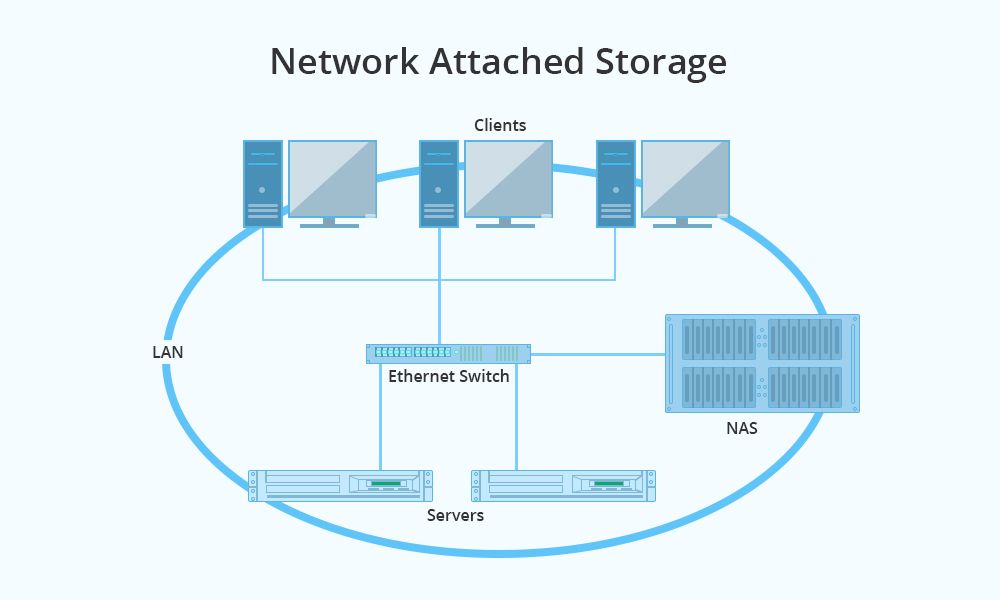
Both Network Attached Storage (NAS) devices and servers are commonly used for data storage and access. NAS is dedicated file storage that connects to a network, often used by individuals and small businesses. Servers are powerful computers that store data and also perform additional functions like running applications or hosting websites.
This article compares NAS and servers, looking at the key differences in costs, setup, scalability, efficiency, data protection, accessibility, backups, and security. The goal is to help readers understand when a NAS or a server is the better choice for networked data storage needs.
Cost Savings
One of the main benefits of using a NAS instead of a traditional server is the potential cost savings. NAS devices are typically less expensive to purchase upfront compared to an equivalently sized server. According to TechTarget, “A basic NAS device is often much cheaper than a server”[1]. This is because NAS devices utilize more affordable consumer-grade hardware components rather than the more robust enterprise-level components used in servers.
Additionally, NAS systems are usually easier and less expensive to scale up over time. If you need more storage capacity, you can simply add more hard drives to the NAS. With a traditional server, scaling storage often requires investing in an entirely new server. NAS systems also allow you to start small and add more storage as needed, while servers typically require more upfront investment.
NAS can also lead to cost savings on IT management and electricity. NAS operating systems are designed to be user-friendly for file sharing and backups, reducing the need for dedicated IT staffing. And with fewer components to power, NAS devices consume less electricity than servers. For budget-conscious small businesses and home offices, NAS provides a very cost-effective networked storage solution compared to buying and maintaining a traditional server.
Ease of Setup
NAS devices are specifically designed to make file storage and sharing easy for users without advanced IT skills. NAS operating systems include simplified web-based setup wizards that walk users through the process of getting the device operational on their network. Many NAS devices can be accessed right out of the box without any configuration required. According to Nakivo, “NAS appliances are preconfigured for file sharing purposes, so setting up shared folders takes a couple of mouse clicks rather than configuring permissions and access rights.”
In contrast, setting up dedicated file server hardware and software typically requires more specialized IT skills and knowledge. File servers run on general purpose server operating systems like Windows Server or Linux which require more complex configuration and administration. As noted by Versitron, “Setting up a file server is meant for those with intermediate networking skills, requiring you to understand DHCP, DNS, Active Directory, along with assigning drive letters and configuring user permissions.” File servers also often rely on separate SAN storage area networks which adds another layer of complexity.
For most small businesses and home users looking for simple networked file storage, a NAS clearly provides a much easier out-of-the-box setup experience compared to a traditional server. As NinjaOne points out, NAS devices are “targeted for ease of use so you can quickly start storing and accessing files.”
Sources:
https://www.nakivo.com/blog/nas-vs-file-server/
https://www.versitron.com/blogs/post/nas-vs-server-which-is-right-for-you
Scalability
One of the key advantages of NAS solutions is how easy they make scaling up storage capacity. With a NAS device, you can simply add more hard drives or replace existing drives with higher capacity ones to expand available storage. This process is seamless and doesn’t require reconfiguring the NAS or downtime. NAS vs Server: Which Is Right for You?
In contrast, scaling up storage capacity on a traditional server is much more complex. It may require migrating data to new disks or RAID arrays, adding an external SAN (Storage Area Network) or upgrading to a new server altogether. There is often significant downtime involved. NAS vs. Server: Which Should I Use for On-Prem Storage? With a NAS, you can simply add more storage as needed, on your timeline.
Energy Efficiency
NAS devices are designed from the ground up with energy efficiency in mind. They utilize low power CPUs, optimized operating systems, and efficient power supplies to reduce power consumption. This translates into real world savings. According to a Reddit user benchmarking power usage, their NAS device consumed just 28 watts idle and 45 watts under load versus a home server which used 80-120 watts idle.
Servers are built for maximum performance and uptime rather than efficiency. They often utilize power hungry components that are overkill for simple file storage and backup tasks. This increased power usage adds up over time. So if you don’t need that level of performance, a NAS can provide huge power savings over a standard server.
For example, one Reddit user found their NAS used less than half the idle power of their server. This efficiency advantage allowed them to keep their NAS running 24/7 while turning off the power hungry server when not needed.
Data Redundancy
One of the main benefits of using a NAS instead of a regular server is increased data redundancy. NAS devices offer built-in RAID support, allowing you to configure multiple hard drives for redundancy and protection against drive failures. According to Dong Knows, RAID enables “data to be written to multiple drives at the same time so that if one fails, data integrity is retained.”
Popular RAID levels like RAID 1, 5, and 6 provide fault tolerance by writing duplicate copies of your data across multiple drives. As Network Storage Works explains, “If one needs maintenance, the other continues operations unaffected.” This prevents data loss and downtime in the event of a failed drive.
Beyond RAID, some NAS devices also offer snapshots and versioning. This lets you restore previous versions of files in case of accidental deletion or corruption. Overall, the redundancy features of NAS make it much safer for critical data than a basic single drive server.
Ease of Access
One of the key advantages of using a NAS instead of a traditional server is how easy it is for multiple users and devices to access files. NAS devices operate as dedicated file storage appliances, optimized for sharing files across networks and the internet. This makes accessing documents, media, backups, and other data seamless no matter where users are located. According to FS, NAS offers simplified data sharing thanks to support for network protocols like SMB, AFP, NFS, FTP, and WebDAV. Multiple users across Windows, Mac, Linux, and other devices can connect at once to access, share, and collaborate on stored files.
In contrast, accessing files on a traditional server is often restricted to specific protocols and operating systems. NAS removes these barriers, ensuring authorized users can easily access stored data anytime, anywhere, on any device. This capability makes NAS an ideal centralized repository for important business information, home media, or other shared data. With NAS, scattered files become unified resources that entire teams or families can utilize.
Backups
One of the key benefits of using a NAS instead of a traditional file server is easier and more flexible data backups. NAS devices have built-in support for various backup solutions that simplify protecting your data (Veeam). Many NAS operating systems like Synology DSM provide integrated backup utilities that automate backing up shared folders and iSCSI LUNs to external drives, remote servers, and public clouds like AWS S3 (Netapp). Popular cloud backup services such as Backblaze also offer NAS integration to securely backup your NAS data offsite (Backblaze). Between built-in OS tools and third party software support, NAS platforms make it simple to configure automated backups on schedules or triggers. This ensures your critical data is protected against localized failures, disasters, human errors, ransomware and more. The flexibility of backing up NAS data locally or to the cloud provides affordable options for various needs and budgets.
Security
An important benefit of using a NAS instead of a traditional server is the security features that NAS often provide. Many NAS systems offer built-in encryption, access controls, and other security tools to help keep your data safe
Encryption ensures data is stored and transferred securely between the NAS and authorized users. The data is scrambled and can only be unscrambled with the right encryption key. Many NAS devices support AES 256-bit encryption, a strong standard used by banks and government agencies. Encryption protects data in case of device theft.
Access controls allow admins to set permissions on who can access, modify or delete files on the NAS. This prevents unauthorized access. Some NAS devices integrate with active directory for easy user and group management. Access logs provide visibility into who accessed which files and when.
Other security features common in NAS devices include firewalls to control network access, antivirus scanning to detect malware, and integration with security cameras for monitoring and alerts. Companies like Synology and QNAP offer robust security software suites tailored for their NAS appliances.
Overall NAS systems provide powerful security tools to lock down storage. Their security capabilities often match or exceed a basic server installation, while being easier to setup and maintain for the average small business.
Conclusion
In summary, NAS devices offer several key advantages over traditional servers for home and small business use cases. NAS systems provide major cost savings compared to servers, both in upfront hardware expenses and ongoing maintenance. They are also much easier to set up and manage without advanced IT skills. NAS allows for simple scalability by adding additional hard drives as storage needs grow over time. The disk redundancy of RAID configurations ensures protection against data loss from drive failures.
NAS systems are designed for optimal energy efficiency, unlike power-hungry servers. The centralized access and backup capabilities make it simple to share files and perform backups across multiple devices. With modern security protocols, NAS devices can provide robust protection for stored data. For home users and small businesses that don’t require all the complexity of a full-fledged server, NAS systems offer an affordable, versatile and user-friendly solution for central file storage and backup needs.
In conclusion, the ease of use, flexibility, energy efficiency and data redundancy of NAS make it an ideal choice over traditional servers for personal and small business file storage needs. NAS systems provide a simple yet powerful solution at a fraction of the cost and complexity of a server.