Solid state drives (SSDs) have become a very popular storage upgrade for computers due to their incredible speed and responsiveness compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs). However, in order to reap the full benefits of SSD performance and endurance, you need to properly configure and format the drive. This article will provide a comprehensive guide on how to improve performance and protect your data on SSD.
Formatting an SSD correctly will boost speeds, extend the drive’s lifespan, and also enable encryption to keep your data secure. In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about formatting an SSD for optimal performance and protection on both Windows and macOS.
The Benefits of a Fresh SSD Format
When you first get a new SSD, one of the initial steps will be formatting the drive so your computer can store and access data on it. While you may be eager to start using the fast new drive, taking the time to format properly has some important advantages:
Erase existing data – Wiping the drive by formatting removes any leftover data from manufacturing or testing. This prevents potential security issues with accessing previous data.
Fix file system errors – A fresh format clears out any corruption or errors that may have occurred on a used drive. This provides a clean slate.
Optimize file system for SSD – The format configuration can be tailored to SSDs instead of HDDs, enabling key optimizations like TRIM, wear leveling, and overprovisioning.
Improve performance – Formatting realigns files and data so they can be accessed faster. It also deploys efficient settings for SSD cell cleanup and maintenance.
Enable encryption – When formatting, you can choose options to encrypt the full drive for enhanced data protection against unauthorized access.
Taking the time to format a new SSD instead of just partitioning or quick formatting an old drive is worth the effort. Optimization is key to SSD lifespan and speed.
Choose the Right File System for SSD
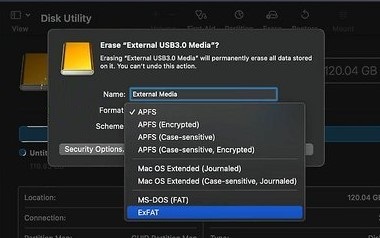
When formatting a drive, you will need to decide which file system to use. The file system manages how data is stored, organized and accessed on the drive.
For SSDs, you’ll want to choose a file system designed specifically to work well with flash-based NAND storage rather than mechanical hard disks. Here are the top options:
NTFS (Windows) – The proprietary Windows file system with optimization features for SSDs like TRIM, drive health monitoring, and encryption support. The best choice for most Windows users formatting an SSD.
exFAT (Cross-Platform) – A compatible file system for Windows and macOS. Lacks some SSD-specific features but has no file size limit. Useful for external SSDs that may connect to different operating systems.
APFS (Mac) – The modern Apple file system optimized for high-performance SSDs and flash storage. Includes strong encryption with secure erase capabilities. Ideal for SSDs used solely with macOS 10.13 or higher.
EXT4 (Linux) – Mature Linux file system with SSD optimizations like TRIM/discard support. A good pick for Linux SSD formatting.
For most users, NTFS or APFS will be the best selections. Avoid older FAT32/exFAT options unless you need cross-platform use on very large external drives. They lack optimizations found in more modern file systems designed for SSD storage.

Securely Wipe Disk with SSD Erase Utilities
Before partitioning and formatting your new SSD, you may want to perform a secure erase on the disk. This wipes all existing data by overwriting the entire drive with zeros or random data.
Securely erasing an SSD that may contain sensitive old data provides extra protection against forensic data recovery. It also helps remove any hidden partitions or clutter before setting up fresh partitions.
On Windows, free tools like Parted Magic have options for securely erasing SSDs using ATA commands. On Mac, you can boot to recovery mode and use Disk Utility’s secure erase feature to securely wipe an SSD.
Zeroing out all cells on a new SSD is not strictly necessary since there should be minimal data. But it can provide extra peace of mind and ensure you are working with a totally clean slate before formatting partitions.
Optimize Partition Alignment
When partitioning a new SSD, it is extremely important to use proper partition alignment for optimal performance. Misaligned partitions can significantly slow down SSD speeds.
Here are some tips for optimized SSD partition alignment:
- Create partitions in multiples of 1024KB blocks for best alignment with internal erase blocks on the SSD hardware.
- Start partitions at minimum 1MB offset boundaries. A 2MB or 4MB offset is better if drive space allows.
- Use default partition alignment settings in SSD formatting tools like the Windows Disk Manager, DiskPart, or macOS Disk Utility. These auto-align partitions.
- If manually specifying partition boundaries, ensure the offset and sizes are multiples of 1024KB (1MB) for proper alignment.
- Avoid very small partitions less than 128MB as these can cause excessive wear on SSDs. Larger partitions better distribute writes across all cells.
Taking the time to optimize partition alignment avoids performance slowdowns. Alignment makes sure writes go to complete erase blocks rather than partially filled ones.

Choose the Right Format Settings
When selecting formatting options, there are a few key settings to enable for optimal SSD performance and lifetime:
1. File System – Use NTFS on Windows or APFS on Mac as mentioned above.
2. Allocation Unit Size – Select smaller cluster or block sizes during quick format, ideally 4KB or 8KB for SSDs. Larger blocks waste space.
3. TRIM Support – Ensure TRIM is enabled. This allows the SSD to automatically clean up deleted blocks and work efficiently.
4. Overprovisioning – Leave some drive space unpartitioned so the SSD controller can manage worn cells. 5-10% is ideal.
5. Drive Health Monitoring – Enable SSD monitoring features like S.M.A.R.T. to check disk errors, health status, and lifetime estimates.
Choosing the right format settings for your SSD ensures top performance, optimized cell usage, and full advantage of capabilities like TRIM/garbage collection for cleaning up invalid data.

Enable Full Disk Encryption
For maximum data protection, you should enable full disk encryption when formatting your SSD. This will encrypt all stored data on the drive so it is completely unreadable without the encryption key passphrase.
Here are instructions for enabling full disk encryption:
Windows BitLocker
- Open Control Panel > BitLocker Drive Encryption
- Click Turn on BitLocker
- Choose New Encryption Mode
- Select Encrypt Used Space Only or Encrypt Entire Drive
- Choose AES 128-bit or 256-bit encryption
- Save the recovery key!
MacOS FileVault
- Go to System Preferences > Security & Privacy
- Click FileVault tab
- Click Turn On FileVault
- Follow prompts to enable and set password
Once enabled, you will need to enter your encryption password when booting up to unlock the SSD. But all your data will be securely encrypted at rest when powered off.

Maintain Your SSD Properly
Once formatted and configured optimally, be sure to maintain your SSD properly for continued maximum performance and lifespan:
- Minimize unnecessary writes by disabling hibernation and pagefiles if you have enough RAM.
- Enable the TRIM command if not on by default in your operating system. TRIM is essential.
- Avoid completely filling up the SSD. Leave 10-20% free space for wear leveling.
- Upgrade your SSD firmware when updates are available for enhanced reliability and compatibility.
- Monitor SSD health stats and lifetime write totals with disk utility tools.
- Consider additional partitioning as needed to distribute writes across more blocks.
Proper maintenance and settings will ensure your SSD keeps running fast while avoiding excessive read/writes to any one group of cells. A formatted SSD still needs your help to thrive!
Conclusion
The steps you take when preparing a new SSD have significant impacts on performance and reliability over the drive’s lifetime. While it takes a small time investment up front, properly wiping, partitioning, formatting, and encrypting your SSD allows it to work optimally for years to come.
With the right technique, you can enable top speeds, healthy wear leveling, and enhanced security for your solid state drive. Follow the recommendations in this guide and your SSD will continue delivering lightning-fast response times and ample storage space while keeping your data protected.
Invest wisely when buying an SSD, but invest your time as well when formatting and configuring for the best experience. Your SSD is a crucial component powering your computing. Ensuring optimal performance means your computer will boot faster, launch apps quicker, transfer data more reliably, and last longer between upgrades.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why does partitioning and alignment matter for an SSD?
A: Proper partition alignment is crucial for SSD performance. Misaligned partitions can significantly slow down speeds. Aligning partitions correctly makes sure writes go to full erase blocks rather than partial ones.
What is overprovisioning and why does it help SSDs?
A: Overprovisioning means leaving extra unused space on an SSD so the controller can efficiently manage wear leveling and replace worn-out cells. Around 5-10% overprovisioning is recommended for performance and longevity.
Do SSDs need special file systems?
A: Yes, modern file systems like NTFS, APFS, and EXT4 have optimizations specifically for SSDs like TRIM, wear leveling, and caching. Older ones like FAT32 lack these features.
How does full disk encryption impact SSD performance?
A: Enabling encryption introduces a small amount of latency for encrypting/decrypting data. However modern SSDs are fast enough this is usually a negligible effect. Encryption provides valuable added security.
What is TRIM and why is it important for SSDs?
A: TRIM is a command that enables SSDs to automatically clean up and reuse deleted blocks/cells. This maintains speed and efficiency over time as cells wear out. TRIM should always be enabled.
How can SSD Lifespan be maximized?
A: Limit unnecessary writes, enable TRIM, allow overprovisioning space, upgrade firmware, monitor health stats, maintain at least 20% free space, and avoid filling drive to capacity.
What causes data loss or corruption on SSDs?
A: Main causes are sudden power loss, wear leveling or garbage collection errors, buggy firmware, electrical issues, and improperly removing the drive. Encryption helps protect against data recovery in these cases.
What is the best SSD Optimization software?
A: Popular utilities include Intel’s Toolbox, Samsung Magician, and SSD Tweaker. But OS built-in tools like TRIM are usually sufficient for most needs. Third party software is not required.
