With the growth of digital data showing no signs of slowing down, finding the right storage solution is an important consideration for both personal and business users. The two main options are cloud storage services that keep data on remote servers, and external hard drives that store data locally. But which is better? Here we examine the pros and cons of each to help you decide which meets your needs.
Cloud Storage Overview
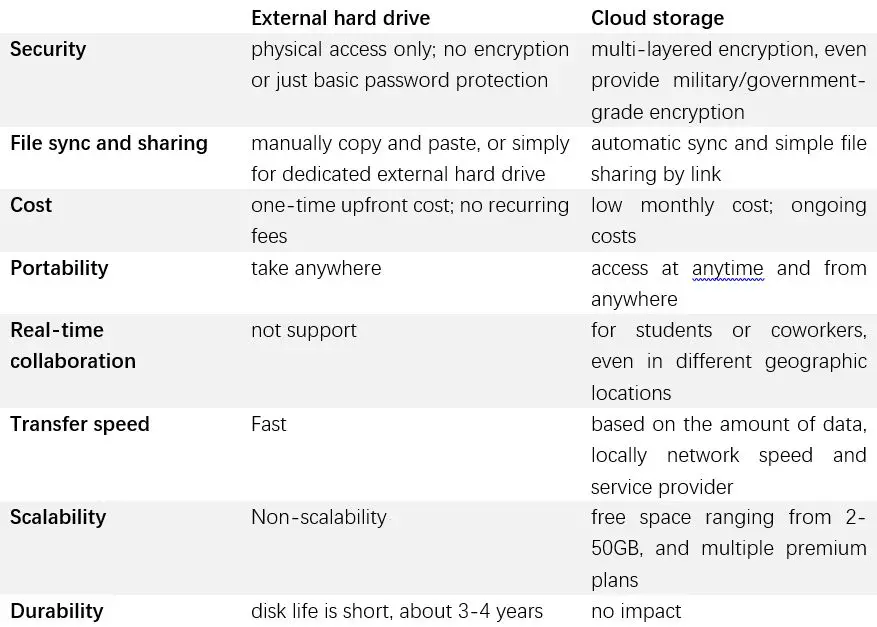
Cloud storage services provide users with online storage space to upload files to. Rather than storing data locally on a computer or external hard drive, files are uploaded via the internet to remote servers owned and operated by the cloud provider. Users can then access their files from any device with an internet connection.
Some of the major benefits of cloud storage include:
- Accessibility – Files can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, across all types of devices.
- Collaboration – Cloud services make sharing and collaborating on files easy.
- Reliability – Data on servers is regularly backed up, leading to fewer instances of data loss.
- Scalability – Cloud storage space can easily be increased as needed.
Leading cloud storage providers include Dropbox, Google Drive, Apple iCloud, Microsoft OneDrive and Amazon Cloud Drive. They provide users with varying amounts of free storage space, with the option to upgrade to paid plans for more storage capacity.
External Hard Drive Storage Overview
External hard drives are physical storage devices that connect to a computer, usually via USB. They provide localized offline storage, rather than storing data through an internet connection.
Benefits of using an external drive include:
- Speed – External hard drives provide faster data transfer speeds compared to uploading to the cloud.
- Convenience – No need for an internet connection to access files.
- Capacity – External drives come in large capacities up to 10TB for locally storing large files and archives.
- Privacy – Data is not shared on external servers so remains private.
- Ownership – Users have complete control over their data.
Leading external hard drive brands include Western Digital, Seagate, Toshiba, LaCie and Samsung. Portable hard drives are powered via USB connection, while desktop drives require a separate power supply.
Cloud Storage Pros
Let’s now dive deeper into the specific advantages of using cloud storage services:
Accessibility
The ability to access files anywhere with an internet connection is a major advantage of the cloud. Users can view and share files across multiple devices like laptops, tablets and smartphones. Cloud syncing ensures files are kept up to date across devices. This enables easy collaboration with colleagues and clients.
Backup & Recovery
Reputable cloud storage providers have robust systems in place to backup data and prevent loss. Local external hard drives are prone to failure and can result in permanent data loss if a backup is not maintained. With cloud storage data is redundantly distributed across multiple physical servers in data centers. If one server fails, data is replicated across the remaining servers. This provides an added layer of protection against data loss.
Disaster Recovery
The distributed nature of cloud servers across different geographic regions safeguards against localized disasters such as fires, floods and earthquakes. Users can easily restore their data if disaster strikes as it is backed up remotely. External hard drives are susceptible to damage if kept in the same physical location as the user.
Collaboration
Cloud platforms allow for easy collaboration by enabling file sharing via simple links. Users can quickly provide others access to documents with editing permissions. This is useful for teams working together on projects. External hard drives require physically connecting to the device or making local network shares to enable collaboration.
Scalability
With cloud storage it is easy to scale up capacity as your storage needs grow. Providers enable seamless upgrades to higher tier plans for more space. Sudden spikes in storage requirements can be managed flexibly in the cloud. In contrast external drives have fixed capacities. If you need more space you will have to purchase an additional drive.
Automatic Updates
No user intervention is required to keep software up to date with cloud services. The service provider handles updates remotely. With external hard drives you must manually install software updates to applications, security patches and drivers.
Broad Compatibility
Cloud storage can be accessed on all major operating systems like Windows, macOS and Linux. It can also be accessed on mobile platforms like Android and iOS. External hard drives may have compatibility limitations if interconnected between operating systems and devices.
External Hard Drive Pros
Now let’s examine some of the key upsides of using local external hard drives for data storage:
Speed
External hard drives provide much faster data transfer speeds, especially for larger files and batch operations. Uploading and downloading data to the cloud is constrained by internet data speeds. Transferring files locally to external storage is much quicker thanks to connection interfaces like USB 3.0 and Thunderbolt.
Privacy & Security
Keeping data on an external drive ensures it stays completely private and within your control. There is no reliance on a third-party cloud provider. You decide the encryption level protecting the data. Cloud platforms are prone to security breaches exposing data to malicious actors.
Reliability
Although cloud servers have redundancy, connectivity issues can still lead to disruptions. Working offline prevents relying on an internet connection to access your data. This provides more consistency for time sensitive tasks that need reliable access to large files.
Ownership
There are no monthly subscription fees associated with owning an external hard drive. One upfront purchase provides ongoing use of the storage space. With cloud services you essentially rent the storage capacity and never truly own it.
Specific Use Cases
External drives are better suited to specific use cases compared to the cloud such as:
- Storing large media files like videos, photos and music locally.
- Performing system backups to image drives for disaster recovery.
- Handling sensitive data like financial records that require air-gapped storage.
Cost Effectiveness
The ongoing subscription fees for abundant cloud storage capacity can become expensive over time. Large external hard drives provide a cheaper long term solution for archival type storage of infrequently accessed data.
Cloud Storage Cons
There are also some downsides to cloud storage to be aware of:
Reliance on Internet Connectivity
An internet connection is required to access data in the cloud. Slow speeds or outages can hamper accessibility. External drives work offline providing continuous access.
Recurring Fees
Cloud storage requires ongoing fees based on the amount of capacity required. This cost over time can exceed a single upfront payment for an external drive with comparable capacity.
Limited Control
You must rely on the cloud provider for appropriate security and backup of your data. With external storage you have full control to manage data integrity.
Potential Security Risks
Despite security measures, data breaches of cloud providers do infrequently occur. Keeping sensitive data offline negates this threat.
File Size & Format Limitations
Many cloud providers impose limits on maximum file upload sizes. Large files like videos may need to be compressed. Some file types may be incompatible for syncing or require conversion before uploading.
External Hard Drive Cons
And here are some weaknesses of external drives to consider:
Physical Damage Risk
Storing data on a portable external drive exposes it to potential physical damage through drops, accidents and hardware failure. Cloud storage benefits from extensive redundancy across servers.
Single Point of Failure
External hard drives are a single point of failure with the risk of irrecoverable data loss if the drive fails. The distributed nature of cloud servers provides redundancy if one server goes down.
Limited Accessibility
Data stored on the hard drive can only be accessed from one location at a time. Cloud storage enables ubiquitous access from anywhere.
Collaboration Difficulties
Sharing large files directly from an external drive is cumbersome. Cloud platforms allow seamless collaboration through file sharing capabilities.
Manual Updates
Software and firmware patches need to be manually maintained on external drives. Cloud storage providers handle updates behind the scenes.
Security Responsibility
Users must implement adequate encryption and access controls on external hardware for security. Cloud platforms come with built-in protection.
Cloud vs External Drive Security Comparison
Security is a key consideration when evaluating cloud vs local storage. Let’s compare the two options:
| Security Issue | Cloud Storage | External Hard Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption | Encrypted by provider with user controls. | User managed encryption. |
| Backups | Automated redundant backups across servers. | Manual user driven backups. |
| Multi-factor authentication | Used by all major providers. | Not applicable. |
| File recovery | File version histories enable rollbacks. | No versioning, rely on backups. |
| Breach potential | Higher target for hackers. | Lower target when kept offline. |
| Physical security | Data center biometrics and surveillance. | User responsibility entirely. |
This comparison shows that while cloud providers implement strong security controls, keeping data isolated on external media also has advantages if proper user driven security is in place.
Cost Comparison
How do costs stack up between cloud and external storage solutions? Let’s run some numbers.
Short Term Costs
For a small amount of infrequently accessed archival data, an external hard drive is very economical. A 6TB portable hard drive costs around $120. Purchasing 6TB of storage on a cloud service would cost at least $60/year, and likely much more for advanced plans with full collaboration features.
Long Term Costs
Over an extended timeframe the subscription fees for cloud services add up. Let’s compare costs for 10TB of storage over 5 years:
- 10TB External Hard Drive – $350 one time cost.
- 10TB Cloud Storage – Approximately $1200+ in subscription fees over 5 years.
For sizable storage and multi-year timeframes, an external drive can provide significant savings compared to cloud.
Plan Upgrade Costs
Needing additional capacity with cloud services incurs immediate recurring upgrade fees. External drives allow buying just what you need upfront. Let’s compare upgrade costs for 2TB extra:
- External Hard Drive – $80 for 2TB portable drive.
- Cloud Storage – Around $120/year in added subscription fees.
The cloud costs continue each year versus a single fixed cost for a hard drive upgrade.
Adopting a Hybrid Approach
With their respective pros and cons, cloud storage and external hard drives both offer compelling benefits. Adopting a hybrid approach can allow you to get the most out of both options:
- Use external storage for large media files, backups and data requiring high reliability and control.
- Utilize cloud services for ubiquitous access and collaboration on files where convenient access is required.
- Cloud storage also works well for day-to-day documents while external drives provide economical archival storage.
Splitting data between the cloud and external storage based on use case plays to the strengths of each medium.
Backup Cloud Data to External Drives
An excellent practice is to use external drives to backup your cloud hosted data for enhanced redundancy. If data loss occurs in the cloud, your local backup provides recovery capabilities. This combines the convenience of cloud storage with the data integrity benefits of external hardware.
Sync Cloud Data with Local Drives
Many cloud providers like Dropbox support synchronizing cloud data to a local external drive. This creates a local copy of cloud hosted files. You gain the advantages of cloud access and collaboration with the reliability of local external storage.
Conclusion
In summary, cloud storage services provide anywhere access, collaboration capabilities and disaster recovery protections exceedingly hard to replicate with external drives. However local external hard drives offer faster transfer speeds, better reliability and privacy along with large capacities for lower long term costs.
Users with significant storage requirements, privacy needs and time sensitive data transfers stand to benefit more from external drive solutions. When ubiquitous access and sharing are higher priorities, cloud services make more sense.
Employing a hybrid approach allows tapping into the key advantages of both storage mediums based on use case. External local storage serves as an economical way to back up and sync cloud hosted files. With careful planning it is possible to design a robust storage architecture leveraging the strengths of both cloud and external hard drives.