When installing Windows 7, one of the choices you need to make is which file system to use for the boot drive. The file system controls how data is stored and retrieved on a drive. The main options for Windows 7 are NTFS, FAT32, and exFAT. Choosing the right file system can impact performance, compatibility, and features. In this article, we’ll compare the pros and cons of NTFS vs FAT32 vs exFAT to help you decide which is the best disk format for Windows 7.
NTFS Overview
NTFS (New Technology File System) is the default file system for Windows 7. Here are some of the key features and characteristics of NTFS:
- Supports file compression to save disk space.
- Supports file-level encryption for security.
- Allows files up to 16 TB in size.
- Fast performance for reads and writes.
- Reliable disk recovery features.
- Allows permissions for files and folders.
- Best for internal hard drives.
Overall, NTFS has all the advanced features you expect from a modern file system. It’s optimized for performance on internal drives and has excellent security tools. The main downside is limited compatibility with other operating systems.
FAT32 Overview
FAT32 (File Allocation Table) has been around since the days of Windows 95. Here are some key details about FAT32:
- Compatible with all versions of Windows.
- Also works with macOS, Linux, game consoles, cameras, etc.
- File size limit of 4 GB.
- No built-in file compression or encryption.
- Lower performance than NTFS.
- Higher chance of disk errors.
- Simple file permissions only.
- Best for removable media like USB drives.
The main appeals of FAT32 are its simplicity and wider device compatibility. But it lacks security features and has performance limitations. The 4 GB file size limit makes FAT32 a poor choice for larger media files.
exFAT Overview
exFAT was introduced in 2006 as an optimized FAT32 replacement. Here are its main capabilities:
- Compatible with Windows and modern macOS.
- Also works with Linux, game consoles, and cameras.
- Supports files larger than 4 GB.
- Faster than FAT32 for large files.
- No built-in file compression or encryption.
- Minimal permissions system.
- Good for high-capacity removable media.
In a sense, exFAT aims to bridge the gap between FAT32 and NTFS. It removes the file size limit while adding just enough features for use with external drives. But exFAT lacks the encryption, compression, and performance of NTFS.
Comparing NTFS vs FAT32 vs exFAT
To summarize the differences:
| Feature | NTFS | FAT32 | exFAT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum file size | 16 TB | 4 GB | 16 EB |
| Maximum volume size | 256 TB | 2 TB | 64 ZB |
| File compression | Yes | No | No |
| Encryption | Yes | No | No |
| File permissions | Yes | Basic | Basic |
| Performance | High | Low | Medium |
| Windows support | All | All | Vista and later |
| Mac support | Read only | Yes | Yes |
| Linux support | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Game console support | Limited | Yes | Most |
As you can see, NTFS has the most features and best performance but limited compatibility. FAT32 is universally compatible but has limitations like the 4 GB file size cap. exFAT strikes a balance with compatibility across more devices and no file size limit, but lacks NTFS features.
NTFS vs FAT32 vs exFAT: Which Should You Use?
Based on the differences, here are some guidelines for when to use each file system:
NTFS:
- Use for Windows system drives and partitions.
- Use for drives that will only be accessed by Windows.
- Provides best performance and most features.
FAT32:
- Use for removable media you will use with Macs or non-Windows devices.
- Okay for small USB drives.
- Avoid for media drives due to 4 GB file size limit.
exFAT:
- Good choice for external drives to transfer large files between Windows and Mac.
- Also good for large USB flash drives.
- Supports larger media files despite lack of NTFS features.
In general, NTFS is best for internal Windows drives, FAT32 for small removable drives to use with multiple systems, and exFAT for large external drives for transferring big files between Windows and Mac.
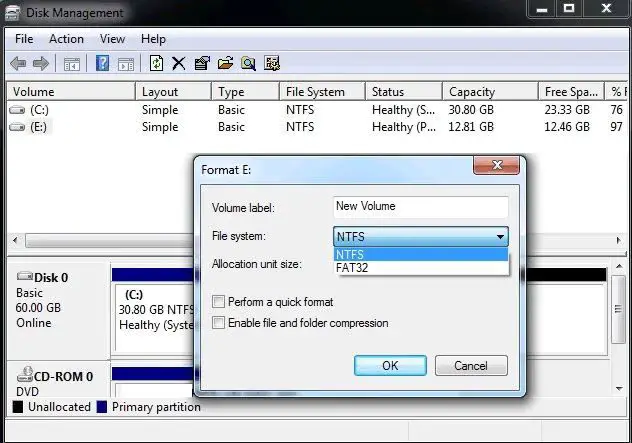
How to Format a Drive in Windows 7
Formatting a drive to change the file system is straightforward in Windows 7:
- Attach the drive to your computer and make sure it shows up in Windows Explorer.
- Open the Computer or My Computer window.
- Right-click on the drive and choose Format.
- In the Format dialog, choose your desired file system from the File System dropdown.
- Give the drive a Volume Label if desired.
- Check Quick Format for a faster format.
- Click Start to begin formatting.
This will erase all data on the drive and reformat it, so make sure to back up your files first!
Tips for Choosing Your Disk Format
No single file system is perfect for every situation. But a few tips can help guide your file system decision:
- For internal Windows drives, always choose NTFS for best performance.
- Only use FAT32 for removable drives if you need universal compatibility.
- exFAT is ideal for large external drives used with Windows and Mac.
- For flash drives, you can use FAT32 if under 32 GB and exFAT for larger capacities.
- Refer to your device’s manual for recommended file system if unsure.
- Back up your data before reformatting drives to change file systems.
Picking the right file format takes a little planning but ensures your drives meet your performance and compatibility needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about disk formats for Windows 7:
Is FAT32 good for Windows 7?
FAT32 works with Windows 7 but has limitations like no file compression, encryption, or permissions. It’s mainly useful for small, removable drives when compatibility across devices is needed. For Windows system drives, NTFS is preferred.
Can I use exFAT instead of NTFS in Windows 7?
You can use exFAT but will lose many NTFS features like file compression, permissions, and disk quotas. NTFS is the native Windows file system and best choice for internal drives. Use exFAT for external storage with very large files.
Is NTFS read-only on Mac?
By default, Mac can only read NTFS drives. To get full read-write access on Mac, you need a third-party NTFS driver software. Some solutions are Paragon, Tuxera, and iBoysoft. Or you can format as exFAT for a drive used on Mac and Windows.
Does FAT32 have size limits?
Yes, FAT32 has a maximum file size of 4 GB. That’s why it’s not ideal for large media files or other large data. NTFS and exFAT don’t have this file size restriction.
Should I format my external drive to NTFS or exFAT?
For external drives to transfer files between Windows and Mac, use exFAT. It has wider compatibility than NTFS without the limits of FAT32. Or use exFAT for large USB flash drives.
Conclusion
Choosing between NTFS vs FAT32 vs exFAT requires understanding their compatibility, features, performance, and limitations. For internal Windows drives, NTFS is the best choice. FAT32 works for small removable drives but has a 4GB file size limit. exFAT is a good middle ground for external drives, with compatibility on modern Windows and Mac systems. Consider the requirements of each drive and format it accordingly. Just remember to always backup your data first before reformatting a drive to change file systems.