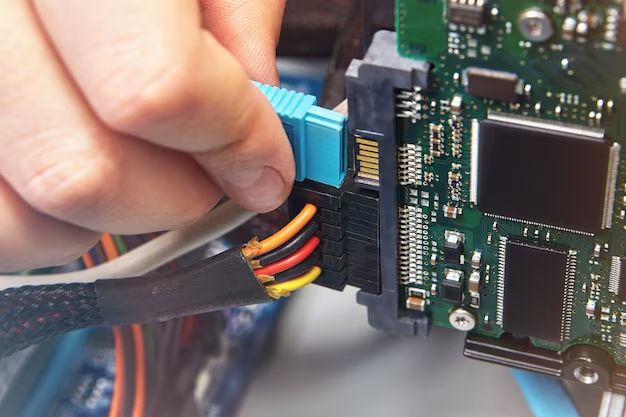
A SATA cable is used to connect storage devices like hard drives and solid state drives to a computer’s motherboard. Knowing where to plug in the SATA cable is important for getting your storage devices running properly.
What is a SATA Cable?
SATA stands for Serial Advanced Technology Attachment. SATA cables are used to connect storage devices like hard drives, solid state drives, and optical drives to a computer’s motherboard or SATA controller card.
SATA cables utilize a serial connection, meaning the data is transferred one bit at a time. This is different from the parallel connections used on older IDE cables that transfer multiple bits at once. SATA cables help reduce clutter and improve airflow inside the computer case compared to bulkier IDE ribbon cables.
There are several types of SATA cables:
- SATA data cables – Used to connect storage drives to the motherboard. These cables have a small connector on one end and a L-shaped connector on the other end.
- SATA power cables – Used to connect storage drives to the power supply. These cables have a large L-shaped connector on one end and a 15-pin connector on the other end.
- eSATA cables – Used for external SATA connections. eSATA cables allow you to connect external hard drives for increased storage capacity and data backups.
The SATA standards have evolved over time for faster data transfer speeds:
| Standard | Speed |
|---|---|
| SATA I | 1.5 Gb/s |
| SATA II | 3 Gb/s |
| SATA III | 6 Gb/s |
Modern motherboards typically include multiple SATA ports to support connecting multiple storage drives. Many power supplies also include multiple SATA power connectors.
Where to Plug In SATA Data Cables
SATA data cables use a very small connector on one end that plugs into the storage drive, and a L-shaped connector on the other end that plugs into the SATA port on the motherboard. The small connector attaches to the 7-pin or 15-pin SATA data socket on a 3.5″ or 2.5″ storage drive respectively. Then the L-shaped connector attaches to any open SATA port on the motherboard.
On a motherboard, SATA ports are normally labeled as SATA0, SATA1, SATA2, etc. Some motherboards may also color code the SATA ports for easier identification. The SATA ports will be located along one edge of the motherboard or around the chipset area.
Here are some tips for connecting SATA data cables correctly:
- Consult your motherboard manual to identify the SATA port locations.
- Match up the L-shaped SATA connector orientation to the port shape before inserting.
- Insert the SATA cable firmly but gently until it clicks into place.
- Avoid excessive bending or crimping of the SATA cable.
- Use the SATA ports numbered 0-3 for best performance since they connect directly to the chipset.
- Keep data cables away from power cables to avoid signal interference.
SATA Controller Cards
If your motherboard does not have enough SATA ports, you can install a SATA controller card in a PCI-E expansion slot. This will provide you with extra SATA ports to connect more storage drives. The SATA ports on a controller card function the same way as ports connected directly to the motherboard chipset.
Where to Plug In SATA Power Cables
SATA power cables have an L-shaped connector that attaches to the drive, and a larger 15-pin connector that plugs into the power supply. The L-shaped connector attaches to the 15-pin socket on a 3.5″ hard drive or 2.5″ SSD that provides them with +12V and +5V power.
On the power supply side, there are typically multiple SATA power connectors available that are labeled as HDD1, HDD2, HDD3, etc. Modular power supplies may have detachable SATA power cables that you plug in only when needed. Always make sure to match the L-shaped connector orientation before plugging in SATA power cables.
Here are some best practices for connecting SATA power:
- Use a separate SATA power cable for each drive for better stability.
- Plug in the SATA data cable before attaching the SATA power connector.
- Double check that the SATA power cable is firmly inserted on both ends.
- Do not force SATA connections. If there is resistance, the connector is probably misaligned.
- Avoid using SATA-to-Molex power adapters which can be unreliable.
Hot Swap vs Non Hot Swap
Most SATA ports and drives support hot swapping. This means they can be connected and disconnected while the computer is running. However, there are a few caveats:
- The SATA ports must specifically support hot swap. Refer to your motherboard manual for this info.
- Hot swap works best when combined with AHCI mode instead of IDE mode for the SATA controller in the BIOS.
- The operating system must support hot swapping drives like Windows 10 and Linux. Older versions may not detect new drives on the fly.
- Drives must be unmounted or ejected before removing to avoid data corruption.
If your SATA ports or drives do not support hot swapping, then the system must be fully shut down before connecting or disconnecting any SATA cables to avoid issues.
Troubleshooting SATA Connections
If your drive is not detected properly after connecting the SATA cables, here are some things to check:
- Re-seat SATA cable connections at both ends to ensure they are properly inserted.
- Try a different SATA port and cable if possible to isolate the issue.
- Verify SATA controller mode is set to AHCI in BIOS and you have latest drivers.
- Check for loose power cables that may be interrupting power delivery.
- Ensure older SATA drives have the jumper set to Master/Single setting instead of Cable Select.
- Try updating motherboard BIOS and drive firmware to latest available versions.
- Test drive health using manufacturer diagnostics or third party tools.
If drives are still not recognized properly after troubleshooting cabling and connections, the drive itself or controller may be faulty and require replacement.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do SATA cables matter for performance?
For most workloads, SATA cables make little difference in performance. Any decent quality SATA cable will provide the rated speeds. That said, poorer quality cables with thinner gauge wires may impact signal integrity at longer lengths. For best results, choose shorter SATA cables (less than 2 feet) with thicker 28-30 AWG wire.
Where does the SATA power cable plug into?
The SATA power cable plugs into connectors coming from the power supply labeled HDD1, HDD2, etc. Modular power supplies will have detachable SATA power cables to connect. Make sure to fully insert the SATA power cable into the drive and power supply.
Can I use one SATA power cable for multiple drives?
It is possible to connect multiple drives to one SATA power cable using splitters. However, it is generally recommended to use dedicated SATA power cables for each drive. Sharing cables can cause voltage drops that lead to stability issues.
What is a SATA express connector?
SATA Express is a short-lived standard that provided PCI Express lanes for faster SSD performance. It used a unique connector that is backwards compatible with SATA connections. SATA Express saw little adoption and was quickly replaced by M.2 SSDs.
Can you boot from SATA drives?
Yes, SATA hard drives and SSDs are fully supported as bootable devices. After installing an OS, make sure to select the correct SATA device as the first boot device in your motherboard BIOS or boot menu.
What’s the difference between SATA 2 and SATA 3?
SATA 2 and SATA 3 refer to the interface versions SATA II and SATA III that operate at 3Gbps and 6Gbps. The cables are the same, but SATA 3 has higher bandwidth potential. SATA 3 is backward compatible with SATA 2 drives.
Conclusion
Connecting SATA cables is straightforward once you know where to plug them in. The data cables attach storage drives to motherboard ports labeled SATA0, SATA1, etc. The power cables attach drives to connectors on the power supply labeled HDD1, HDD2, etc. Follow best practices for cable connections, port selection, and hot swapping. Troubleshoot issues by reseating connections, verifying port modes, and testing components to isolate faults. With quality SATA cables attached securely, you will have dependable connections to your storage drives.